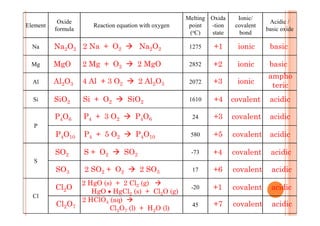
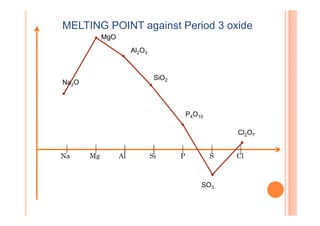
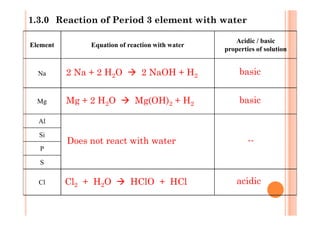
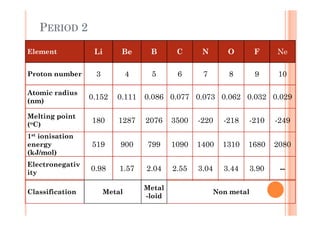
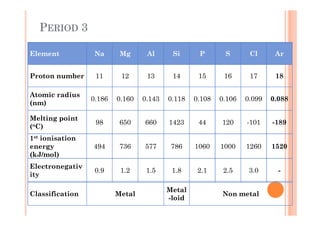
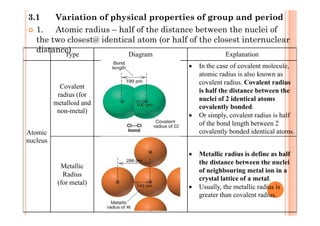
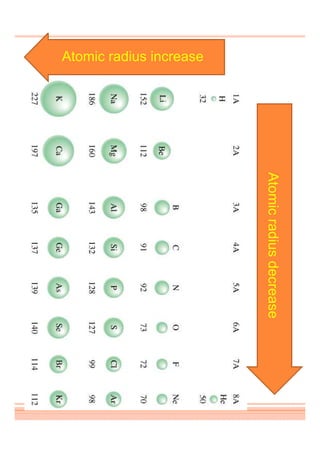
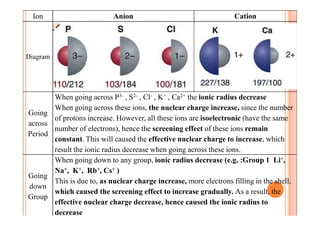
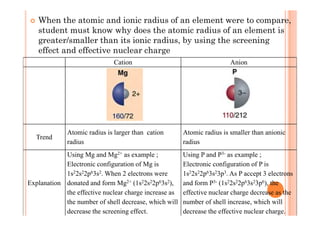
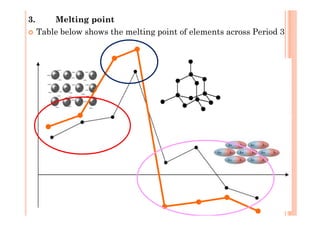
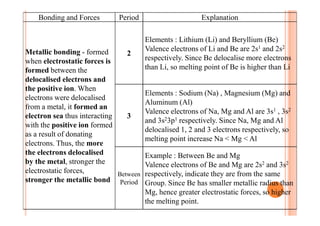
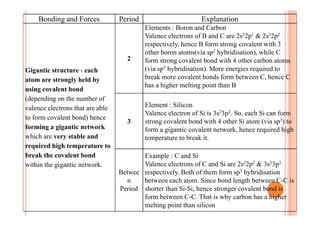
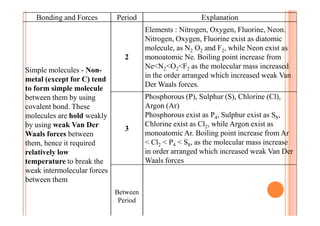
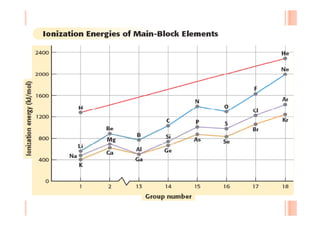
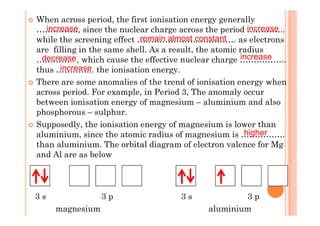
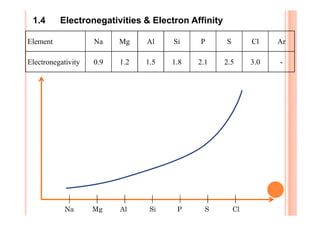
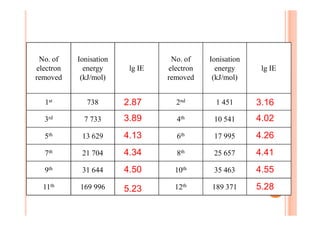
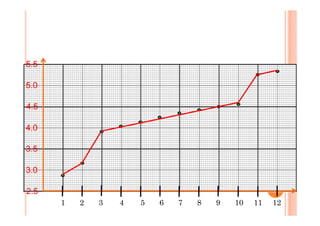
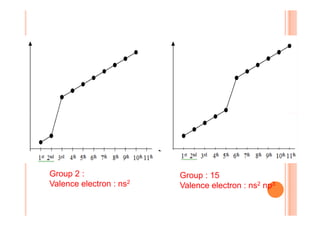
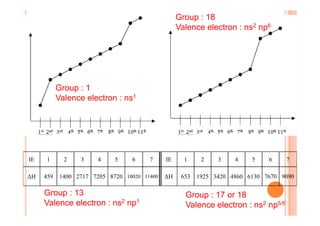
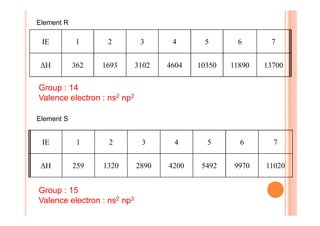
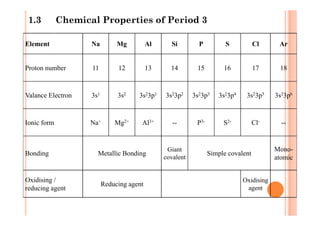
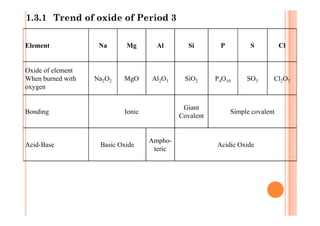
This document discusses periodicity and trends in properties across and down periods of the periodic table. It explains that atomic radius generally decreases across periods as nuclear charge increases, outweighing constant screening effects. Atomic radius increases down groups as nuclear charge rises but screening effects also increase. Ionic radius follows similar trends as atomic