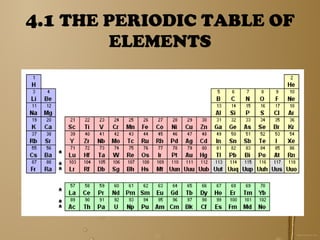
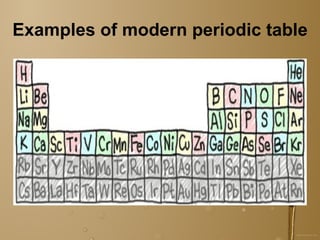
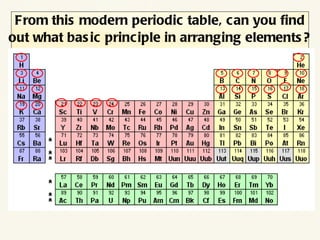
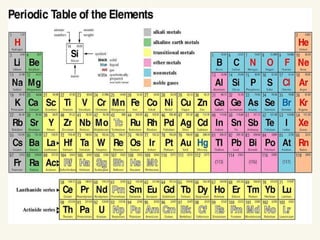
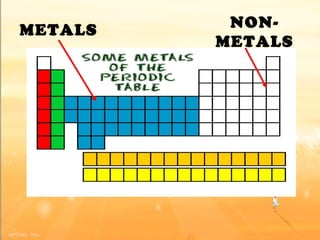
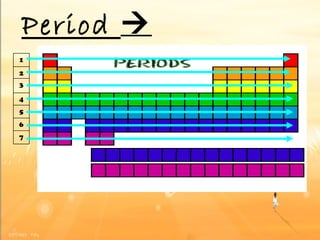
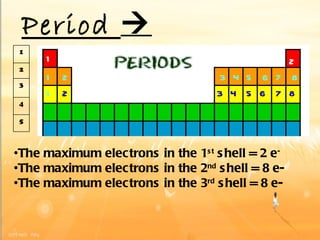
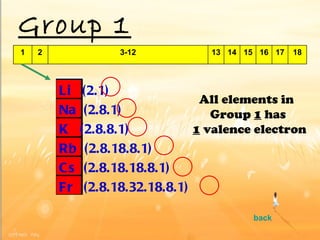
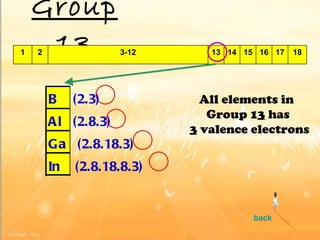
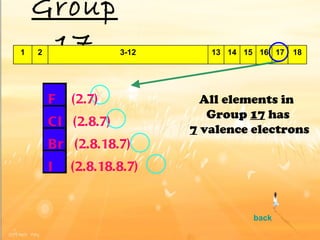
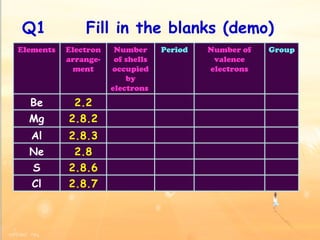
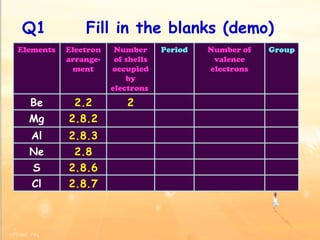
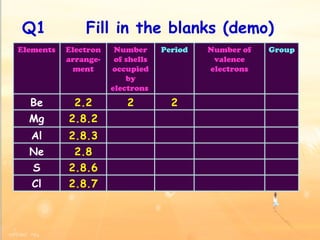
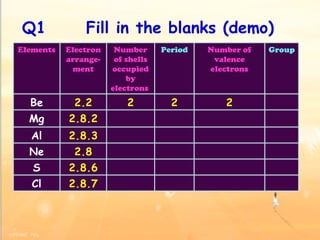
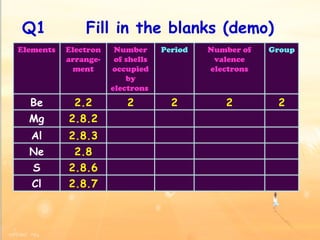
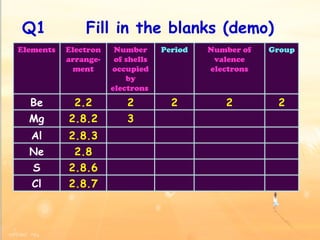
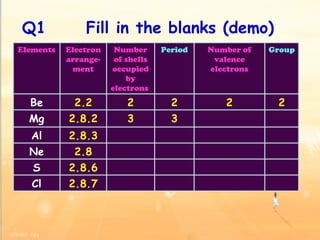
