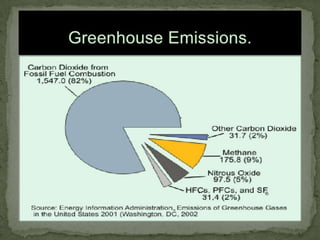
The presentation discusses the concepts of greenhouse effect, climate change, and global warming, highlighting their distinct processes and causes, including human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation. It outlines the mechanisms by which the Earth's atmosphere traps heat, leading to rising temperatures, changing weather patterns, and potential remedies to mitigate these effects. It emphasizes the urgent need for alternative energy sources and actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.