10-Plasmids.pptx
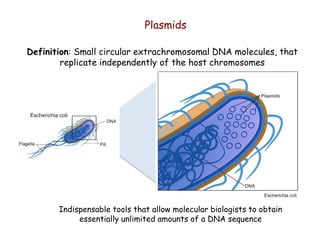
- 1. Plasmids Indispensable tools that allow molecular biologists to obtain essentially unlimited amounts of a DNA sequence Definition: Small circular extrachromosomal DNA molecules, that replicate independently of the host chromosomes
- 2. How are plasmids constructed? What functional elements are found in our yeast overexpression plasmids? How are plasmids purified?
- 3. GFP gene This gene encodes green fluorescent protein, which glows in UV light Kanamycin resistance gene the enzyme encoded by this gene stops the antibiotic kanamycin from working Origin of replication this is needed so that the plasmid can be copied, using the bacterium’s DNA copying machinery The plasmid
- 4. A Brief History of Plasmids • Genetic evidence for the existence of plasmids initially came from studies carried out in the laboratories of J. Lederberg and W. Hayes in the early 1950s • 1952:It was Joshua Lederberg who proposed the term plasmid in 1952 for extranuclear structures that are able to reproduce in an autonomous state. • he word 'plasmid' was first coined by Joshua Lederberg in 1952. He used it to describe 'any extrachromosomal hereditary element'. Lederberg first used the term in a paper he published describing some experiments he and his graduate student Norton Zinder conducted on Salmonella bacteria and its virus P22. J. Lederberg, 1952, Physiol. Rev. 32, 403-430
- 5. • In the late 1950s, a number of laboratories took up the study of plasmids once the discovery was made that extrachromosomal antibiotic resistance (R) factors are the responsible agents for the transmissibility of multiple antibiotic resistance among the enterobacterial • The earliest studies on R plasmids, carried out mainly by scientists in Japan (8), and the pioneering work on colicinogenic (Col) plasmids by P. Fredericq of Belgium in the mid-1950s (9) resulted in the identification of a variety of naturally occurring plasmids that, subsequently, were analyzed in the 1960s for the plasmid properties of autonomous replication, mobility, incompatibility, and host range.
- 6. • The list of plasmids available for study during this period was augmented significantly by the isolation by several laboratories of F-prime factors from E. coli strains that carried a chromosomally integrated form of the F factor (10). • The detailed genetic analysis of these F-prime plasmids contributed greatly to our understanding of the chromosomal state of a plasmid and the mechanics of chromosomal gene transfer from donor to recipient bacterium
- 7. • have no distinct 5’ or 3’ beginning or end. • double-stranded DNA molecules • ranging from a few to several hundred kilobases • provide one or more benefits to the host such as resistance to antibiotics, degradative functions, and virulence.
- 8. The structure of a plasmid
- 9. The structure of a plasmid • Origin of replication (OR), antibiotic resistance gene (ARG) and multiple cloning site (MCS). • between 1 to more than 1,000 kbp
- 10. • The final breakthrough came in 1973, when the first artificial plasmid was constructed by Boyer and Cohen. By then, scientists had discovered that special proteins, known as restriction enzymes, could “cut” DNA by cleaving its intramolecular bonds. Particularly, Boyer has isolated a restriction enzyme, EcoRI 1, which could recognize and cut a particular sequence of DNA to produce unpaired DNA bases on one strand, known as “cohesive end” or “sticky end” (Figure 1) [3].
- 11. Plasmids used in molecular biology have been constructed in the lab Molecular cloning Enzymes are used to insert desired pieces of foreign DNA into plasmids Bacterial cells are transformed with the plasmids. Copies of the plasmids are purified from bacteria.
- 12. Shuttle vectors have origins of replication and selectable markers for propagation in both bacteria and yeast We are using plasmids that have been termed shuttle vectors, because they can be propagated in either bacteria or yeast Plasmids are propagated in bacteria, which grow quickly and maintain multiple copies of the plasmids non-pathogenic strain of Escherichia coli Saccharomyces cerevisiae deletion strains Plasmid-encoded genes are expressed in yeast, and phenotypes are analyzed
- 13. How are plasmids constructed? What functional elements are found in our yeast overexpression plasmids? How are plasmids purified?
