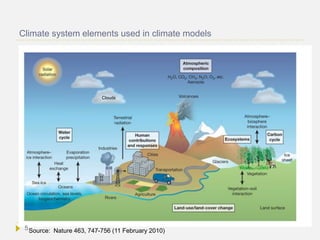
Climate models use mathematical equations and global grids to simulate and predict climate conditions based on physical principles and observational data. They show reasonable agreement with past climate trends and are used to project future climate change under different greenhouse gas emission scenarios. However, uncertainties remain regarding some processes like cloud formation. Current models estimate global warming of 0.3-1.7°C by 2100 under a low emission scenario and 2.6-4.8°C under high emissions, with greater warming over land and in polar regions. The models also predict more hot days and heat waves along with rising sea levels.


![ Reliability of climate models has to be tested against what happened with climate in the
past.[125] If a model can correctly simulate trends from a particular starting point somewhere
in the past, it can be used to predict with reasonable certainty what might happen in the
future. However, different models include different entry elements and may therefore
generate different predictions. Results can also vary due to different greenhouse gas or
aerosol inputs, the model's climate sensitivity to greenhouse gases (= the change in
temperature upon doubling of CO2 in the atmosphere), the use of differing estimates of
future greenhouse gas emissions (for example the rate of methane leakage during shale
gas extraction) and so on. A model-based prediction is therefore presented under different
scenarios with respect to humanity’s future demographic expansion and behavior. Which
scenarios are most realistic is uncertain, as the projections of future greenhouse gas and
aerosol emission are themselves uncertain.
Certain processes represented in the model may be too complex or too small-scale to be
physically represented in the model. In that case the process is replaced by a simplified
process. This manipulation is known as parameterization. Various parameters are used in
these simplified processes. An example are clouds. Cloud formation is notoriously complex
and climate model gridboxes for clouds have a resolution of 5 km, which is much larger than
the scale of a typical cumulus cloud (1 km). Therefore the processes that such clouds
represent are parameterized.
Because of simplification by parameterization and uncertainty in scenarios, climate models
always enclose estimates of uncertainty levels.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-4-320.jpg)
![Reliability of climate models
Models have accurately predicted climate change trends in the past. For example, the
vulcanic eruption of Mt. Pinatubo allowed to test the accuracy of models by entering the
eruption data and then observe how climate changed. The observed climatic response was
found consistent with the prediction. Predictions of atmospheric CO2 levels made by IPCC
in 1990 were also fully confirmed by the later observations (see slides on ‘Climate change in
the atmosphere’). Models also correctly predicted greater warming in the Arctic and over
land, greater warming at night, and stratospheric cooling.
Other predictions underestimated climate change, such as arctic ice melting and sea
level rise predicted by the IPCC Third Assessment report. Precipitation rates also
increased significantly faster than global climate models predicted.
Still others slightly over-estimated the rise in atmospheric methane concentrations (see
IPCC AR5 WG1).
An important uncertainty factor in climate predictions is climate sensitivity – being the
temperature response to a doubling of the atmospheric greenhouse gas concentration –,
because it is affected by climate feedbacks. Higher climate sensitivity will result in more
warming, in case of a positive feedback.[Ref] If a negative feedback is acting, a given
greenhouse gas rise will result in less sensitivity.
Climate models are still not well predicting the effect of clouds [Ref] , due to lack in
knowledge of cloud generation processes. Uncertainties in methane release from
permafrost and leakage during methane extraction from shale gas by fracking, are other
examples of prediction uncertainties.
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-6-320.jpg)
![Climate sensitivity
Projections of climate change in the future are dependent on the sensitivity of the climate
system to the greenhouse radiative forcing. It is therefore essential to have an accurate
estimate of this sensitivity. Climate sensitivity is a measure of the surface temperature change
in °C per W/m2 sustained radiative forcing. In practice it is expressed as the temperature
change associated with a doubling of the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere relative
to pre-industrial levels (~280 ppm). There are two ways to look at climate senstivity:
equilibrium climate sensitivity (ECS) and transient climate sensitivity (TCS). The former is
calculated over the time span needed to reach full equilibrium between sustained CO2
forcing and the climate system. TCS is defined as the average temperature response over a 20-
year period to CO2 doubling with CO2 increasing at 1% per year.[Ref] TCS is lower than ECS,
due to the "inertia" (slowliness) of ocean heat uptake and ice sheet feedbacks.
