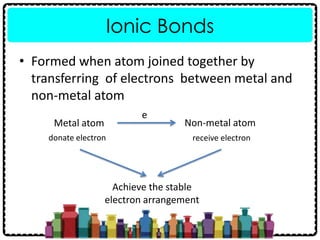
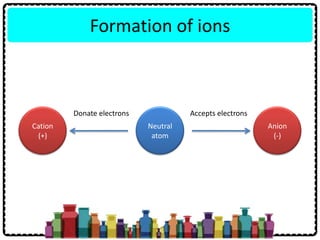
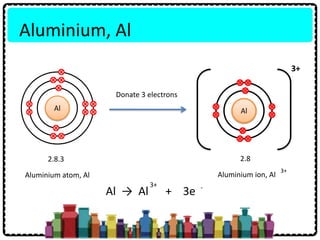
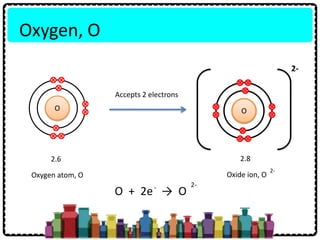
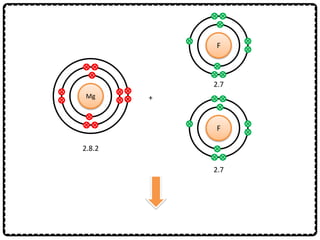
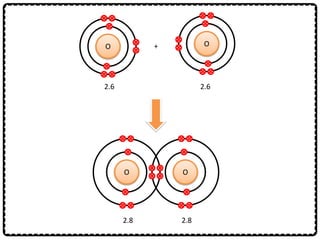
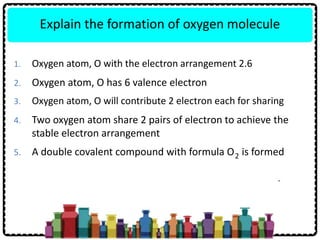
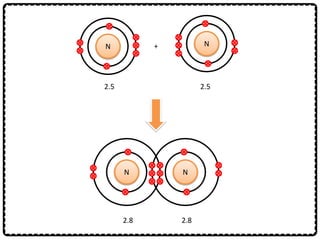
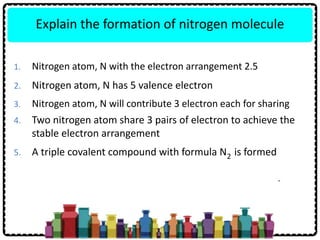
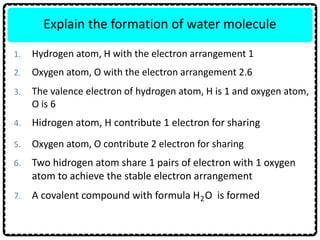
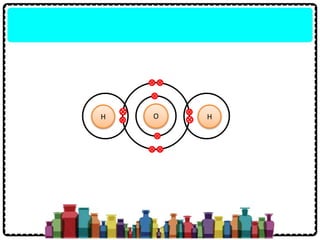
1) Chemical bonds can be either ionic or covalent. Ionic bonds form when electrons are transferred between metals and non-metals to form ions. Covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between non-metals.
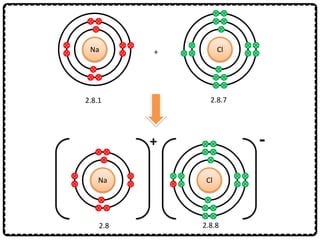
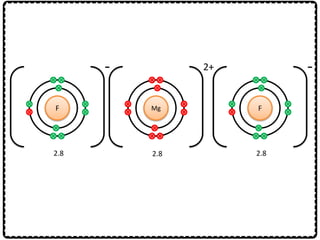
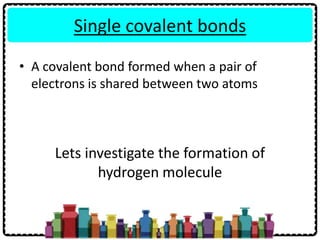
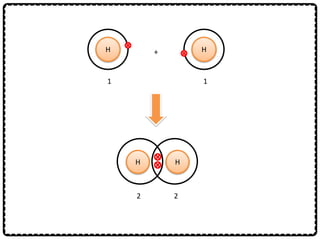
2) Sodium chloride forms when sodium donates an electron to chlorine to form ions that are attracted in an ionic bond. Hydrogen molecule forms when hydrogen atoms share an electron pair in a single covalent bond.
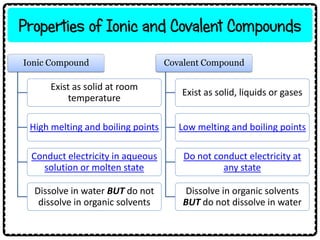
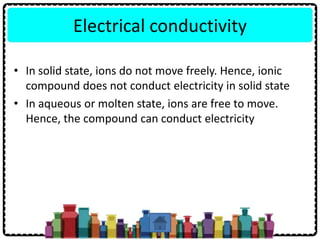
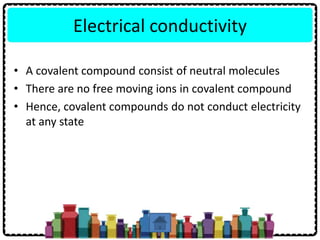
3) Ionic compounds have high melting points, conduct electricity when molten or dissolved, and dissolve in water but not organic solvents. Covalent compounds have lower melting points, do not conduct electricity, and dissolve in organic solvents but not water.