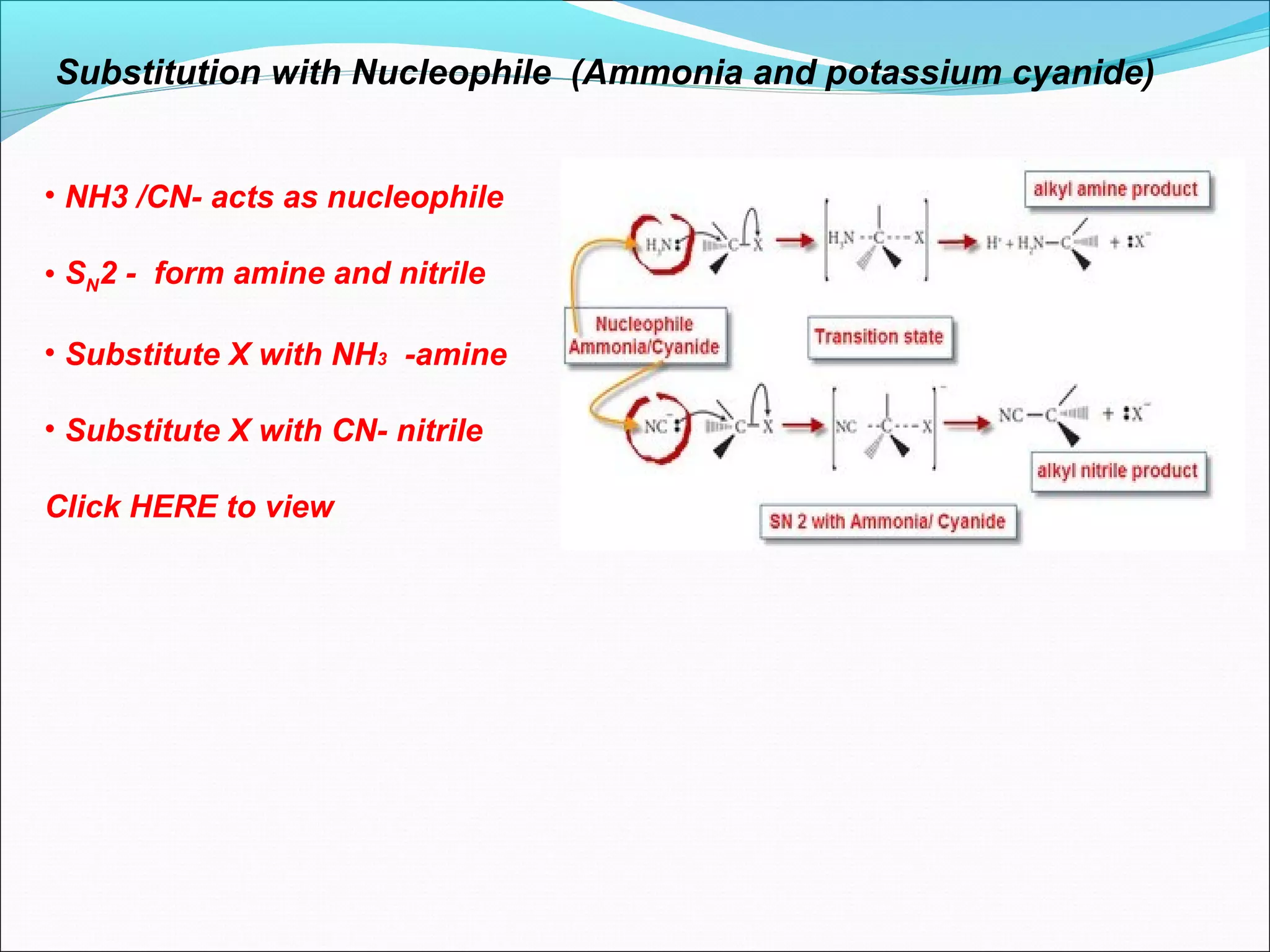
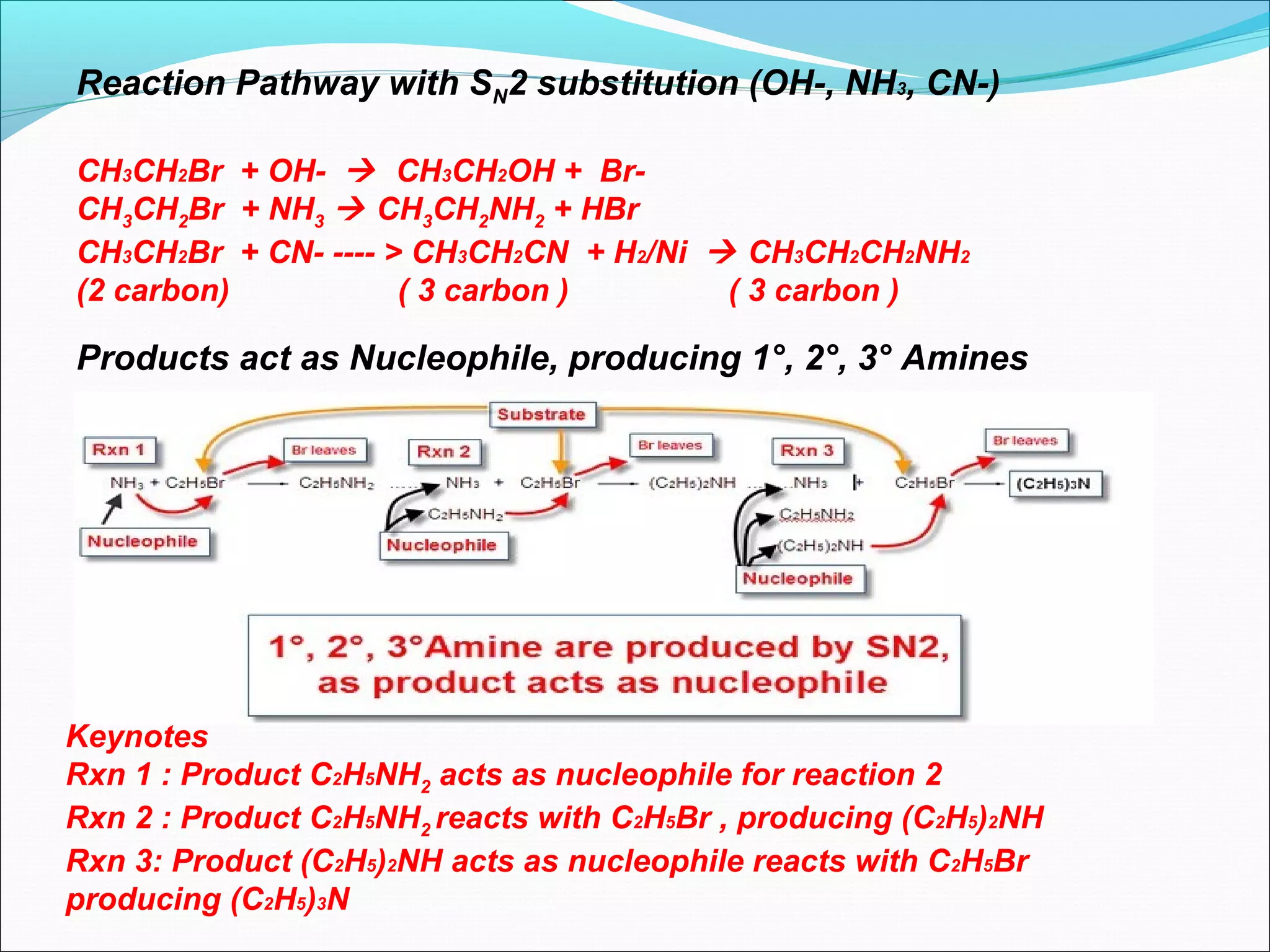
This document discusses nucleophilic substitution reactions, specifically SN1 and SN2 mechanisms. SN1 is a two-step reaction that proceeds through a carbocation intermediate, depending on the concentration of the substrate. SN2 is a one-step bimolecular reaction where bond breaking and formation occur simultaneously. Tertiary halogenoalkanes typically undergo SN1, while primary halogenoalkanes usually undergo SN2 due to steric and inductive effects. Factors like the nature of the halogen, halogenoalkane, and nucleophile affect the rate of these substitution reactions.



![Mechanism of Nucleophilic Substitution (SN1 and SN2 )
SN1 - Substitution Nucleophilic Unimolecular
• SN1 - 2 steps, unimolecular ( first order)
• 1st step - slow/rds, Carbocation formation
• 2nd step - fast, Nucleophilic attack
carbocation
• Rate = k [substrate], First order overall
• Rate depend on conc substrate
NOT conc nucleophile
• Nature of the nucleophile doesn’t
affect the rate
Click HERE for more info](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleophilicsubstitutionsn1sn2nucleophilehalogenoalkaneinorganicchemistry-141013133729-conversion-gate02/75/Nucleophilic-substitution-sn1-sn2-nucleophile-halogenoalkane-in-organic-chemistry-4-2048.jpg)

![SN2 - Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular
• 1 step mechanism, Bimolecular collision
• Rate = k[substrate][nucleophile], Second order overall
• Rate depend on conc of substrate and nucleophile
• Bond making/breaking occur together result in trigonal bipyramidal shape
• Inverted configuration (backside attack by Nucleophile)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleophilicsubstitutionsn1sn2nucleophilehalogenoalkaneinorganicchemistry-141013133729-conversion-gate02/75/Nucleophilic-substitution-sn1-sn2-nucleophile-halogenoalkane-in-organic-chemistry-6-2048.jpg)