Doubling CO2 level results in forcing of 3.7 W/m2. In a simple physical environment a doubling
of CO2 would result in 1 °C warming. However, in the real atmosphere complex positive and
negative feedbacks are operating (water vapor, cloud and ice albedo, aerosols, ozone…),
influencing radiative forcing. The net warming effect was found to be ~3 times higher.
Feedbacks can also become stronger with time. For example ice sheets may melt at a given
time point at a much faster rate due to a sudden collapse of large ice shelves allowing massive
release of ice into the sea. Icebergs drift away to warmer water and melt, hereby decreasing
albedo, resulting in more warming. Addition of these longterm feedbacks to climate
models was found to lead to a higher value of ECS, but most climate models have not
included these feedbacks yet. Thus, future climate change may be more deleterious than
presently expected.
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-7-320.jpg)
![ Current climate models span an ECS range of 2.6–4.1 °C, most clustering around 3 °C."[Ref]
The IPCC AR5 concensus value of ECS, calculated by multimodel ensembles, is between
1.5°C and 4.5°C, is extremely unlikely <1°C, and very unlikely >6°C. Notice that
feedback contribution, being not constant over time, induces a level of uncertainty in any
climate model.
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-8-320.jpg)
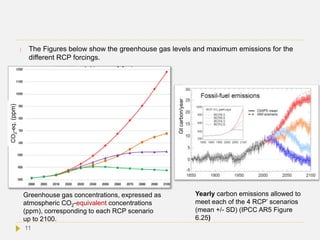
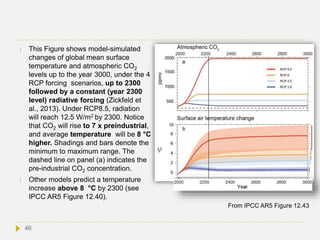
![IPCC radiative forcing scenarios
IPCC AR5 introduced a new set of scenarios, to project future climate change with
climate model simulations. These scenarios are called RCPs (Representative
Concentration Pathways). These are based on the radiative forcing that emission
rates would cause in the years to come. The main RCPs are RCP2.6, RCP4.5,
RCP6.0, and RCP8.5, named after the radiative forcing values that are projected
for the year 2100 i.e. +2.6, +4.5, +6.0, and +8.5 W/m2, respectively.[2]
In the RCP8.5 scenario radiative forcing is set to reach 8.5 W/m2 by 2100 and to
continue to rise for some time thereafter. RCP6.0 and RCP4.5 are intermediate
“stabilization pathways”, where radiative forcing does not further rise after 2100. In
the RCP2.6 scenario, radiative forcing peaks at 3 W/m2 before 2050 and then declines
to 2.6 by 2100.
To each forcing scenario there is a corresponding greenhouse gas level in the
atmosphere (see next slides). In order to remain within this future greenhouse gas
concentrations adopted in the RCP scenarios, the maximum cumulative fossil fuel
emissions should be not higher than 272 Gt, 780 Gt, 1062 Gt and 1687 Gt carbon
equivalents up to 2100 for RCP2.6, RCP4.5, RCP6.0, and RCP8.5, respectively (see
next slides).
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-9-320.jpg)
![ Although theoretically possible, [Ref] RCP2.6 is a
scenario difficult to attain, since 1) in 2012
radiative forcing was already 2.9 W/m2, 2) to
realize RCP2.6, atmospheric CO2 must be
stabilized at 450 ppm (see next slide) which
requires a ~70% reduction of CO2 emissions
relative to the level in 2000 (see section 5). 3)
Both RCP2.6 and 4.5 scenarios already include
‘carbon dioxide removal’ (CDR) programs (see
section 5) to remain within the radiative forcing
limit and these CDR programs are presently
considered difficult to realize on a sufficient
global scale and with sufficient safety.
Trends in radiative forcing for 4 different
scenarios (IPCC RCP scenarios). Forcing is
relative to pre-industrial values and does not
include land use (albedo), dust, or nitrate
aerosol forcing (van Vuuren 2011).
