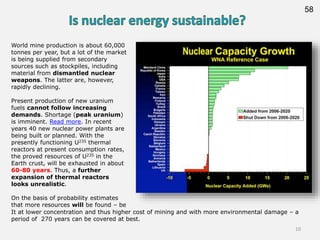
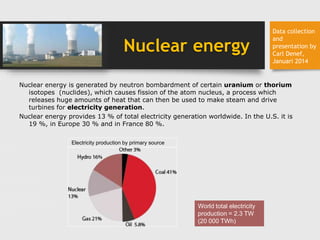
Nuclear energy is generated through fission of uranium or thorium isotopes, which releases heat that is used to generate electricity. It currently provides 13% of the world's electricity, with higher percentages in some countries like France. Uranium is mined through various methods and enriched before being used as fuel in nuclear reactors, where it generates energy through fission. Spent fuel poses environmental and safety risks and challenges with long-term storage, but some methods like fast breeder reactors and thorium reactors could help mitigate these issues. The nuclear power debate involves considerations of both benefits like low-carbon energy production and risks relating to safety, waste disposal, and weapons proliferation.
![Uranium is mined either in open pit, by
standard underground mining or by in
situ dissolving of the minerals and
pumping the solution to the surface. In
open pit mining, the ore is exposed by
drilling and blasting and then mined by
blasting and excavation. Workers need to
stay in enclosed cabins to limit exposure
to radiation. Water is extensively used to
suppress airborne dust levels and in deep
undergound mines to cool. There is less
waste material removed from underground
mines than open pit mines. However, this
type of mining exposes underground
workers to the high levels of radioactive
radon gas, unless sufficient ventilation is
installed.
The naturally occurring oxide forms and not
the uranium metals are used for safety
(the oxide melting point is much higher
than that of the metal and it cannot burn,
being already in the oxidized state).
Before use as fuel uranium is enriched.
Today (2013) 437 nuclear power
reactors are operational in
31 countries.[4] The total identified and
probable (yet undiscovered) uranium
resources are about 15 megaton,
representing a power capacity of 235 TW.
World production is ~60,000 tonnes/year
generating ~380 GWelectric power (~1 TW
primary heat power from the reactors)
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearenergy-140804080846-phpapp02/85/Nuclear-energy-2-320.jpg)




![There are serious safety and environmental
concerns with U235 thermal reactor power
plants.
Health issues: Because uranium ore emits
radon gas, uranium mining can be a health
hazard, unless adequate ventilation systems
are installed.
Environmental issues: Nuclear power
plants are almost always built near lakes,
rivers and oceans because running a nuclear
reactor requires a large amount of cooling
water. A typical 1 GW nuclear reactor needs
approximately 1500 m3 per minute and this
warmer water is then discharged back into
the local ecosystem causing adverse effects
for the aquatic life.
Safety: The 1979 accident at Three Mile
Island, the 1986 Chernobyl disaster, the
1995 Monju accident and the recent
Fukushima nuclear disaster in Japan clearly
demonstrated the potential catastrophic
danger of nuclear power plants. This played a
part in stopping new plant
construction in many countries and to shut
down facilities in some others.
Radioactive waste disposal: About 10,000
tonnes of highly radioactive nuclear waste is
stored each year,[99] mainly at individual
reactor sites (over 430 locations around the
world). Of particular concern are
Technetium99 (half-life 220,000 years) and
Iodine129 (half-life 15.7 million years). Other
products are unconverted U235 , plutonium
and curium. About 95% of the depleted
uranium is stored as uranium hexafluoride
(UF6), in steel cylinders in open air close to
enrichment plants. There is no consensus yet
where to safely longterm store nuclear
waste.
Misuse of fuel for nuclear weapon
production (from plutonium)
Nuclear terrorism
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearenergy-140804080846-phpapp02/85/Nuclear-energy-7-320.jpg)
![The nuclear power debate
There are multiple organizations which have taken a position on nuclear power – some are proponents,
and some are opponents.
Opponents
• Friends of the Earth International, a network of environmental organizations in 77 countries.[183]
• Greenpeace International, a non-governmental environmental organization[184] with offices in 41
countries.[185]
• Nuclear Information and Resource Service (International)
• World Information Service on Energy (International)
• Sortir du nucléaire (France)
• Pembina Institute (Canada)
• Institute for Energy and Environmental Research (United States)
• Sayonara Nuclear Power Plants (Japan)
Proponents
• World Nuclear Association, a confederation of companies connected with nuclear power production.
(International)
• International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)
• Nuclear Energy Institute (United States)
• American Nuclear Society (United States)
• United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority (United Kingdom)
• EURATOM (Europe)
• Atomic Energy of Canada Limited (Canada)
• Environmentalists for Nuclear Energy (International)
8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearenergy-140804080846-phpapp02/85/Nuclear-energy-8-320.jpg)
![Attempts to mitigate the nuclear radioactive waste problem
• Reprocessing of the spent U235 fuel can potentially recover up to 95% of the
remaining uranium and plutonium which can be reused as fuel (MOX). The
radioactivity left consists largely of short-lived fission products, and its volume is
reduced by 90%. Reprocessing is done in the UK and France, and to a lesser
extent in Russia, India and Japan. However, it is not allowed in the U.S.[129] The
Obama administration has disallowed reprocessing on the basis of nuclear weapon
proliferation concerns.[130]
• The nuclear waste problem can substantially be mitigated in the future by
using fast breeder reactors that almost completely convert the nuclear fuel,
leaving radioactive waste products in much smaller amounts for much shorter
times (a few hundred years).
• Used Thorium fuel also remains radioactive for only a few hundreds of years.
• Fast breeder reactors also offset the present relative shortage of U235.
• However, fast breeder reactors are much more expensive, the fuel needs to be
more enriched, sodium used as a coolant can explode and burns in air and is very
corrosive and nuclear proliferation concerns remain real. Thorium fuel products
are claimed to be more nuclear weapon proliferation-resistant than other fuel
products since Thorium produces fissionable U233 instead of fissionable plutonium. 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nuclearenergy-140804080846-phpapp02/85/Nuclear-energy-9-320.jpg)