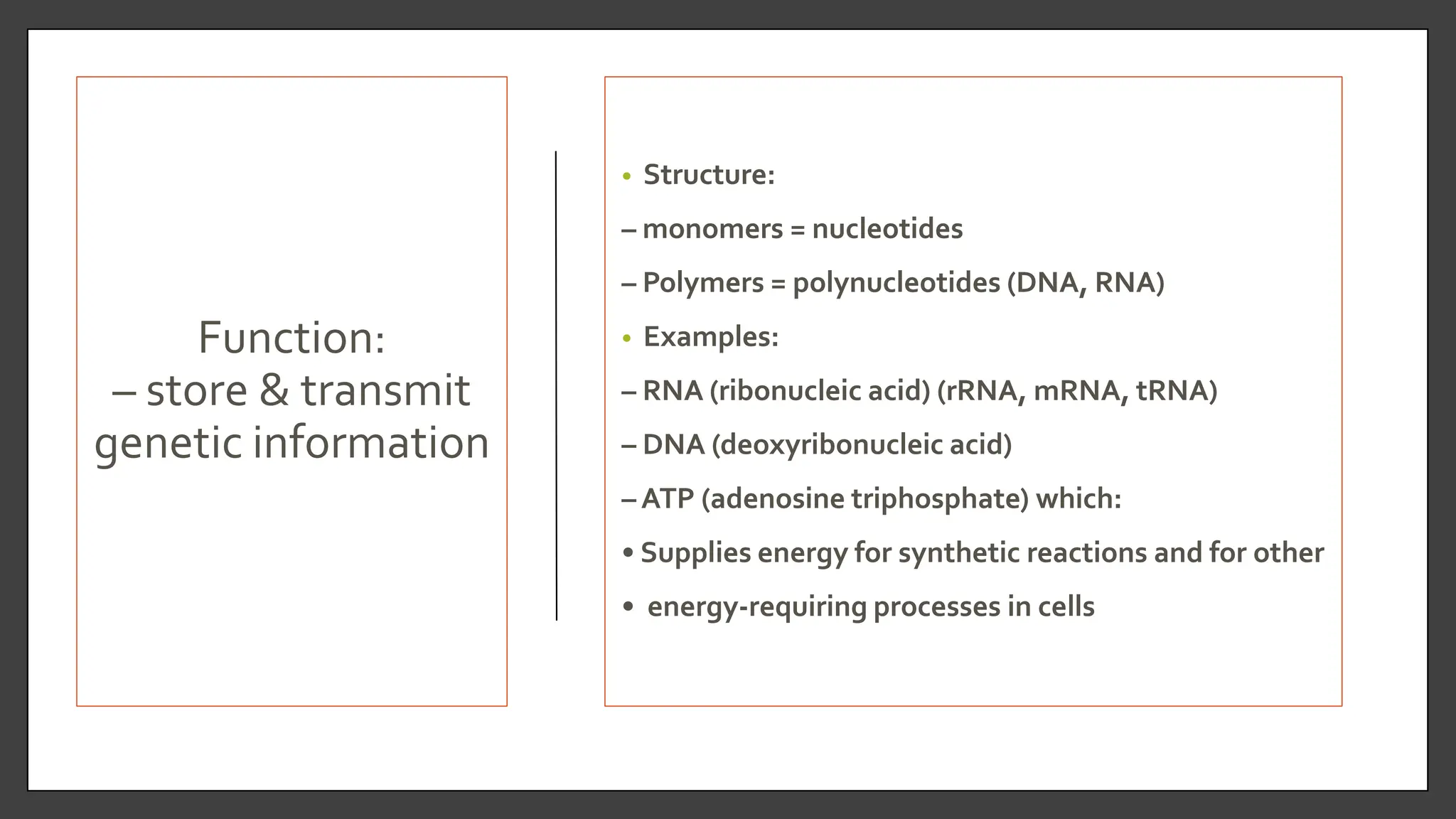
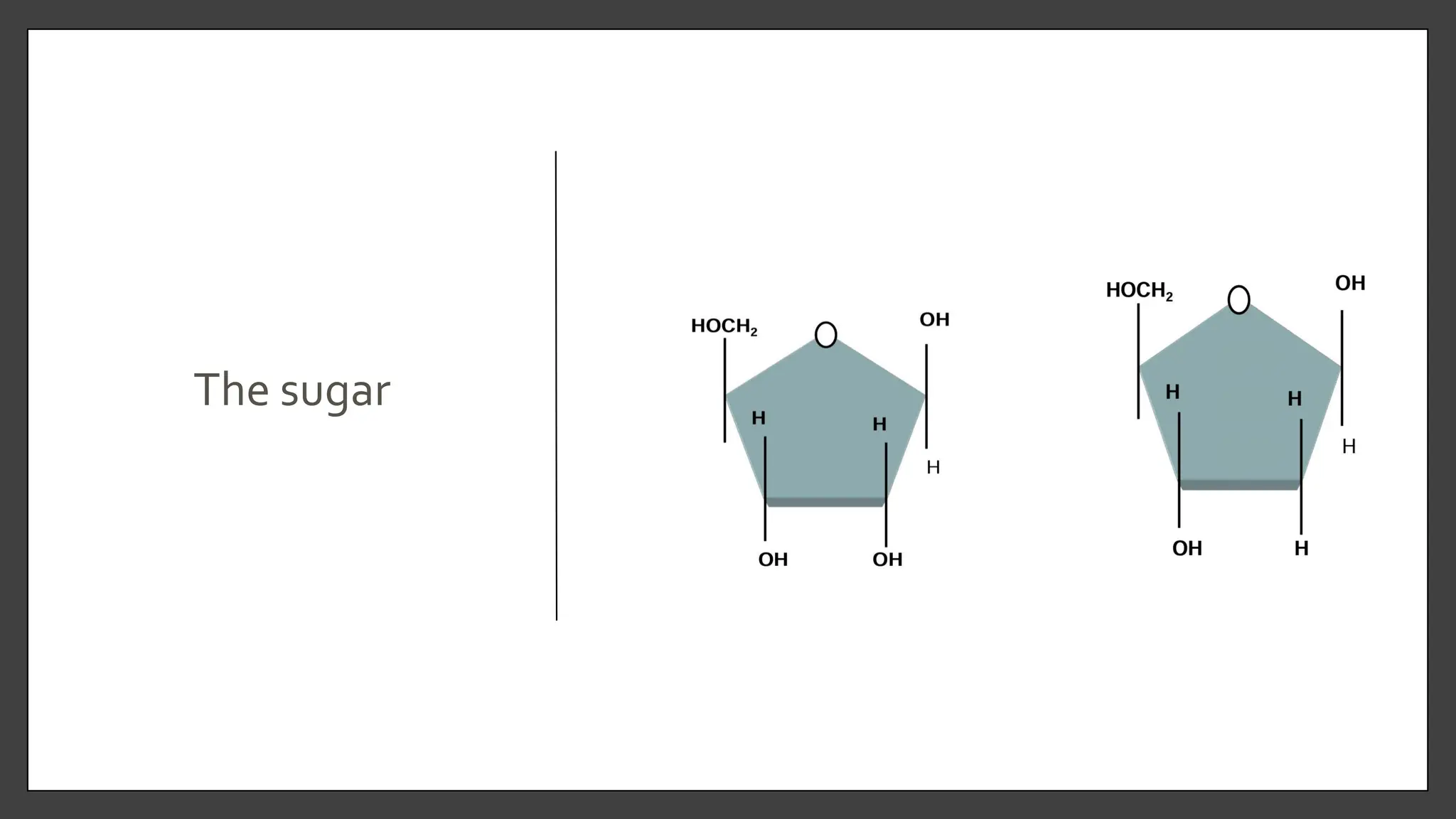
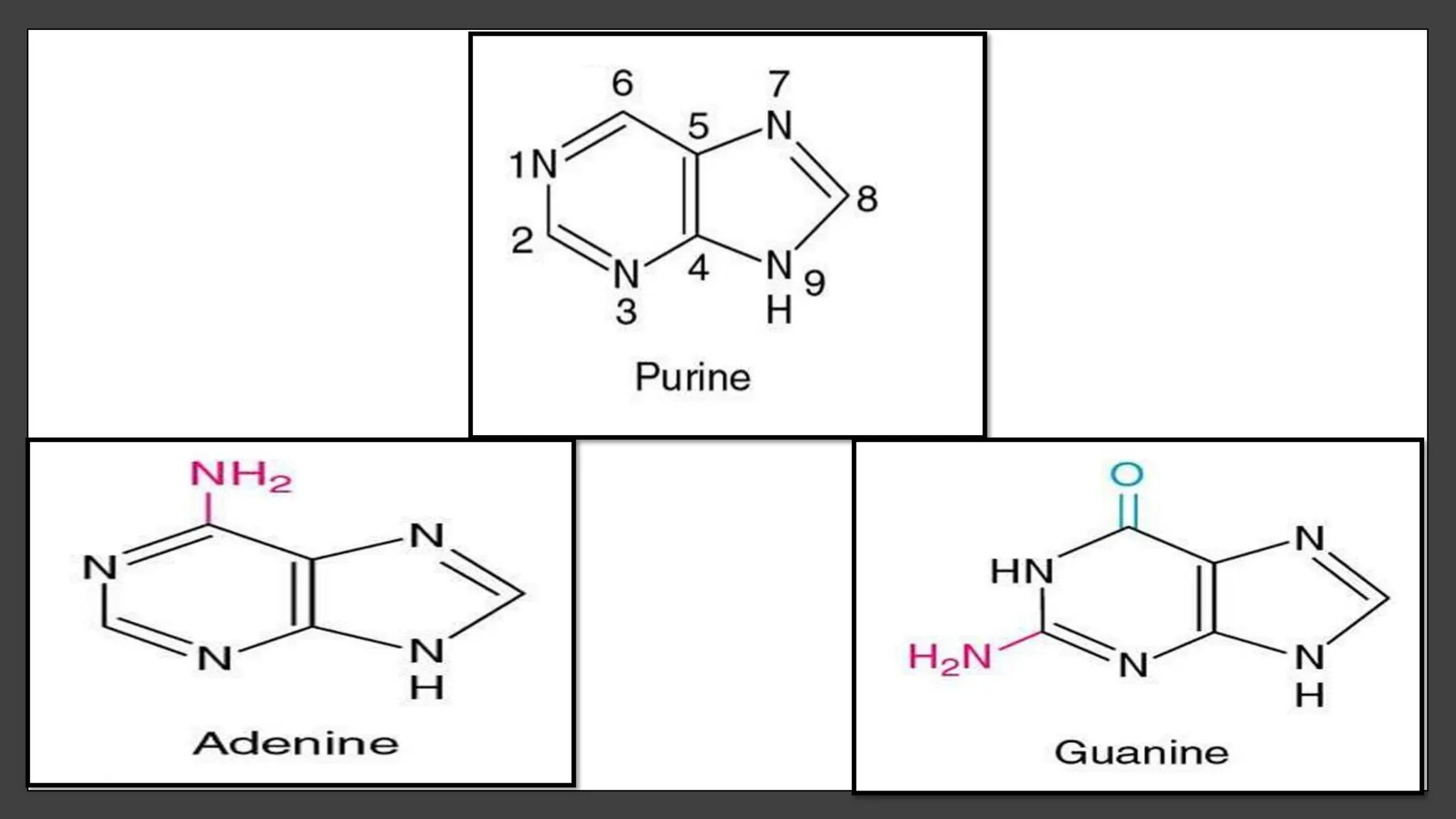