- 14. 1 URA3 2 β-lactamase gene 3 pBR322 ori 4 yeast 2 µm origin 5 GAL1 promoter 6 C-terminal tags 1 2 3 4 5 6 ORF goes here *Plasmid names begin with a lower case “p” The pBG1805*-derived plasmids are complex vectors designed to express S. cerevisiae ORFs
- 15. pYES2.1-based plasmids used for S. pombe ORFs have many elements in common with pBG1805-based plasmids pYES2.1 (5886 bp) used for S. pombe ORFs 1 2 3 4 5 7 2 1 3 4 5 6 URA3 β-lactamase gene pBR322 ori yeast 2 µm origin GAL1 promoter C-terminal tags 7 pBG1805 (6573 bp) used for S. cerevisiae ORFs 1 2 3 4 5 6 ORF goes here ORF goes here
- 16. How are plasmids constructed? What functional elements are found in our yeast overexpression plasmids? How are plasmids purified?
- 17. Plasmids are much smaller than bacterial chromosomes Plasmids are supercoiled in their native form Supercoiling allows plasmids to renature quickly after they are denatured Plasmid purification is based on their distinctive physical properties Plasmids used in molecular biology are highly engineered and contain elements of use to researchers
- 18. Plasmid purification from bacteria relies on their unique physical properties Bacterial cell with plasmids contains MANY different, well-folded proteins 1-2 copies of large (>Mbp) , circular bacterial DNA complexed with proteins Multiple copies of small (5-15 kbp) plasmids Purification involves sequential denaturation and renaturation steps
- 19. Cells are first treated with base and a detergent breaks open membrane and denatures both DNA and proteins Proteins denature irreversibly Chromosomal DNA denatures—will have difficulty renaturing because of its length and many proteins complexed to it Plasmids denature, but strands stay together because of supercoiling
- 20. Extract is neutralized to allow DNA molecules to renature Plasmids renature and are suspended in the SUPERNATANT following centrifugation Proteins and chromosomal DNA form aggregate irreversibly, forming a PRECIPITATE that can be collected by centrifugation When purifying plasmids, use a micropipette to remove the supernatant for further processing steps
- 21. Zyppy purification kit use multiple steps to purify plasmids Alkaline lysis Neutralization Purification of plasmid DNA on a silica resin Elution of purified DNA from he silica resin Let's look at the individual steps……………..
- 22. 1 Transformed E. coli cultures are concentrated by centrifugation 2. The cell pellet is resuspended in 600 µL TE buffer by vortexing 3. 100 µL of 7X Blue Zyppy lysis buffer is added 0.1 N NaOH in buffer lyses the cells GENTLY mix the contents by inverting the tube 4-6 times Solution changes from cloudy to clear when cells are lysed Warning: too much mechanical agitation can shear chromosomal DNA Alkaline lysis
- 23. Neutralization 4. Add 350 µL yellow Zyppy Neutralization buffer Mix by inverting several times A heavy precipitate will begin to form immediately! The initial “glop” will become more granular when neutralization is complete—but don’t overdo it! The precipitate contains denatured proteins and the denatured chromosomal DNA. 5. Spin down the denatured molecules for 3 minutes at top speed. CAREFULLY remove the supernatant containing the plasmid – Don't be greedy! Purity is preferred to yield!
- 24. Purification on Zyppy silica resin 6. Apply the supernatant to the spin column. Place the column in the collection tube. Centrifuge the column for ~15 seconds at top speed. 7. Discard the flow through in the collection tube. Add 200 µL Zyppy EndoWash. Centrifuge ~15 sec. EndoWash contains guanidine hydrochloride and isopropanol. It removes contaminating proteins that are bound to the resin. 8. Discard the flow through in the collection tube. Add 400 µL Column Wash. Centrifuge 1 min.
- 25. Plasmid Elution 9. Transfer the column to a clean, LABELED microcentrifuge tube 10. Add 50 µL TE buffer directly on top of the column. Allow the column to stand upright in the test tube for ~10 min. (Plasmid is being eluted.) 11. Spin the column for 30 seconds. Plasmid DNA will be collected in the microcentrifuge tube. Pure plasmid DNA collects here!