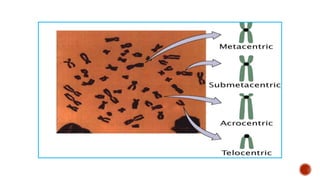
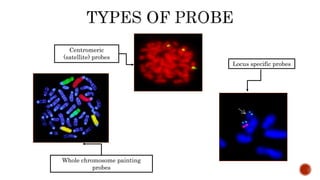
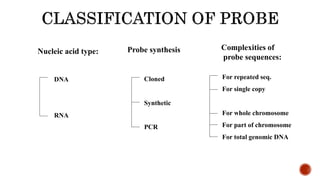
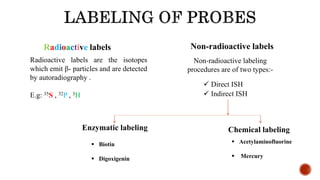
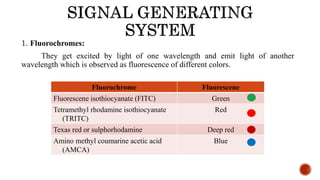
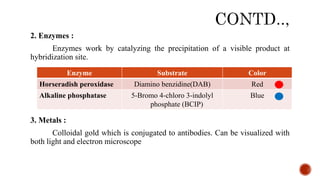
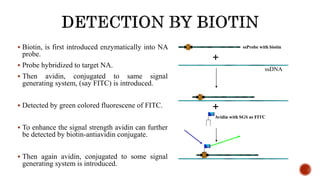
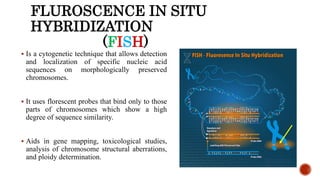
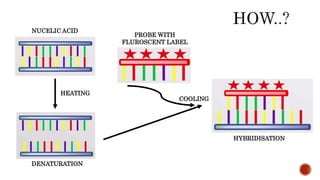
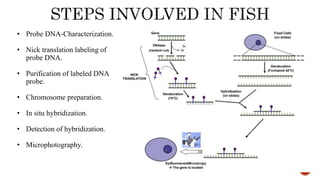
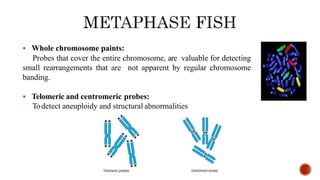
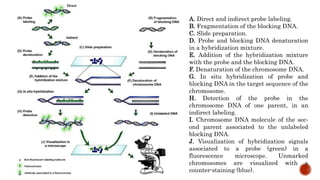
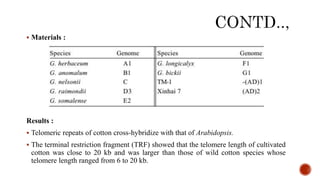
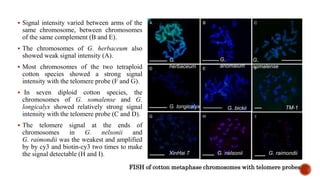
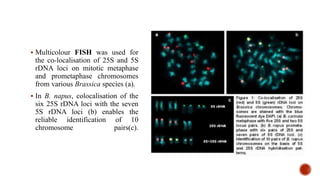
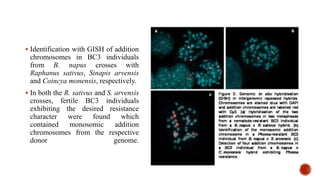
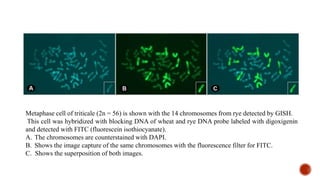
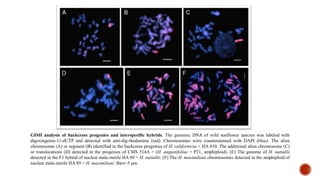
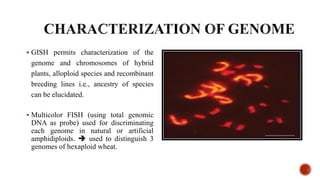
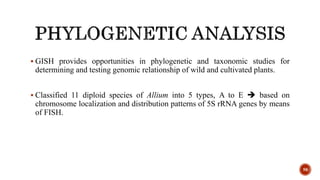
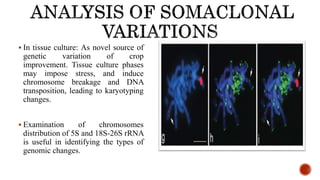
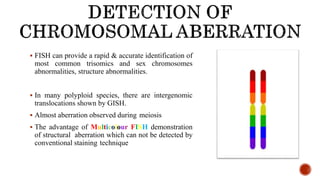
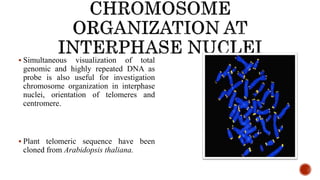
Chromosomes are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus that carry genetic information. They become visible during cell division. In situ hybridization (ISH) allows the localization of nucleic acid sequences on chromosomes using probes. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is a type of ISH that uses fluorescent probes to visualize specific sequences. FISH has applications in gene mapping, detecting genetic abnormalities, and identifying chromosomes.