Source
RCP8.5
RCP6.0
RCP4.5
RCP2.6
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-10-320.jpg)


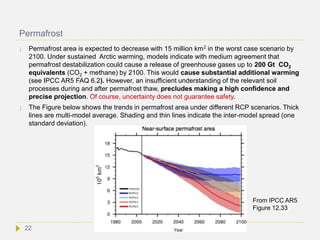
![ Consistent with this result is that during the Middle Pliocene warm intervals, when
global mean temperature was 2°C–3.5°C higher than pre-industrial, ice-sheet models
calculated near-complete deglaciation of Greenland. Some scientists predict that
climate change may make the entire Greenland ice sheet melt in about 2,000 years.[2]
That alone would add 7m to sea level [3].
The surface mass balance of the Antarctic Ice Sheet is projected to increase in most
models because increased snowfall outweighs melt increase. However, ice-shelf
decay due to oceanic or atmospheric warming might lead to abruptly accelerated ice
flow and loss into the sea. It remains uncertain whether East Antarctic ice sheet will
gain or loose mass [Ref]
Also James Hansen has argued that multiple positive feedbacks could lead to
nonlinear ice sheet disintegration by increased ice flow, calving and sudden ice
shelve collapses. More surface melt water would flow to the ice sheet bed, leading to
much faster melting of the ice interior.[Ref]. Moreover, as ice sheets shed ice more and
more rapidly, in ice streams, climate simulations indicate that a point will be reached
when the high latitude ocean surface cools while low latitudes surfaces are warming.
Larger temperature contrast between low and high latitudes will drive more
powerful storms.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-20-320.jpg)

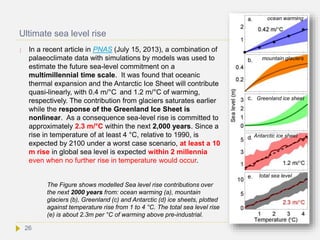
![Sea level rise
Sea level rise is expected to continue for
centuries, even millenia, even when
anthropogenic carbon emissions would
stabilize at the present level[13] This is
because the sea level contribution from ice
sheets continues over these time scales. In
2007, the IPCC AR4 projected that during the
21st century, sea level will rise another 18 to
59 cm, but these numbers do not include
"uncertainties in climate-carbon cycle
feedbacks nor do they include the full effects
of changes in ice sheet flow".[Ref] As shown in
the Figure, IPCC AR5 predicts similar sea
level rise. Projections assessed by the US
National Research Council[Ref] suggest
possible sea level rise over the 21st century
of between 56 cm and 2 m.
The predicted upper limit of sea level rise remains highly uncertain, due to the incomplete
understanding of fast ice streams and glacier collapse that are major contributors of ice
delivery to the sea and sea level rise (See Nature 461, 971-975, 2009).
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-25-320.jpg)


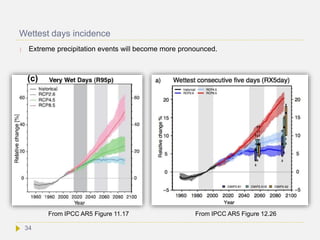

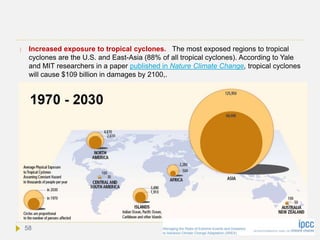
![Tropical cyclones
The intensity of Atlantic hurricanes is expected to increase as the ocean warms. More
heat means more energy to drive atmospheric circulations, evaporation and ocean-air
interactions. Although there have been dramatic improvements in predicting the
trajectory of tropical cyclones, the largest uncertainty exists in the prediction of tropical
cyclone intensity. The frequency of category 4 and 5 tropical cyclones over the 21st
century is expected to increase, the largest increase projected to occur in the Western
Atlantic, North of 20 degrees[Science 327, 454–458 (2010)]. A doubling of atmospheric CO2 may
increase the frequency of the most intense cyclones [J. Clim. 17, 3477 (2004)].
On the other hand, there is evidence that the strong cyclones cause a large amount
of ocean mixingRef, pumping heat from the surface down into the oceanic interior,
which is then redistributed over the globe, particularly through upwelling of the heat in
the equatorial Eastern Pacific, where El Niño originates. This may turn the globe into a
permanent El Niño condition[Ref], which will favor global warming in a closed positive
feedback loop.