radius but is smaller for cations and larger for anions. Melting and boiling points are influenced by type and strength of bonding. Metallic bonding results in higher melting points for metals with more delocalized electrons. Network covalent bonding in nonmetals produces high melting points due to needing to overcome many bonds. Molecular nonmetals have weaker van der Waals forces between molecules. First ionization energies also follow trends














![5.Phosphorus burns readily in air (oxygen) to form acidic oxides.
White phosphorus is a highly toxic substance and will burst into
flames spontaneously when exposed to oxygen to form
phosphorus pentoxide, P4O10. If a limited supply of oxygen
is used during burning, a lower form of oxide, phosphorus
trioxide, P4O6, is produced.
Phosphorous burned with excess oxygen :
P4 (s) + 5 O2 (g) P4O10 (s)
Phosphorous burned with limited oxygen :
P4 (s) + 3 O2 (g) P4O6 (s)
(a) Both oxides are acidic and will dissolve in water to form the
corresponding acids.
Phosphorous pentoxide :
P4O10 (s) + 6 H2O (l) 4 H3PO4 (aq) [Phosphoric acid]
Phosphorous trioxide :
P4O6 (s) + 6 H2O (l) 4 H3PO3 (aq) [Phosphorous acid]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chemistryform6sem2031-150424073018-conversion-gate01/85/Inorganic-Chemistry-Periodic-Table-Periodicity-36-320.jpg)