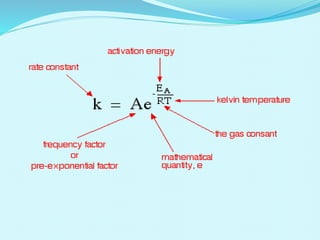
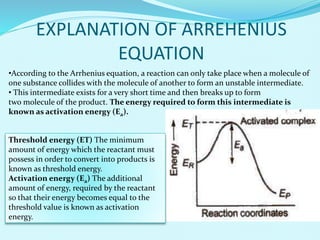
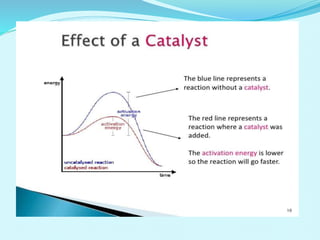
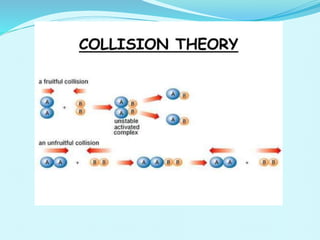
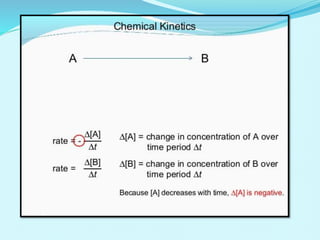
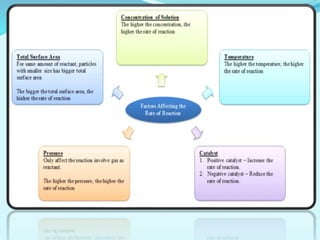
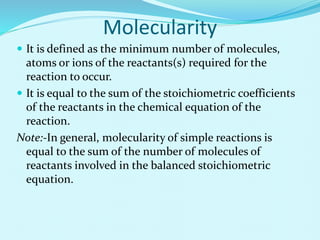
Chemical kinetics deals with the rates of chemical reactions and factors that affect reaction rates. Reaction rates can be fast, slow, or moderately slow. The average and instantaneous rates of reaction are defined. Factors that affect reaction rates include the nature of reactants, concentration of reactants, temperature, and surface area of reactants. The rate law defines how reaction rates depend on reactant concentrations. Order of reaction refers to dependence of rate on concentrations and is determined experimentally. Molecularity refers to the minimum number of reactant molecules required for the reaction. The Arrhenius equation relates reaction rate to temperature through the activation energy. Collision theory proposes that reactions occur through effective collisions of reactant molecules with sufficient energy.









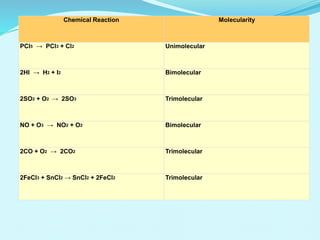
![ORDER OF THE REACTION
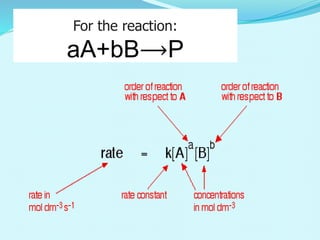
Sum of the power of concentration.
Rate=k [A]m [B]n
• The order of such a reaction is (m + n).
• Order of reaction:- positive, negative, zero and fractional.
• Example:
H 2 + I2 2 HI
reaction order= 1+1= 2
• Reaction order is determined by experiment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class12chemicalkinetics-240104162115-fe1ed3c1/85/class-12-chemicalkinetics-pptx-12-320.jpg)






![• Reaction is said to be first order if its rate is determined by the change of one
concentration term only.
FIRST ORDER REACTION
Consider the reaction, A → products
Let [A]O = Initial Concentration of A, [A]T = The concentration of A after time t
For the reaction to be of first order..
The differential equation describing first-order kinetics is given below:
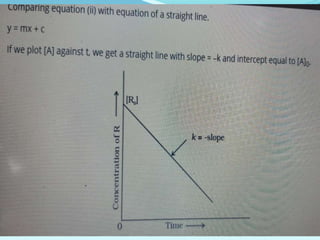
Rate=−d[A]/dt=k[A]……………………………………………….(1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class12chemicalkinetics-240104162115-fe1ed3c1/85/class-12-chemicalkinetics-pptx-24-320.jpg)

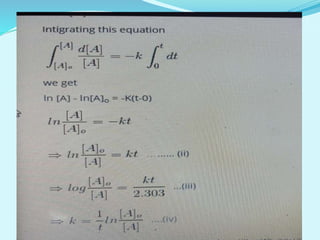
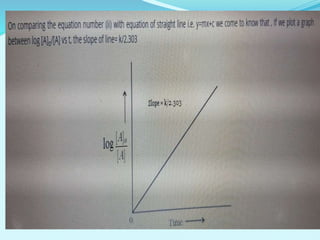
![For a first-order reaction,
the rate constant can be mathematically expressed as follows:
k=2.303tlog[A]0/[A]
From the definition of reaction half-life, at t = t1/2, [A] = [A]0/2.
Substituting these values in the expression for the first-order
rate constant, the following equation is obtained:
k=2.303t1/2log[A0]/([A]0/2)
Rearranging the expression to find the value of t1/2:
t1/2=2.303klog(2)=0.693k
Thus, the half-life of a first-order reaction is given by 0.693/k.
HALF LIFE TIME OF FIRST ORDER
REACTION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class12chemicalkinetics-240104162115-fe1ed3c1/85/class-12-chemicalkinetics-pptx-28-320.jpg)

![Examples: a. Hydrolysis of an ester:
CH3COOC2H5 + H2O(Large excess) → CH3COOH + C2H5OH
The rate law for the reaction can be written as Rate
=K[CH3COOC2H5][H2O]
--Since water is present in large excess, its concentration remains
practically constant during the course of the reaction. Thus
above rate law can be written as Rate = K’[CH3COOC2H5] .
The reaction is actually second order but in practice it
follows first- order kinetics. Thus, it is a pseudo-first order
reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/class12chemicalkinetics-240104162115-fe1ed3c1/85/class-12-chemicalkinetics-pptx-30-320.jpg)