In combination with sea level rise and tides, storm surges may cause more floods.
Moreover, climate simulations indicate that, as ice sheets release ice more and more
rapidly in ice streams and hence cool the ocean at high latitude, a point will be
reached when the high latitude ocean surface cools while low latitudes surfaces are
warming. Larger temperature contrast between low and high latitudes will induce
more powerful storms.[Ref]
43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-43-320.jpg)

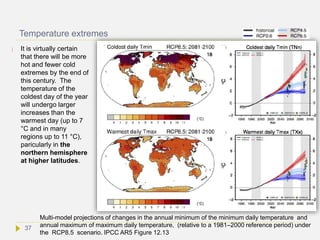
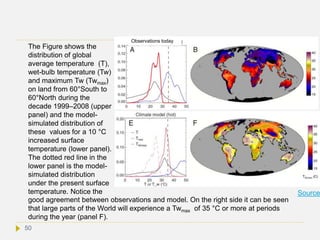
![Is the World inhabitable with a 10 °C rise in
average global temperature?
The human body at rest cannot survive in an ambient sustained wet bulb temperature
(Tw) ≥35°C. The highest Tw (Twmax) anywhere on Earth today is ~30 °C and the most-
common Twmax is 26–27 °C.[Ref] About 58% of the world’s population in 2005 resided in
regions where Twmax ≥ 26 °C. A recent climate model simulation study reported that a
global average temperature rise of 5 °C would result in a Twmax > 35 °C in some
locations. [Ref] For an 8.5 °C increase the most-common value of Twmax would be 35 °C
, which is incompatible with human life. With a 10 °C rise, many regions would
experience a Tw = 35 °C at a particular time each year, even in Siberia (see next
slide). It looks therefore that most of the World would be practically inhabitable
in a 10 °C warmer climate. At this temperature grain and agricultural production
would suffer very much or be destroyed, causing a food crisis. Humans could air-
condition their houses but deployment this over the World will be economically and
energetically extremely demanding and a power failure would be life threatening.
People working outside cannot work in air-conditioned environments and these would
rapidly develop hyperthermia. Poorer countries, which are located in tropical and
subtropical regions, will be hit the most.
During the PETM and EECO average global surface temperature rose 7-14 °C, which
is comparable to the study mentioned above. The question is then: How life could
have adapted to that hothouse? Humans have a body temperature of 37 °C but
many other mammals have a 2 °C and birds a 5 °C warmer body temperature[Ref] [Ref].
47](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-47-320.jpg)
![Non-human mammals and birds therefore may be more heat-tolerant than humans.
Just before the onset of the PETM mammals were small-sized (average = 1 kg)[Ref] [Ref]
[Ref]). This may have allowed their survival at that time, as small body mass is better
adapted to high temperatures (higher surface/mass ratio allowing better cooling).
Bioevolution during the PETM occurred over a time span of 20,000 years. In contrast,
anthropogenic warming extends over a few centuries, too short for a significant
evolutionary adaptation in heat tolerance.
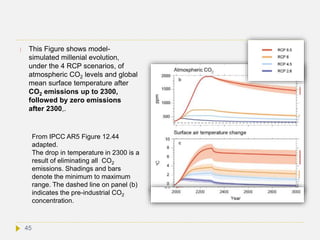
But is this a realistic scenario? RCP8.5 is considered by IPCC as a worst case
scenario maintained up to 2300. If this scenario becomes reality, humans will have
made the World ~5-10 °C warmer by then. Atmospheric concentration would have
risen to ~7 x preindustrial. If fossil fuel burning would further increase, we would be
on the way to a 10 °C rise. However, it looks highly unlikely that humans would not
reduce greenhouse gas emissions as soon as the impacts of climate change become
frightening, which is definitely earlier than 2300. Nonetheless, the temperatures
reached at that time would decrease only very slowly, even under strong reductions or
complete elimination of CO2 emissions. Temperature might even increase temporarily
due to an abrupt reduction of short-lived aerosol emissions and, hence, of aerosol
negative forcing – see IPCC AR5 Ch. 12). Heat stored in the ocean will be released at
an even slower rate. Thus, we would be forced to live in a World with climate
disasters in many regions for many centuries.