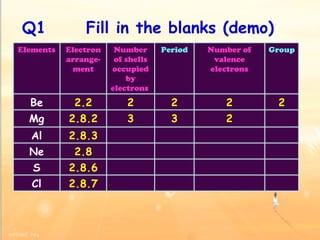
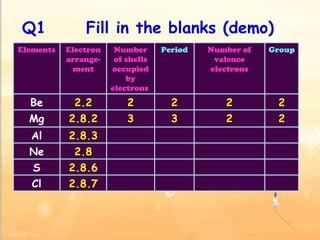
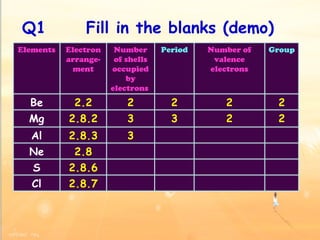
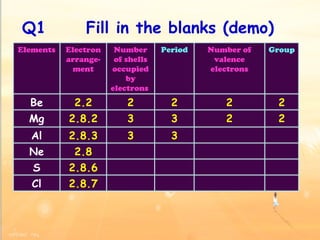
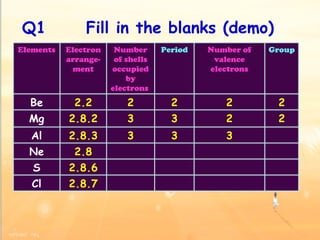
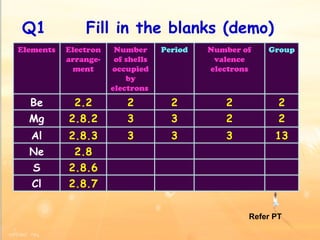
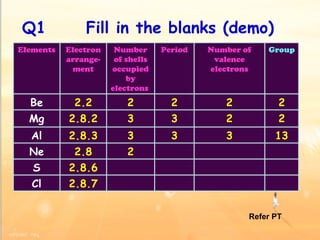
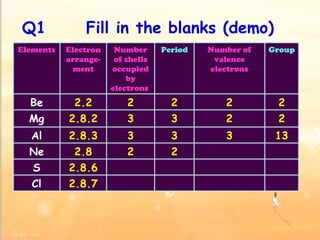
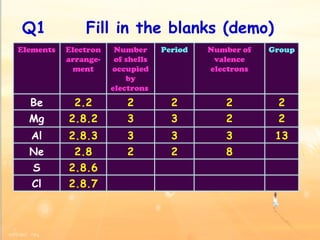
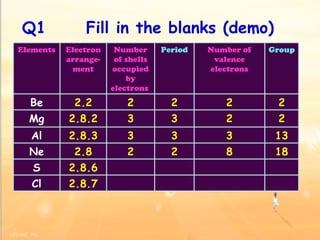
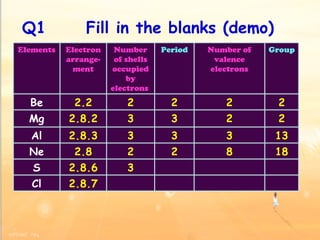
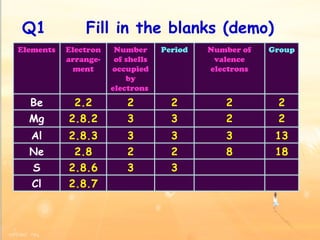
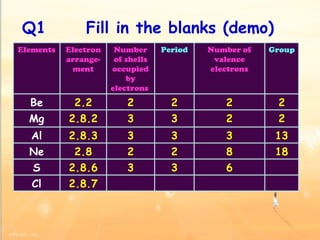
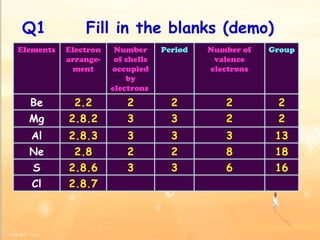
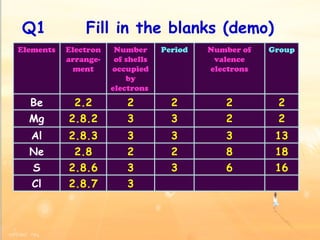
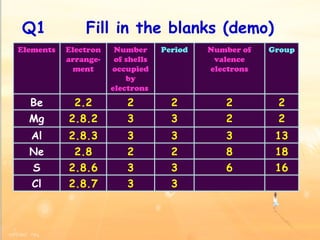
