Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


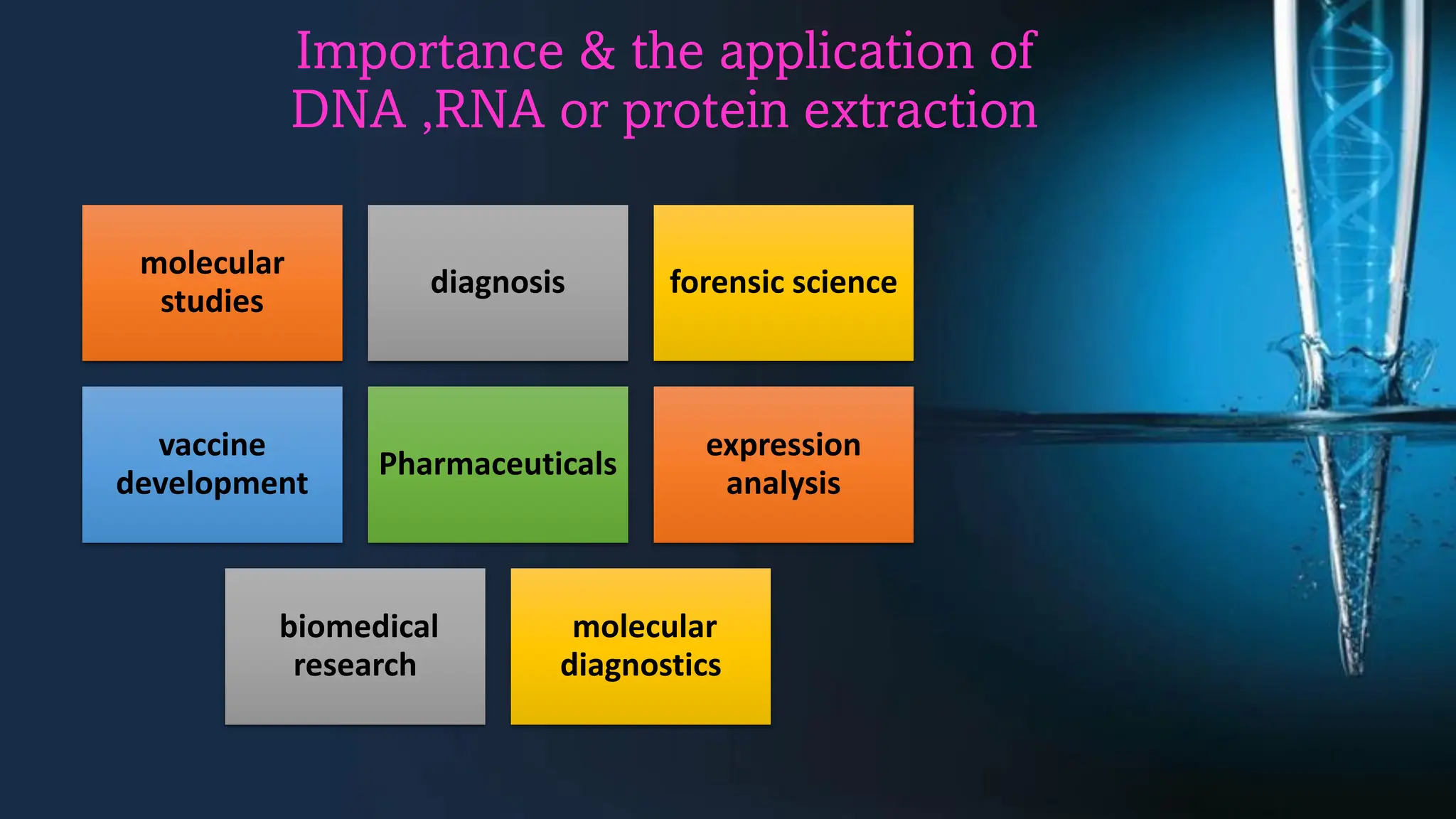

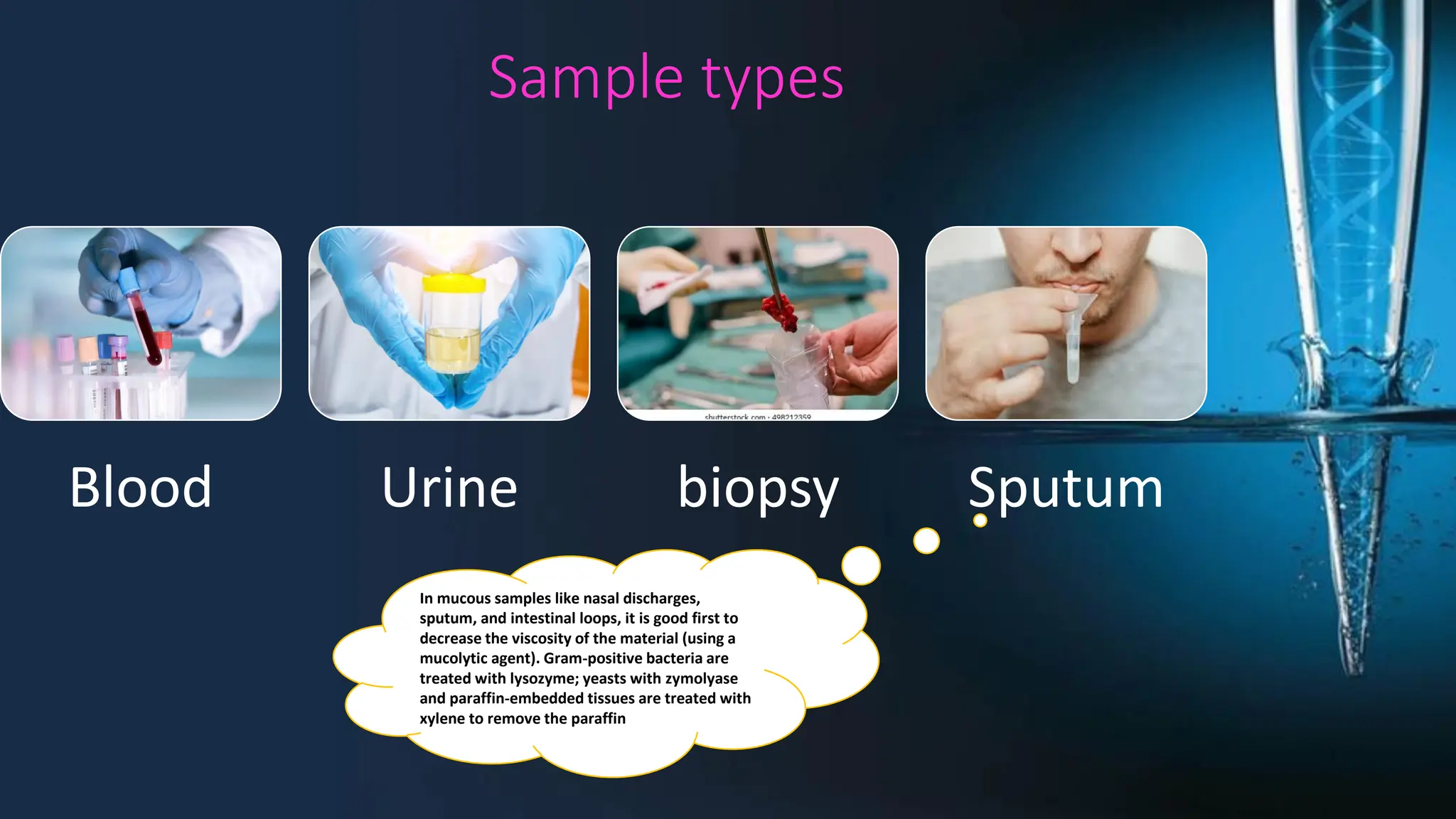
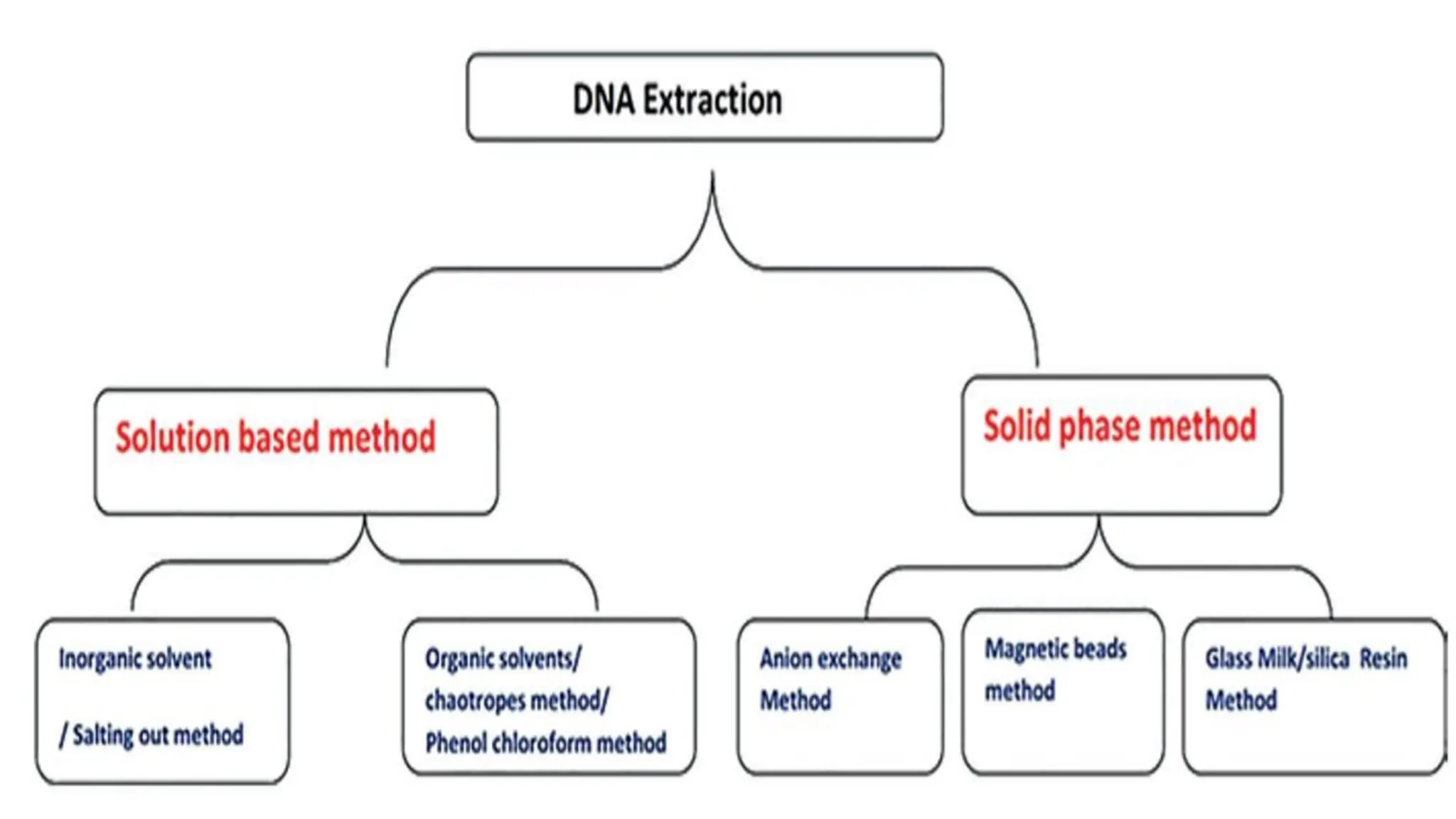