48](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-48-320.jpg)
![ Can a 10 °C rise be reached if we burn all fossil energy? Since it takes
more than 1000 years for emitted CO2 to be removed, the cumulative amount of
emitted CO2 determines future climate. The amount of fossil fuels still available
ranges between 7,300-15,000 gigatonnes carbon equivalent. James Hansen
calculated[Ref] that burning this amount would increase Earth’s average surface
temperature with 16°C. It would make the World practically inhabitable.
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-49-320.jpg)


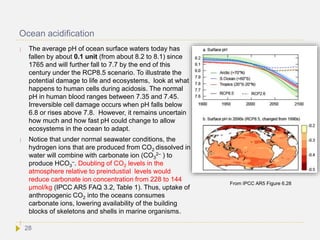
![Ecosystems[Ref]
In terrestrial ecosystems, the earlier timing of spring events, and poleward and upward
shifts in plant and animal range, have been linked with high confidence to recent
warming. Future climate change is expected to particularly affect certain ecosystems,
including tundra, mangroves, and coral reefs. It is expected that most ecosystems will
be affected by higher atmospheric CO2 levels, combined with higher global
temperatures. Overall, it is expected that climate change will result in the extinction of
many species and reduce ecosystems diversity. Since ecosystems provide many
goods and services to humans and other living systems in a mutually dependent
manner, the consequences of ecosystem losses may become a very serious problem.
The current rate of ocean acidification is many times faster than at least the past 300
million years, which included four mass extinctions that involved rising ocean acidity,
such as the Permian mass extinction, which killed 95% of marine species. By the end
of the century, acidity changes would match that of the Palaeocene-Eocene Thermal
Maximum (see slides on palaeoclimate), which occurred over 5000 years and killed
35–50% of benthic foraminifera[Ref] . It has been shown that corals, coccolithophore
algae, coralline algae, foraminifera, shellfish and pteropods experience reduced
calcification when exposed to elevated CO2 in the oceans. [Ref]
Warming of the surface ocean, combined with ocean acidification and reduction
in ocean oxygen concentration will have potentially nonlinear multiplicative impacts
on biodiversity and ecosystems and each may increase the vulnerability of ocean
53](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-53-320.jpg)
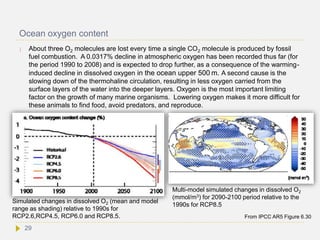
![systems, triggering an extreme impact. In the upper 500 m of the oceans oxygen
levels range between 50 and 300 mmol/m3, with levels highest at higher latitudes.
[Ref] Many marine organisms cannot survive under hypoxic conditions (oxygen
between 60 to 120 mmol/m3 depending on the species).[Ref] [Ref] Multiple studies
reported an impressive increase in the number of hypoxic ocean zones and their
extension, severity, and duration.[Ref] There are several examples in palaeoclimate
records that extreme ocean hypoxia led to the loss of 90% of marine animal taxa.[Ref]
The slowing down of the ocean’s circulation also results in fewer nutrients from the
deep layers into the ocean surface, which endangers oxygen-producing phytoplankton
that live in the ocean surface. Phytoplankton organisms produce half of the
world’s oxygen output (the other half is produced by plants on land). Hence, with
decreasing numbers of these oxygen producers, the level of oxygen in the ocean is
bound to decline further, entailing dramatic shortages in food supply.
