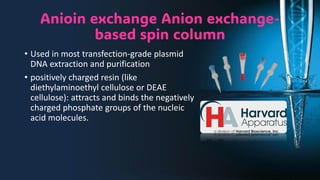
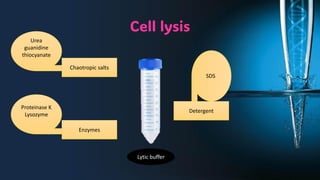
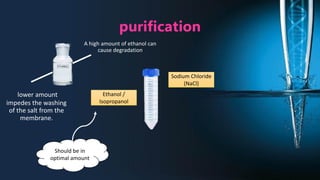
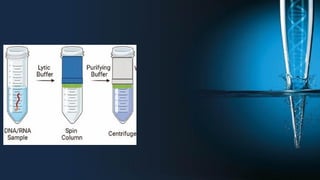
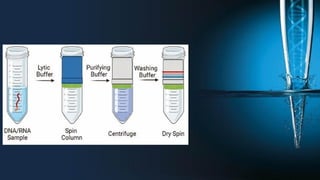
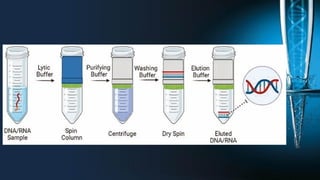
The document discusses the advantages of spin column extraction methods for nucleic acid, highlighting efficiency, scalability, and contamination prevention. It details the mechanisms of various types of spin columns, including silica membrane, anion exchange, and filter paper-based columns, focusing on their binding properties and operational processes. The elution methods for DNA and RNA are also provided, emphasizing conditions for optimal stability and solubility.