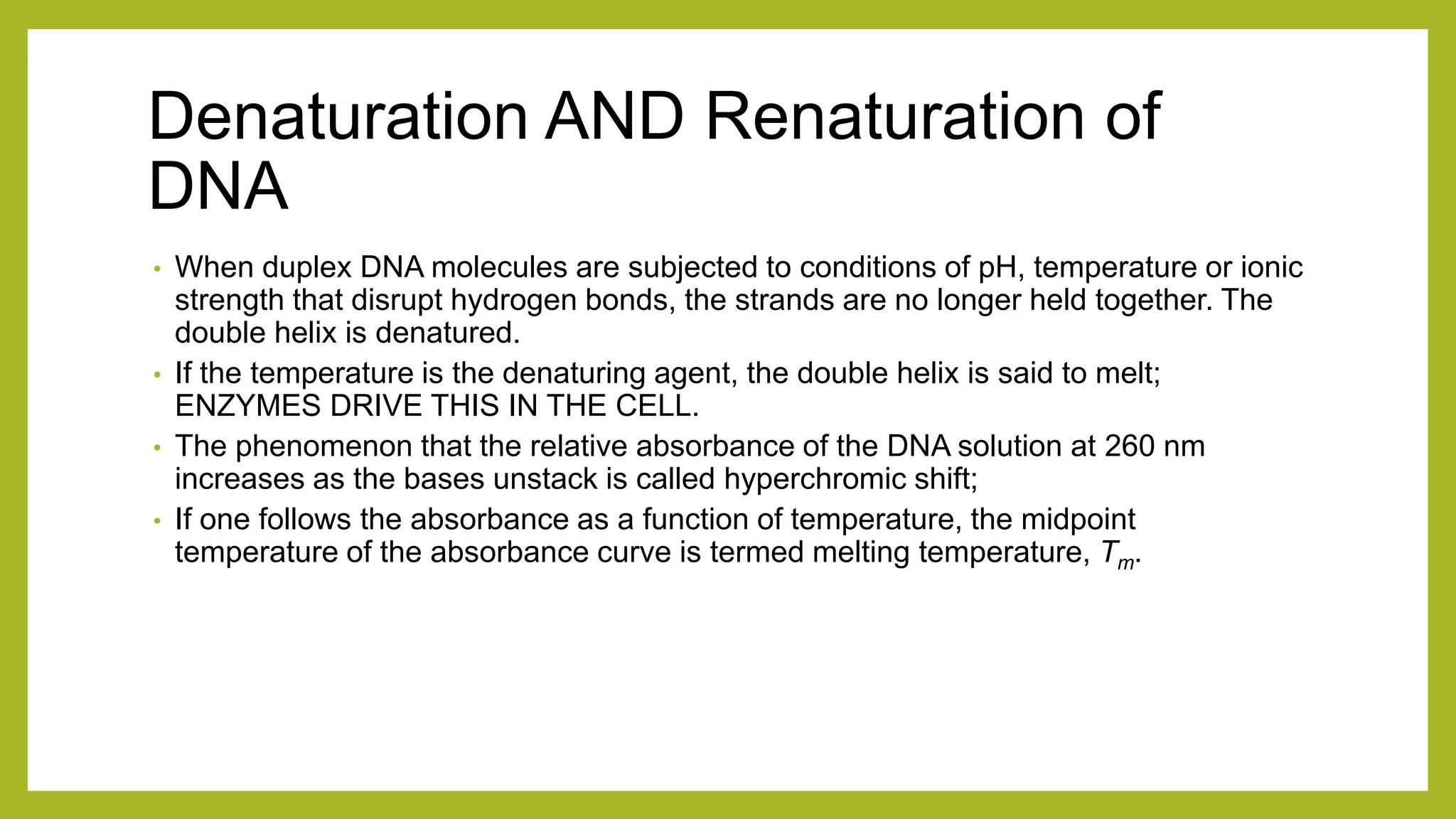
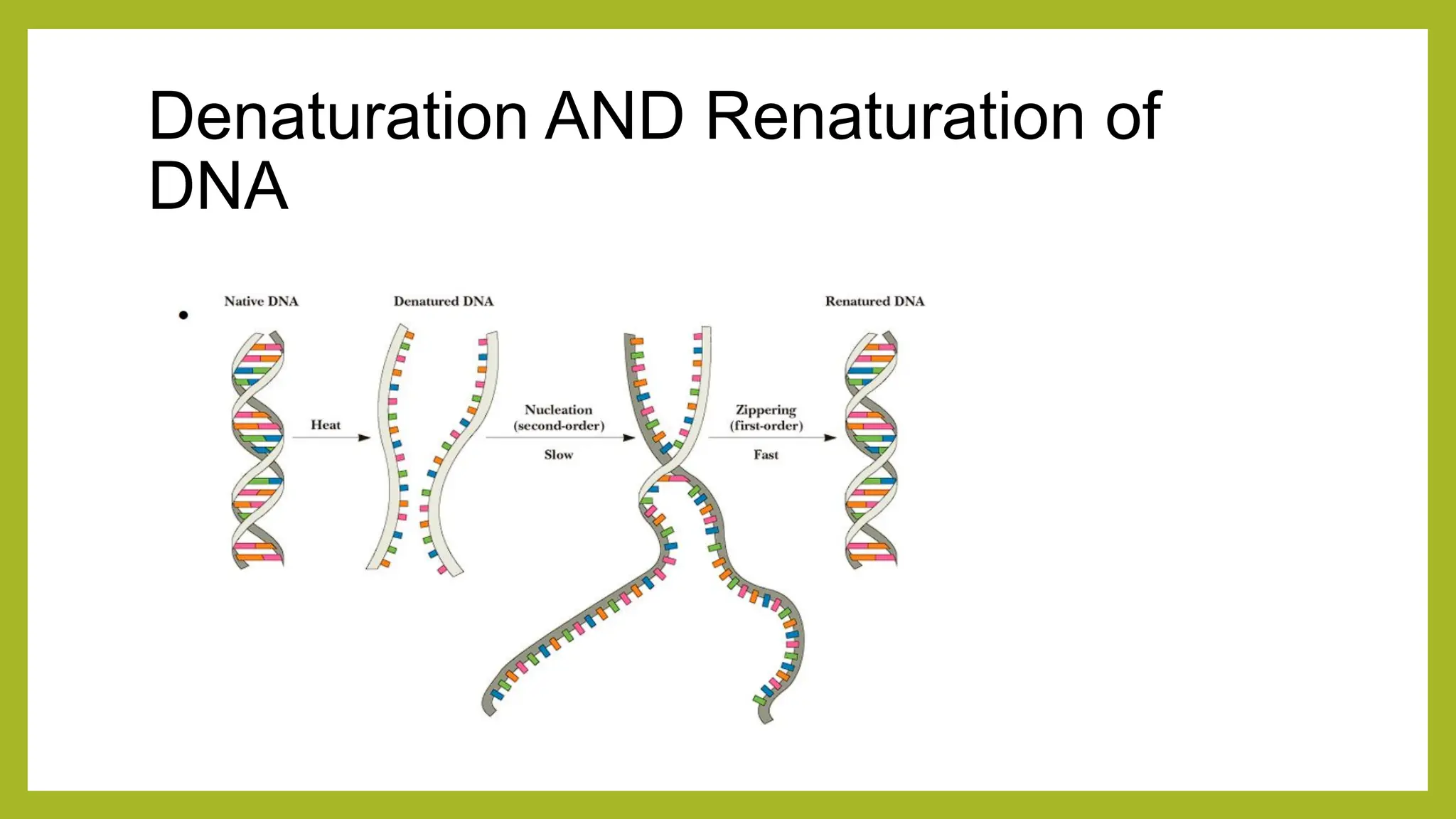
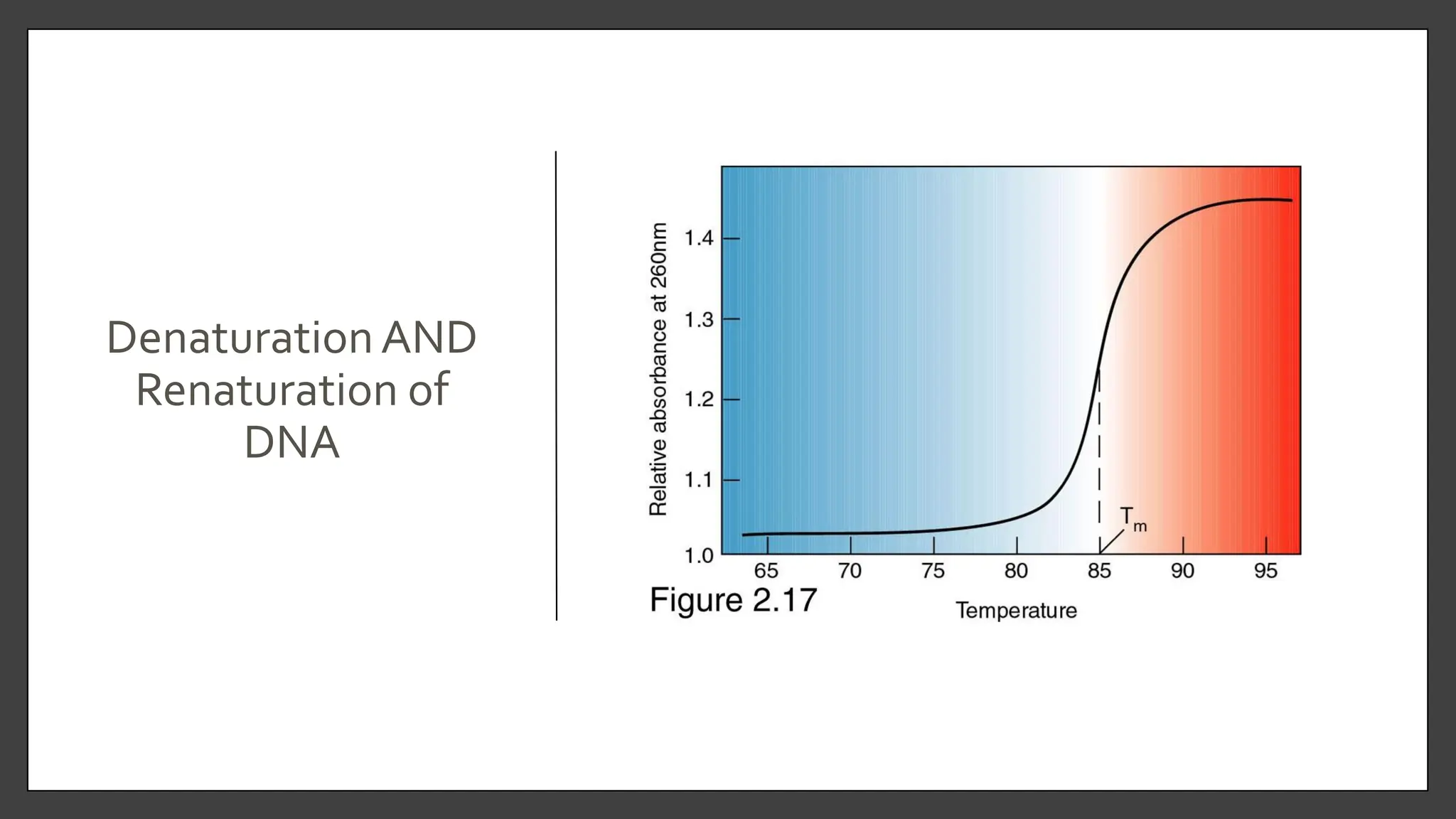
Nucleic acids, consisting of nucleotides that form DNA and RNA, are key for storing and transmitting genetic information. Their double helical structure is stabilized by hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions, while denaturation can occur due to changes in pH, temperature, or ionic strength, leading to increased absorbance at 260 nm. Factors like pH and temperature affect DNA stability, with specific ranges maintaining strand integrity and certain conditions leading to complete denaturation.