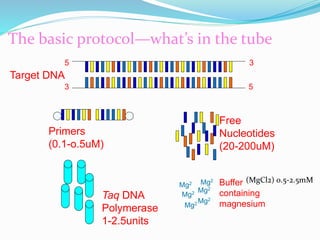
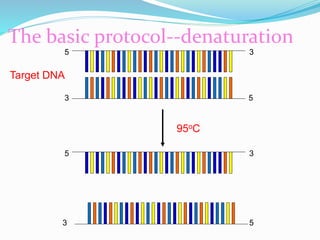
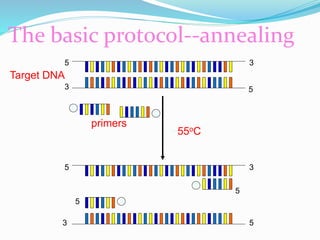
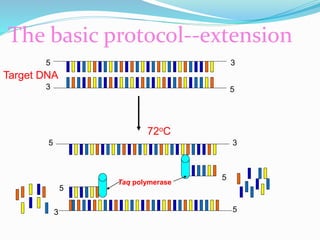
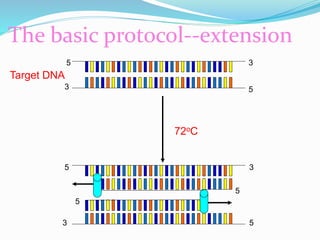
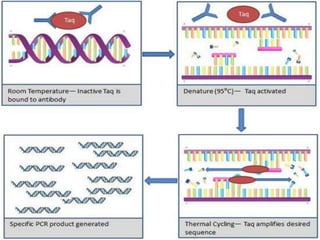
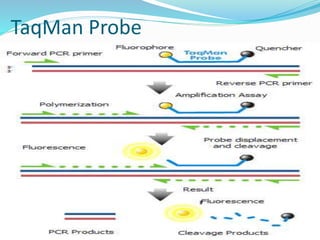
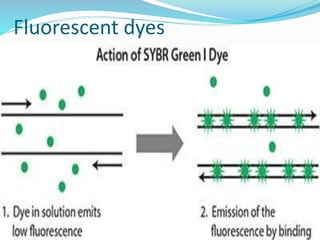
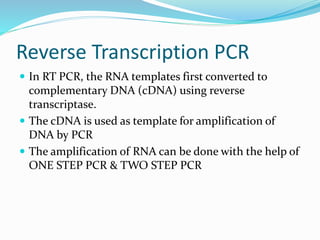
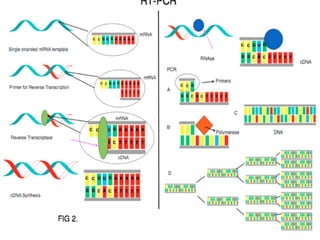
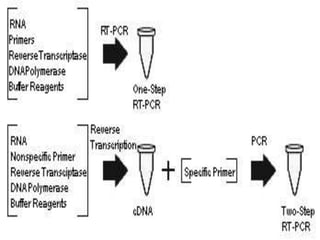
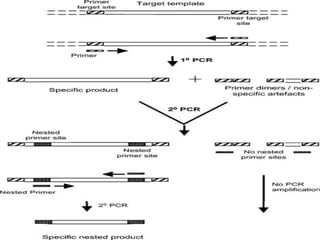
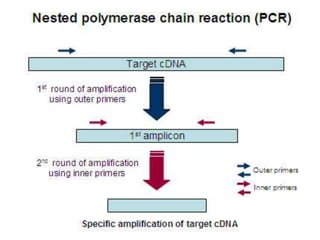
The document outlines various polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques, including standard PCR, hot-start PCR, quantitative PCR (q-PCR), reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), and nested PCR. PCR is a method used to amplify DNA sequences through thermal cycling, involving denaturation, annealing, and extension steps. Modifications and specific methodologies enhance PCR applications, including real-time detection, specificity improvements, and contamination reduction.