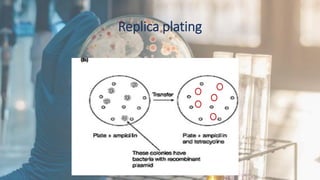
Plasmids are circular, self-replicating DNA molecules that are commonly used as cloning vectors. Key properties of plasmids that make them useful for cloning include their ability to replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome, carry genes for antibiotic resistance or other selectable markers, and accept foreign DNA at specific restriction sites. Common plasmids used for cloning are pBR322, which has features like a high copy number and blue-white screening, and pUC plasmids, which have even higher copy numbers. Plasmids can shuttle DNA between bacterial and yeast cells, and RNA production plasmids contain promoters to transcribe cloned DNA into RNA for applications like Northern blotting.