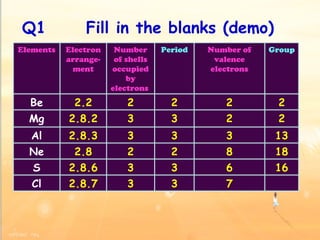
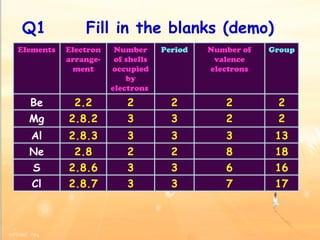
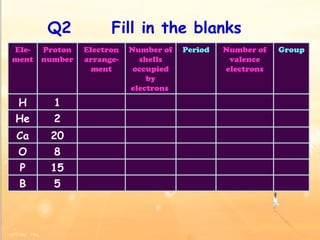
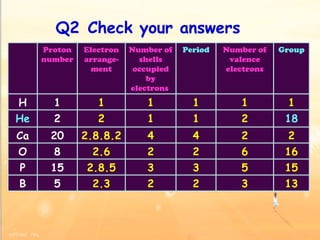
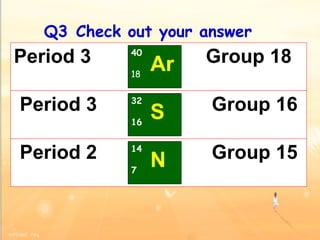
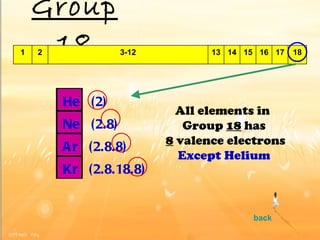
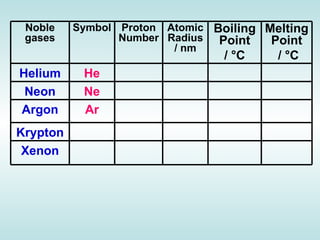
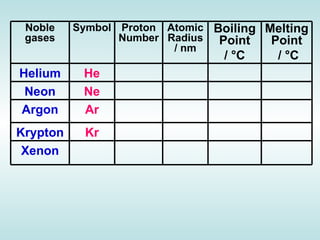
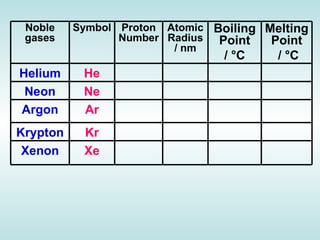
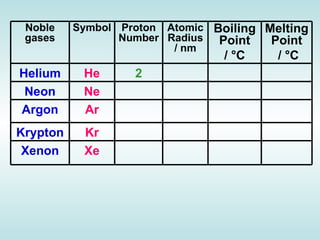
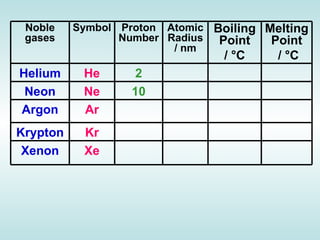
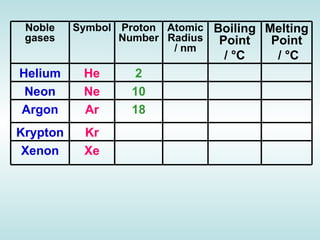
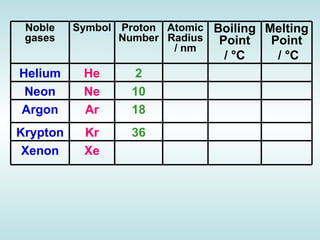
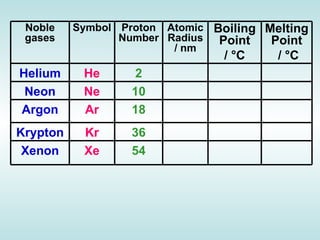
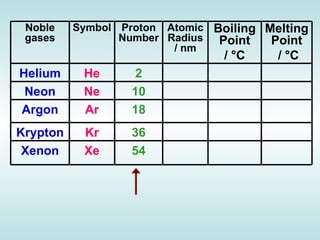
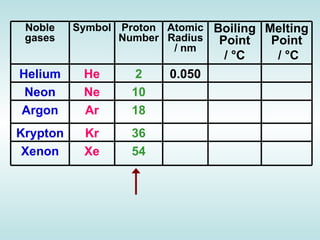
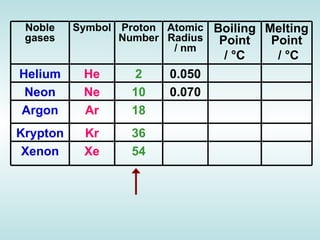