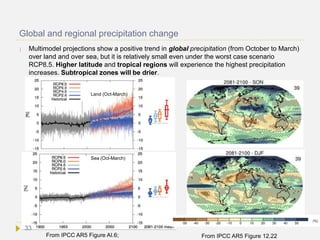
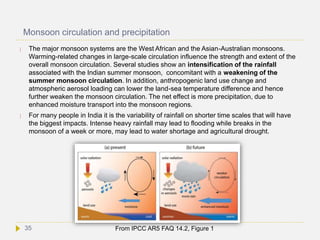
As reported by the IPCC AR5 WG1 chapt. 12, models consistently predict an increase
in dry season length, and a 70% reduction in the areal extent of the rainforest by
the end of the 21st century under a worst case scenario. If the dry season becomes
too long, wildfires combined with human-caused fire ignition, can undermine the
forest’s resiliency. Fire and deforestation could act as a trigger to abruptly and
irreversibly change the forest ecosystem. Forests purify our air, improve water
quality, keep soils intact, provide us with food, wood products and medicines, protect
54](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-54-320.jpg)

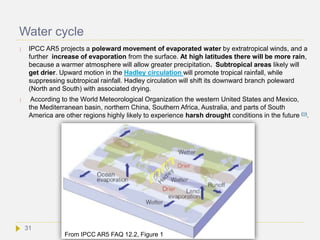
![Socio-economic consequences
Water and food supply:
Ocean warming, oxygen depletion, and acidification will result in reduction in primary
productivity of living species and, hence, in ocean goods and services for humans.
More floods will destroy more crops. Less water means less agriculture, food and
income. Crop yield will be decreased in drier areas.
The Himalayan glaciers provide water for drinking, irrigation, and other uses for about
1.5 billion people. Since most glaciers in the Hindu Kush Himalayan region are
retreating, the concern has been raised that over time the region's water supply may
be threatened. However, recent studies show that at lower elevations, glacial retreat is
unlikely to cause significant changes in water availability over the next several
decades. Other factors, such as groundwater depletion and increasing water use by
human activity could have a greater impact than the decrease of glacier water. On the
other hand, higher elevation areas could experience less water flow in some rivers if
current rates of glacier retreat continue, but shifts in rain and snow due to climate
change will likely have a greater impact on regional water supplies[Ref] . Whatever the
reason, climate change may likely threaten water supply and consequently food
supply.
Glacier recession reduces the buffering role of glaciers, hence inducing more floods
during the rainy season and more water shortages during the dry season.
56](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-56-320.jpg)

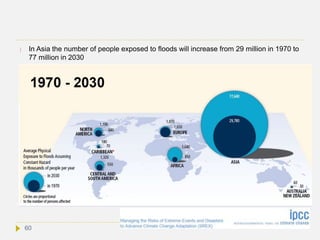
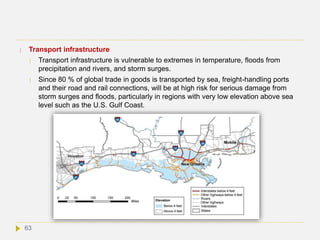
![ Increased exposure to floods.
An increase in the frequency or intensity of floods would be catastrophic in many low-
lying places around the World. Asian countries are particularly at risk, as low-lying
areas (like river deltas and small islands) are densely populated. In Bangladesh
alone, over 17 million people live at an elevation of less than 1 m above sea level, and
millions more inhabit the flat banks of the Ganges and Brahmaputra Rivers. Another
consideration is that poorer countries like Bangladesh do not have the financial
resources to relocate their citizens to lower risk areas, nor are they able to create
protective barriers. Read more
The Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development announced the 10
cities most vulnerable to flooding. Six are in Asia: Mumbai, Shanghai, Ho Chi Minh
City, Calcutta, Osaka, and Guangzhou. The other four are in the United States: New
York City, Miami, Alexandria, and New Orleans. All are coastal, low-lying, and
densely populated[12].
Floodwaters can contaminate drinking water, and sea level rise can lead to the
contamination of private wells, with local catastrophic results.
59](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-59-320.jpg)

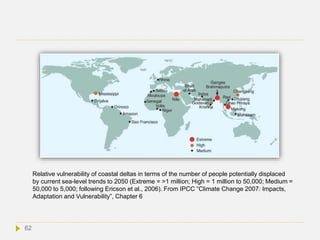


![ Environmental refugees:
There are currently between 25-30 million refugees worldwide as a consequence of
climate events, and their numbers are expected to rise to 200 million by
2100.[14]Unlike traditional refugees, environmental refugees are not recognized by the
Geneva Convention or the United Nations High Commission on Refugees (UNHCR),
and therefore do not have the same legal status in the international community. Most
threatened are people in developing countries - in particular, people in low-lying
regions, on small islands, and arid regions that suffer from drought across North
Africa, farm regions dependent on river water from glacier and snow melt, and regions
of Southeast Asia facing changes in monsoon patterns. These countries have the
least economical power to adapt to climate change.