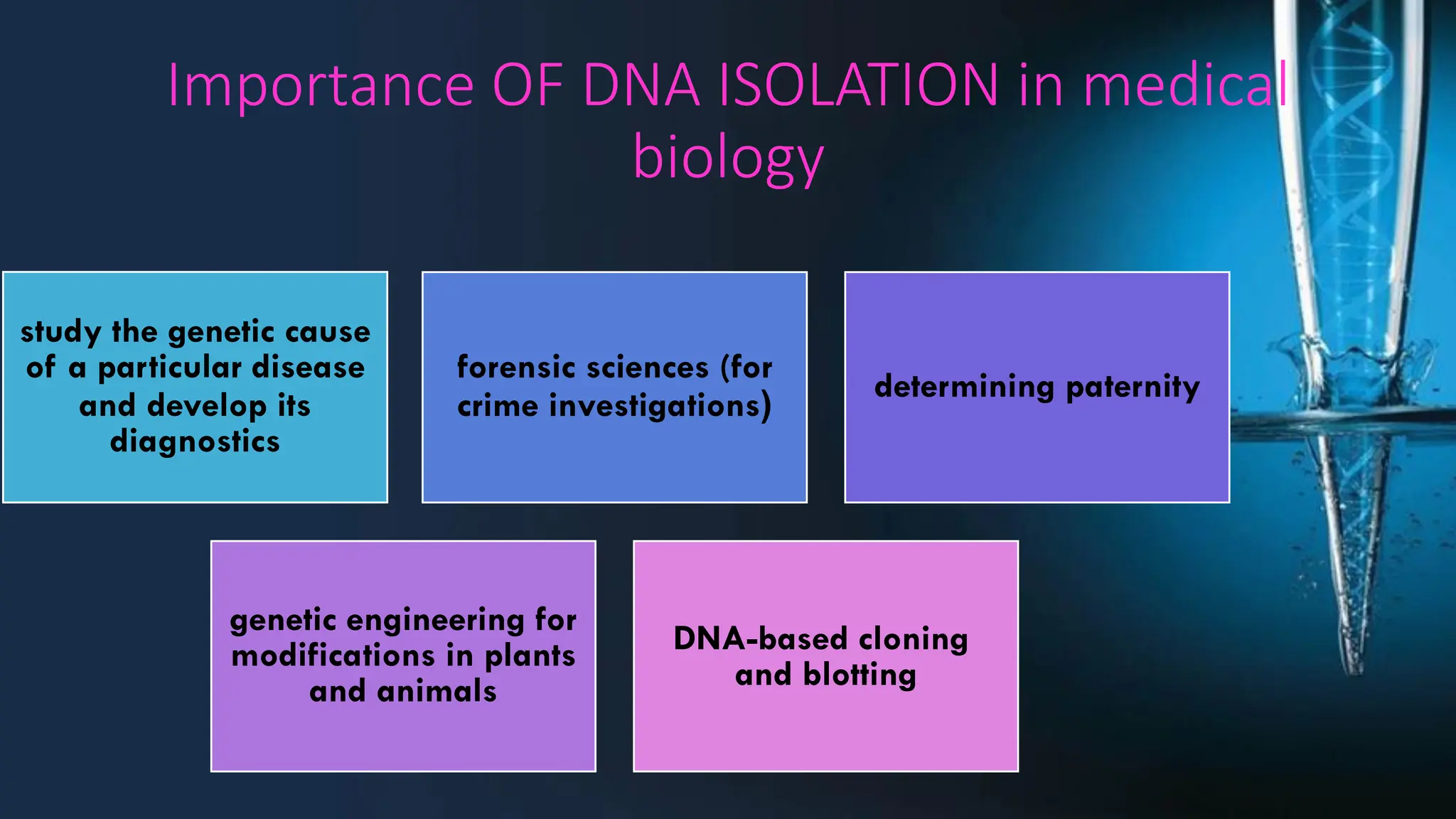

The document discusses DNA extraction as a method to purify DNA from various samples using physical and chemical techniques. It highlights the significance of DNA, RNA, and protein extraction in molecular studies, diagnostics, and forensic science, emphasizing the choice of extraction method based on sample type and planned usage. Key steps in effective nucleic acid purification are outlined, alongside the importance of DNA isolation in medical and forensic applications.







