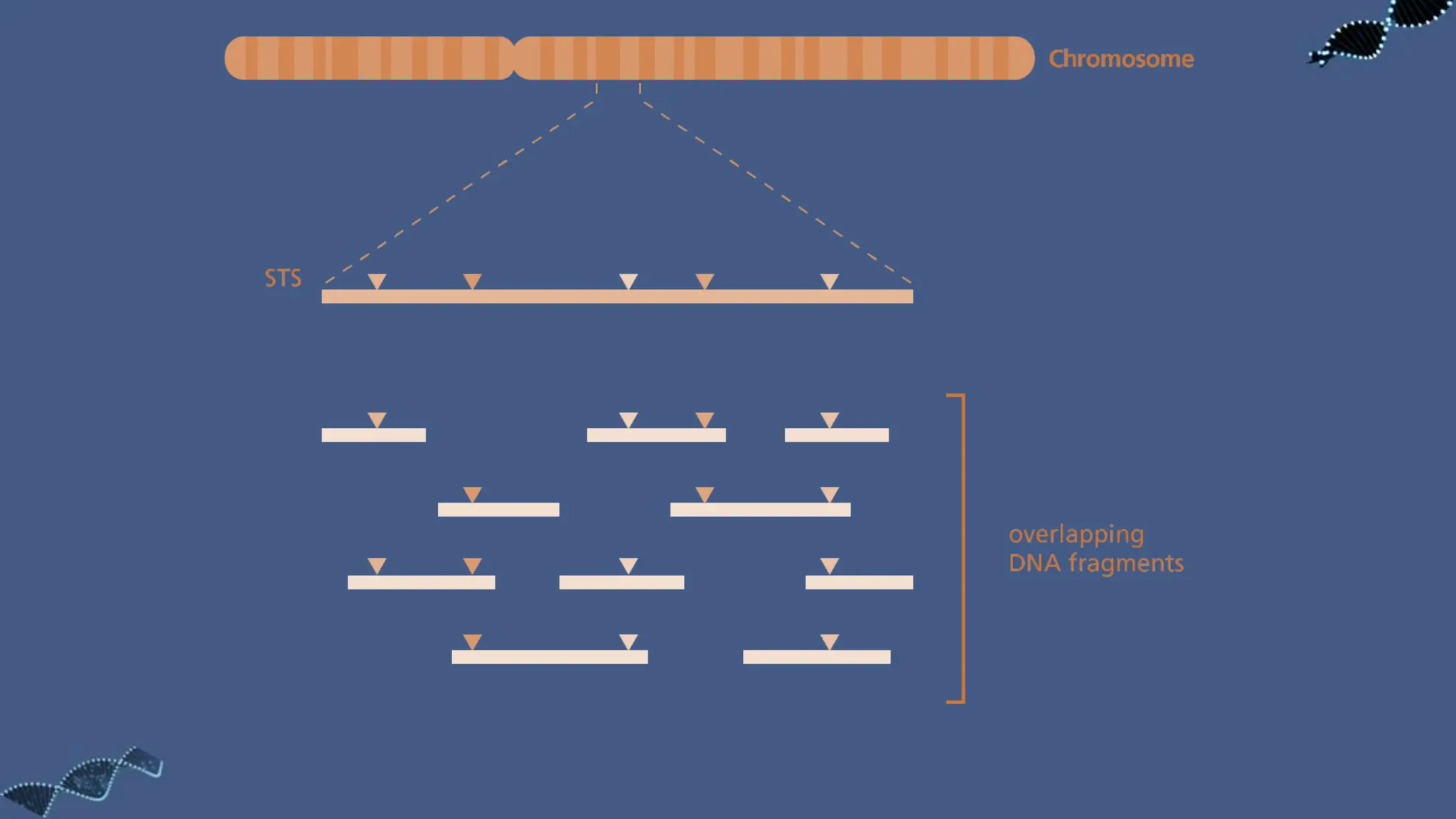
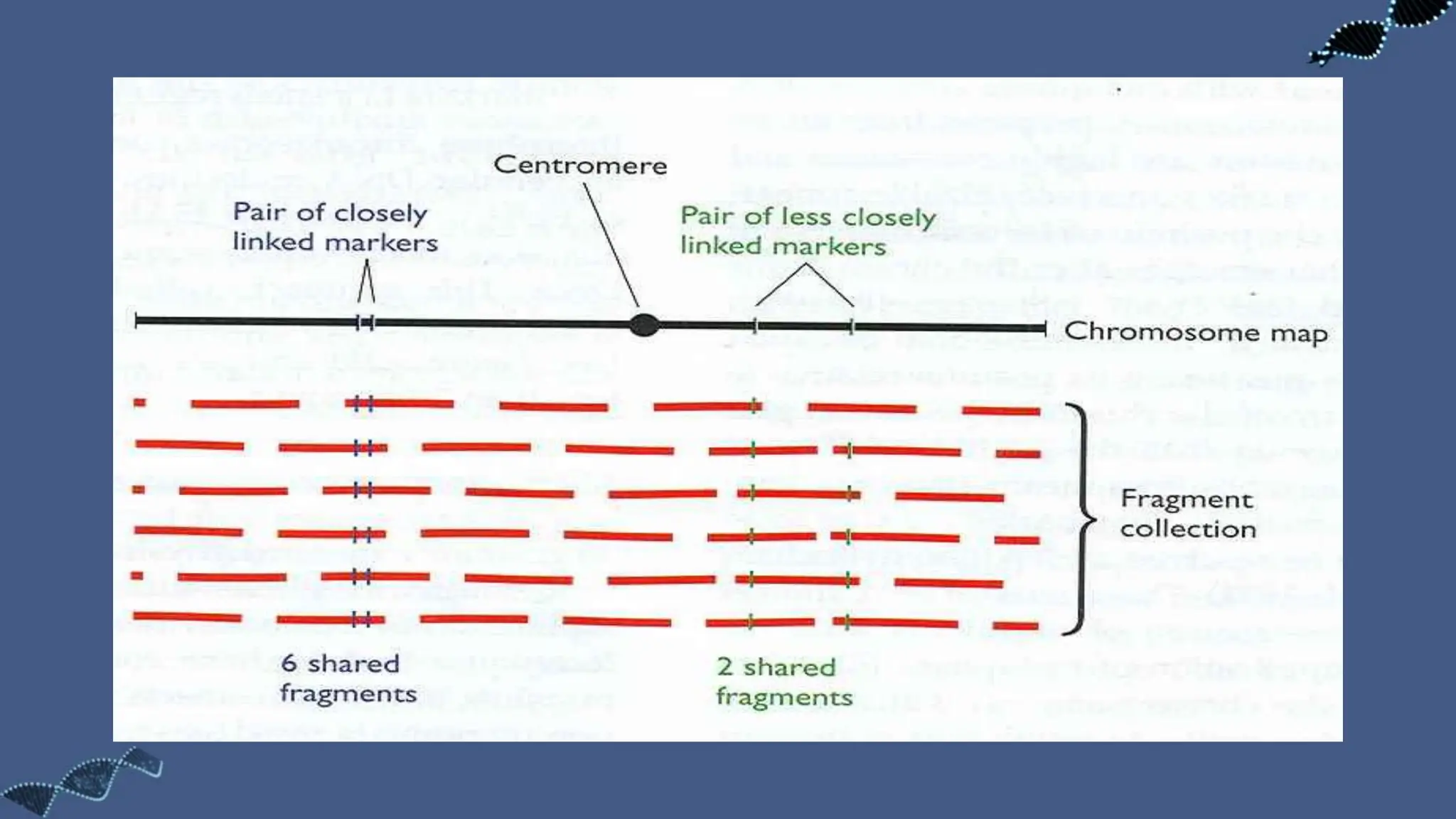
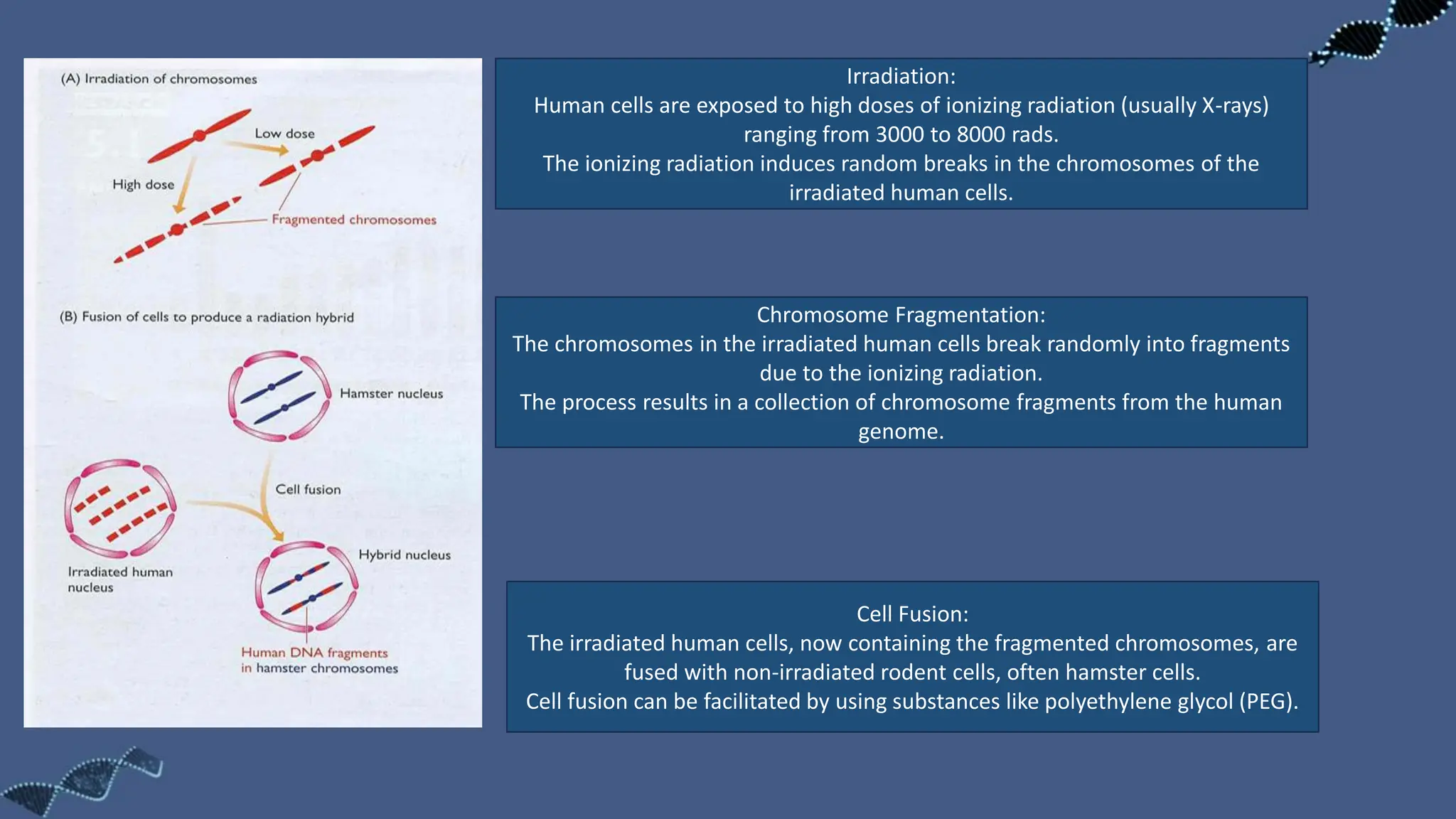
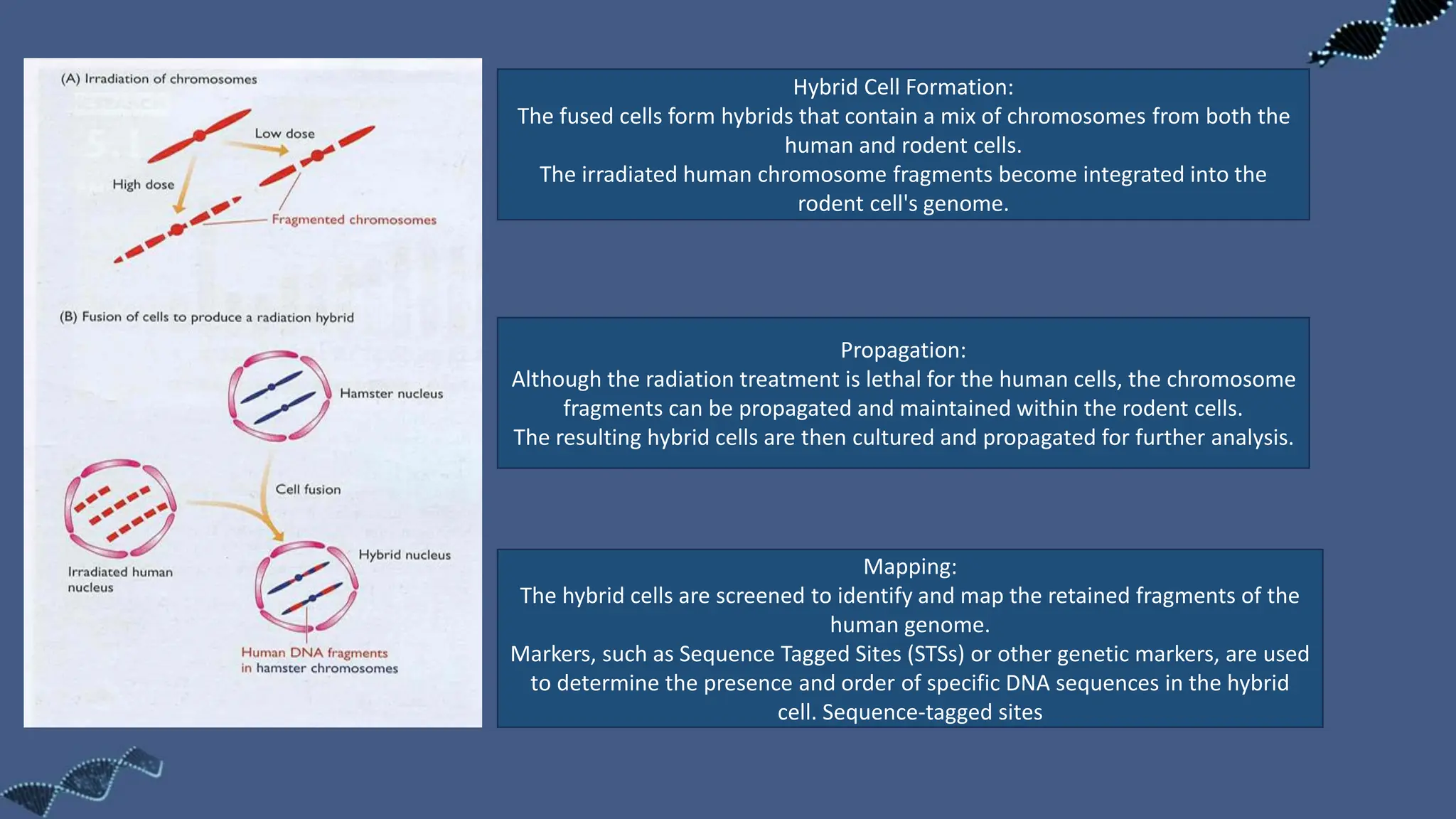
The document discusses the significance of sequence tagged sites (STSs) in physical mapping techniques, focusing on their role in generating detailed genome maps through methods like restriction mapping and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). It outlines the processes involved in obtaining STSs, including chromosome fragmentation induced by ionizing radiation and subsequent cell fusion with rodent cells to preserve human DNA fragments for analysis. Additionally, it describes the creation of a clone library from genomic DNA as a preliminary step for sequencing, emphasizing the advantages of using clone libraries for identifying overlapping DNA fragments.