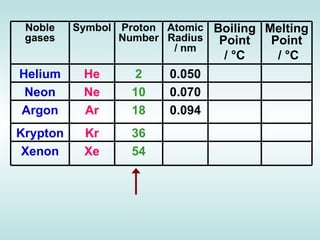
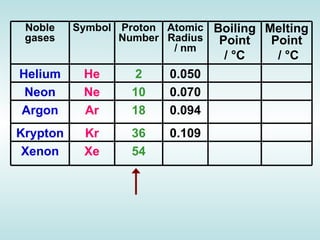
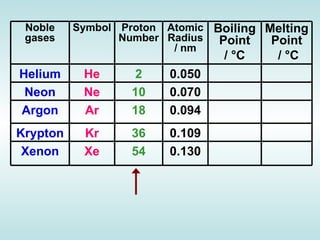
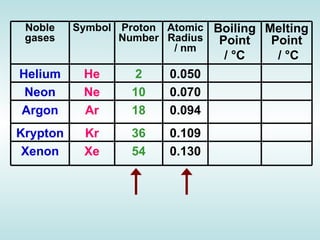
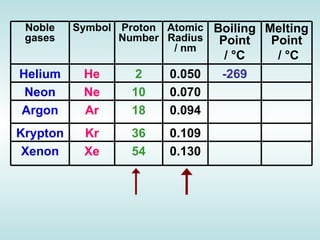
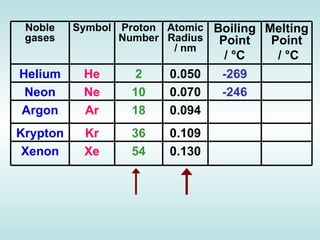
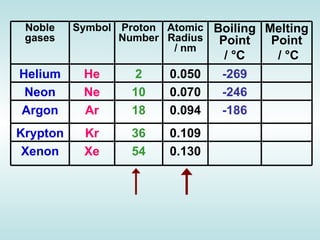
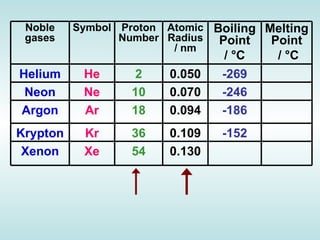
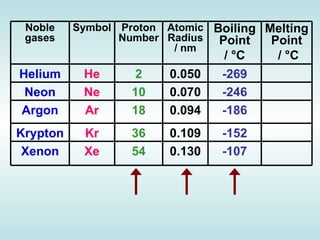
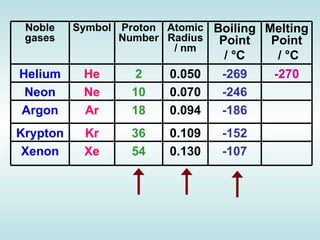
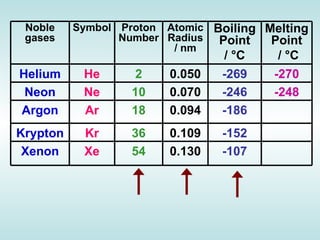
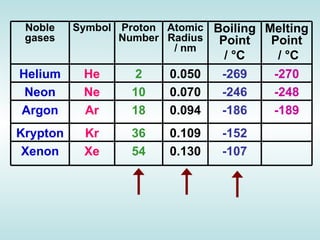
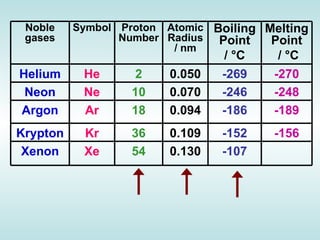
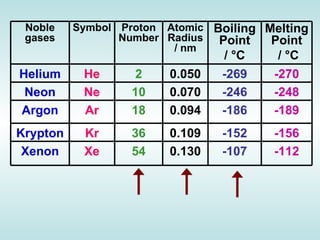
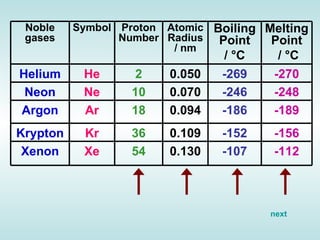
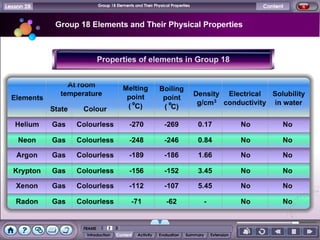
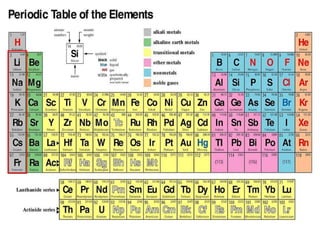