Most international statements on human rights in relation to climate change have
emphasized the potential adverse impacts of climate change on the human rights to
life, health, food, water, housing, development, and self-determination.[13] These rights
are enumerated in the UN conventions of international human rights law, though not
all UN members or UNFCCC parties have signed these conventions.
66](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-66-320.jpg)
![ Worsening of human conflicts.
The impact of climate change will make
the poorest communities across the
world poorer. Many of them experience
conflict and instability, on top of poverty,
which exposes them to a dual risk. The
impact of climate change may entail
more violent conflict, which in turn
counteracts governments and people to
adapt to climate change. Thus, climate
change and violent conflict create a
potential vicious circle of destruction, if
not properly cared of by the international
community.
International peacebuilding NGO
International Alert named 46 countries
where climate change effects may
interact with economic, social, and
political forces to create a high risk of
violent conflict.[15]
1. Afghanistan
2. Algeria
3. Angola
4. Bangladesh
5. Bolivia
6. Bosnia & Herzegovina
7. Burma
8. Burundi
9. Central African Republic
10. Chad
11. Colombia
12. Congo
13. Côte d’Ivoire
14. Dem. Rep. Congo
15. Djibouti
16. Eritrea
17. Ethiopia
18. Ghana
19. Guinea
20. Guinea Bissau
21. Haiti
22. India
23. Indonesia
24. Iran
25. Iraq
26. Israel & Occupied
Territories
27. Jordan
28. Lebanon
29. Liberia
30. Nepal
31. Nigeria
32. Pakistan
33. Peru
34. Philippines
35. Rwanda
36. Senegal
37. Sierra Leone
38. Solomon Islands
39. Somalia
40. Somaliland
41. Sri Lanka
42. Sudan
43. Syria
44. Uganda
45. Uzbekistan
46. Zimbabwe
67](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-67-320.jpg)
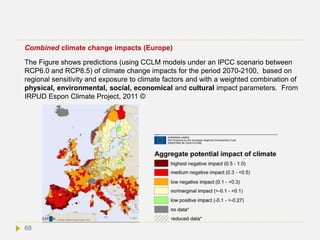
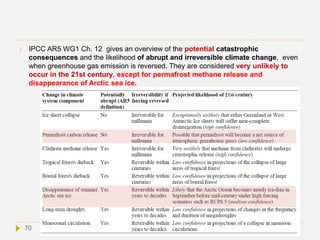
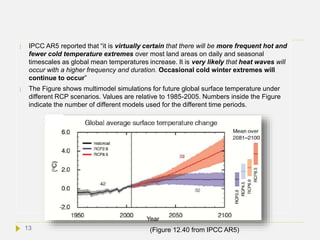
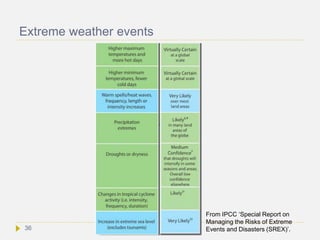
![Potentially abrupt and irreversible changes
(”tipping points”)
According to IPCC AR5 WG1 Chapter 12, abrupt climate change is defined as a
large-scale change in the climate system that develops over a few decades or less,
persists for at least a few decades, and causes substantial disruptions in human and
natural systems. Abrupt changes arise from nonlinearities within the climate system.
They are therefore inherently difficult to assess and their timing is difficult to predict.
Nevertheless, progress is being made on the basis of early warning signs for abrupt
climate change.
AR5 defines a perturbed climate state as irreversible (also known as a “tipping
point”), if the timescale of recovery from this state via natural processes is
significantly longer than the time it took for the climate system to reach this perturbed
state. According to this definition climate change resulting from CO2 emissions are
irreversible, due to the long residence time of the CO2 in the atmosphere and the
inertia of oceans to store the CO2 and the resulting warming (see next slides). A
tipping point is a point such that no additional forcing is required for large change and
impacts to occur.[8] If climate change reaches a state that causes serious disconfort to
humans, potential catastrophic situations emerge for centuties, and even millenia.
69](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/climatechangeprediction-140804075719-phpapp02/85/Climate-change-prediction-69-320.jpg)