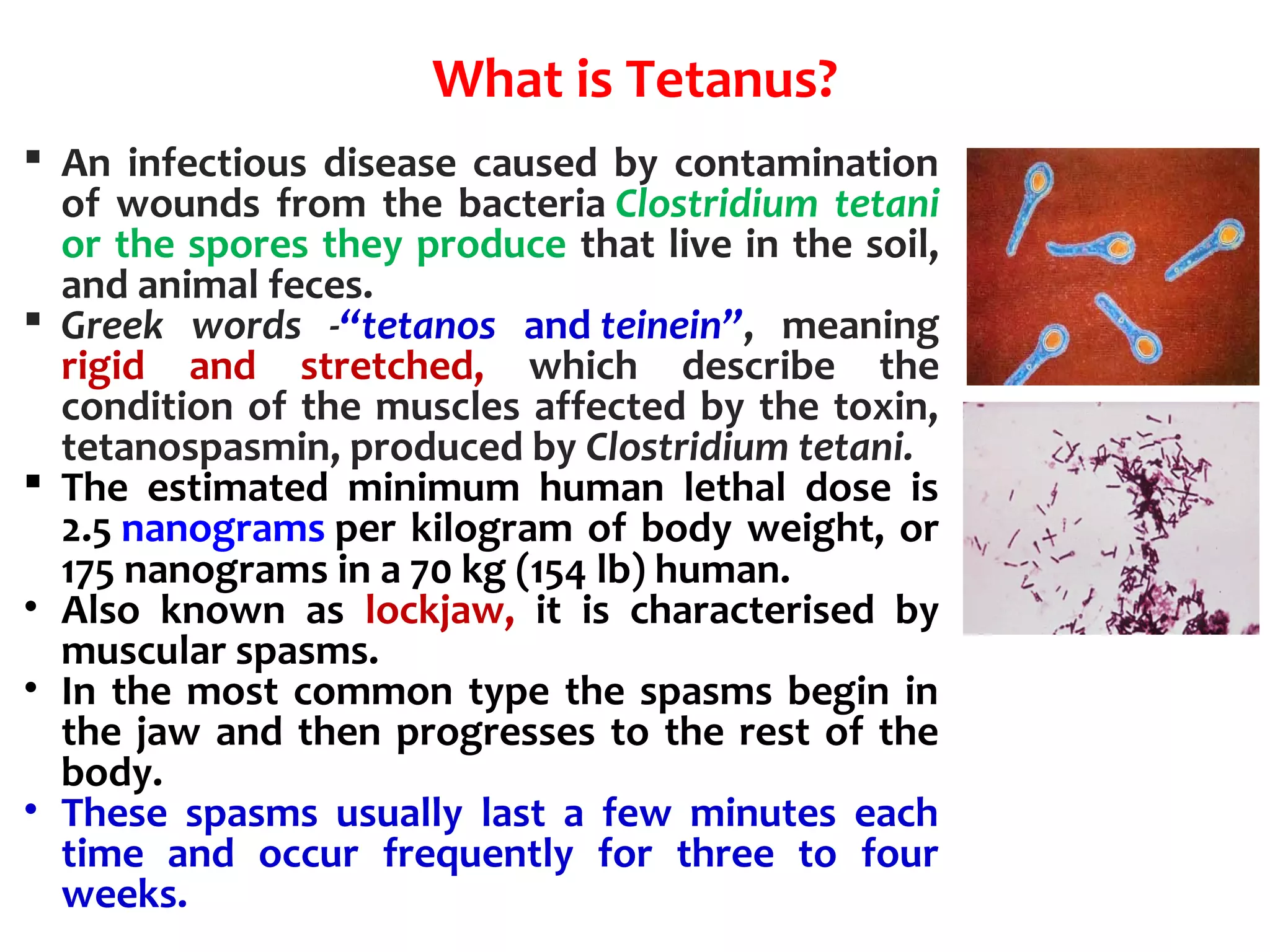
Clostridium tetani is a bacteria that causes tetanus. It produces a neurotoxin called tetanospasmin that is responsible for the symptoms of tetanus. The toxin is released when the bacteria lyse or spores germinate in wounds. It is transported up motor neurons to the central nervous system where it blocks the release of inhibitory neurotransmitters, causing painful muscle spasms characteristic of tetanus. Proper wound care and vaccination can prevent infection from the ubiquitous spores found in soil and animal feces.