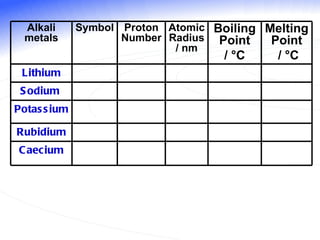
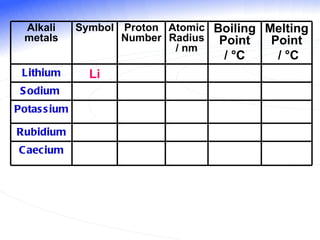
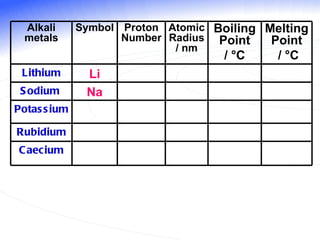
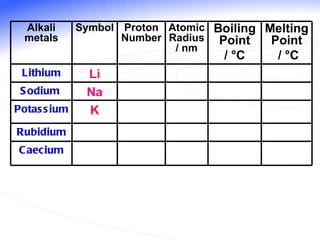
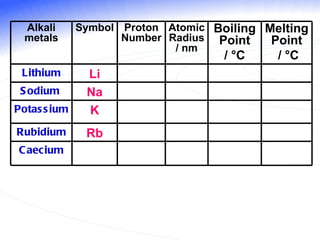
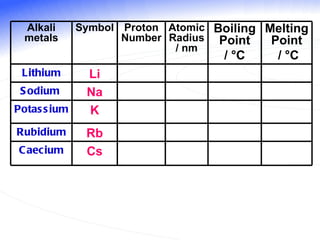
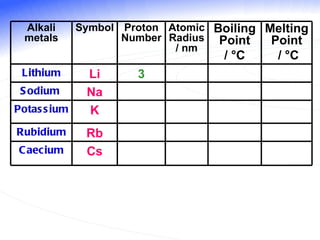
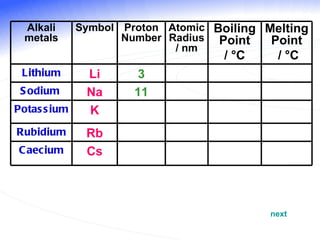
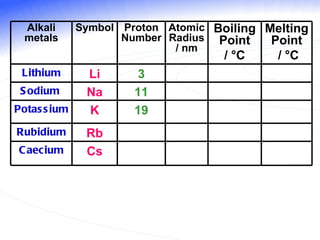
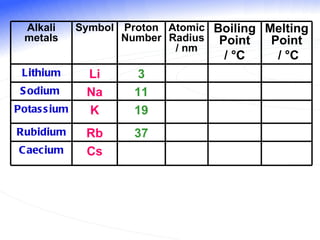
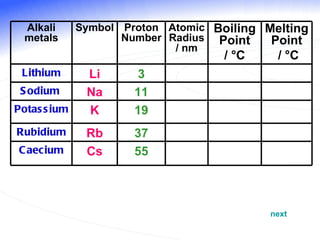
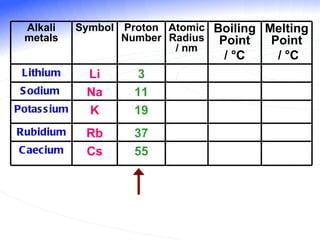
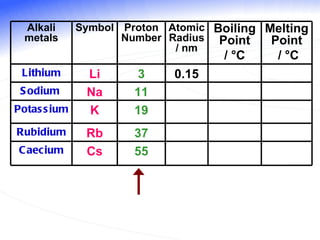
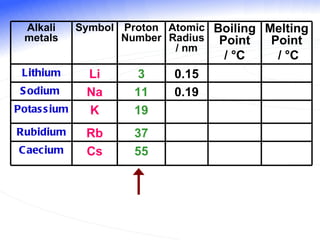
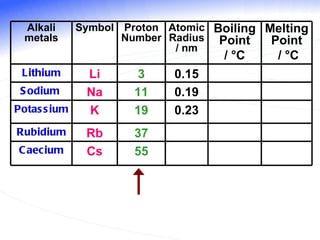
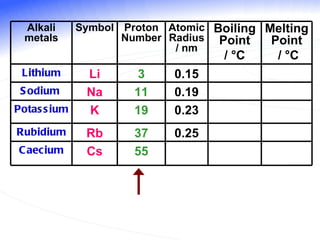
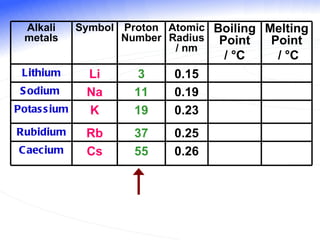
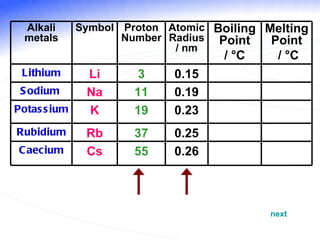
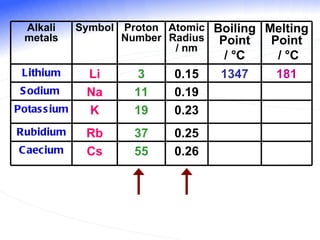
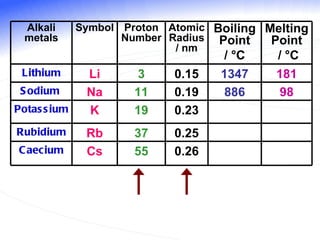
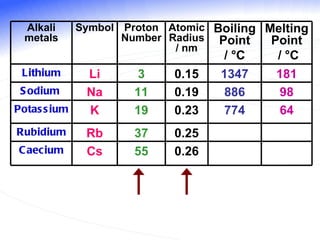
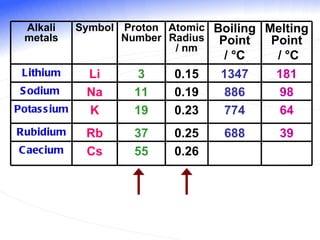
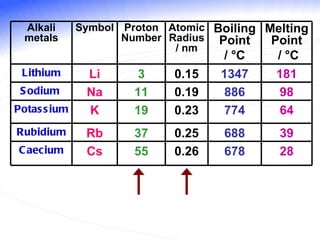
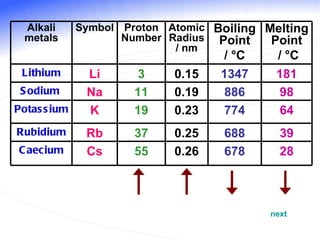
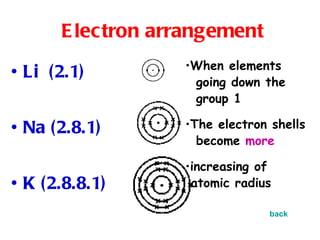
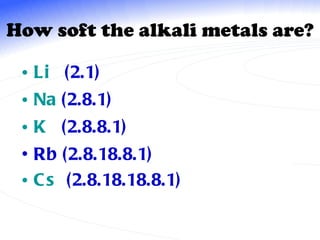
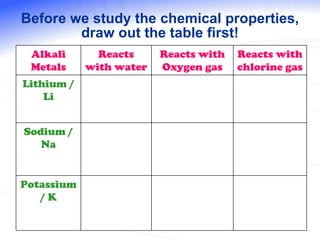
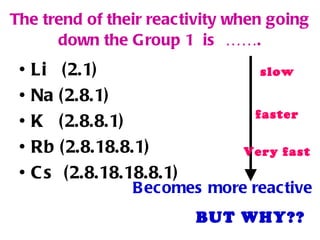
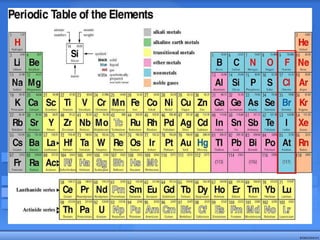
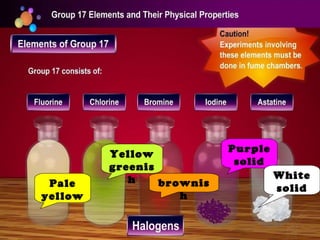
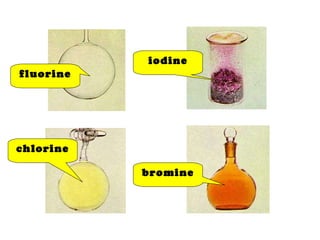
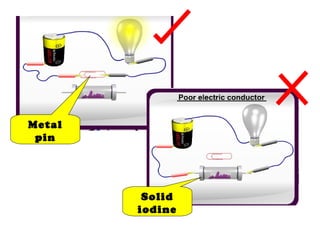
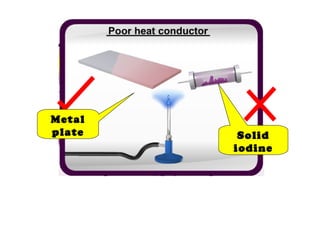
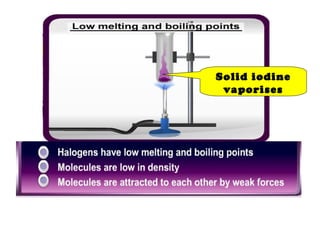
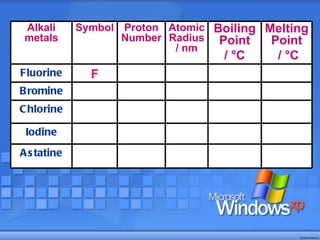
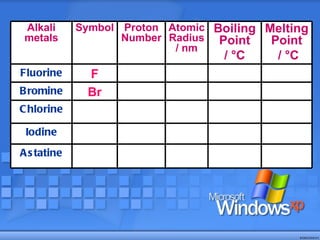
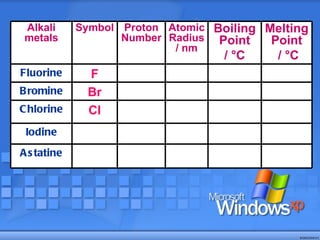
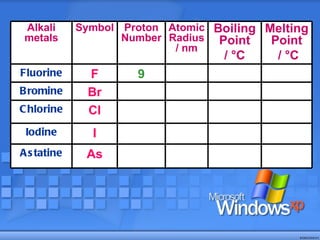
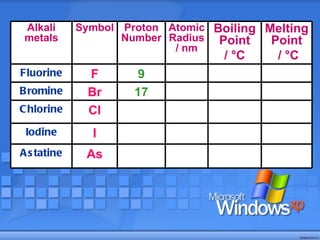
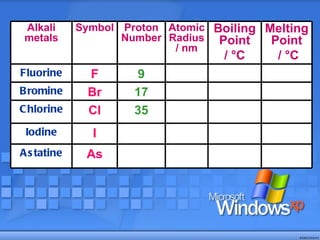
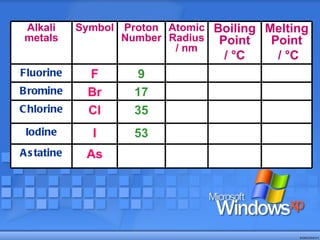
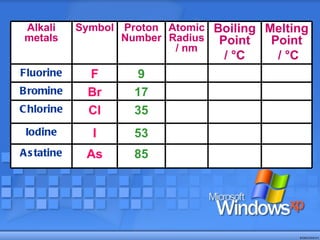
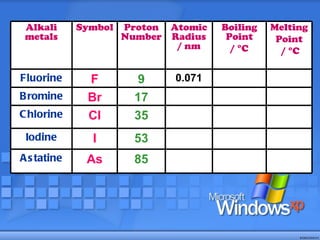
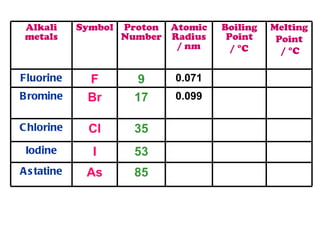
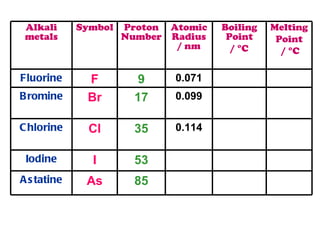
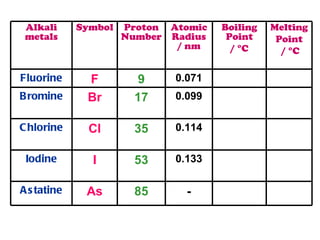
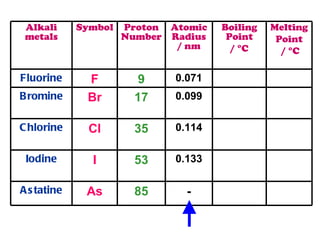
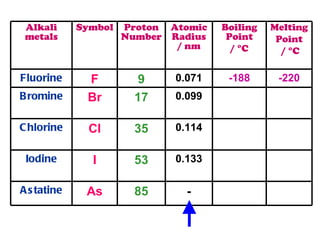
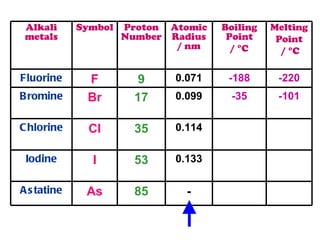
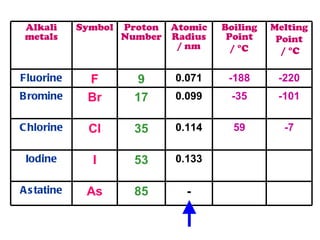
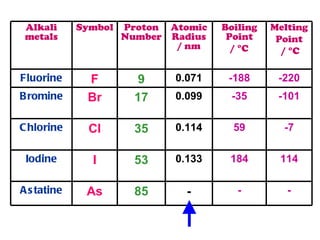
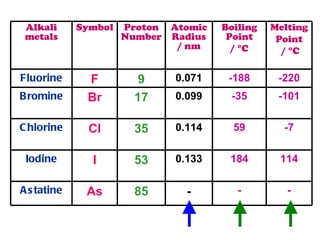
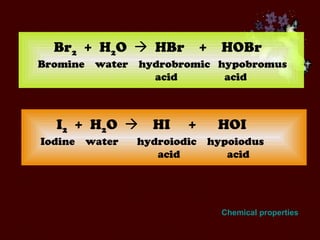
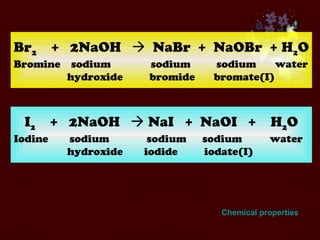
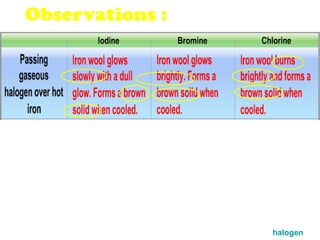
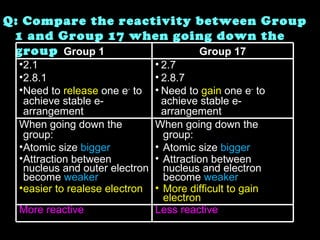
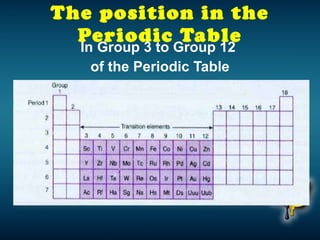
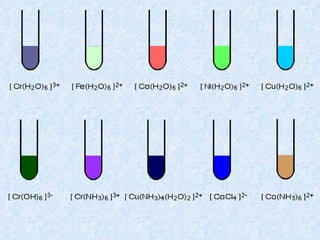
The document discusses the periodic table of elements and its development over time. It explains how elements are arranged based on their proton number and how this arrangement allows prediction of element properties based on periodic trends. Examples are given of common elements and their uses to illustrate the practical importance of the periodic table.