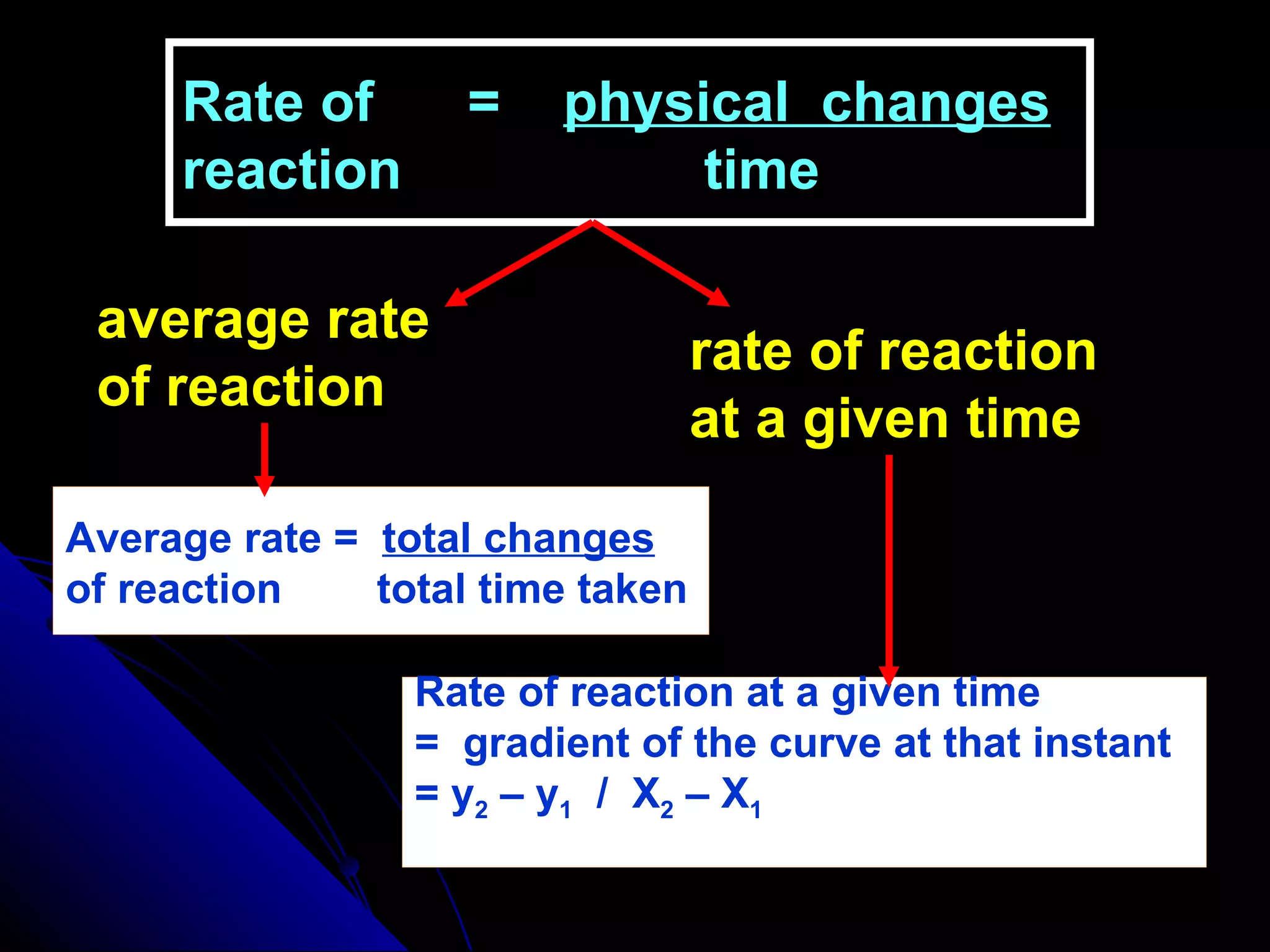
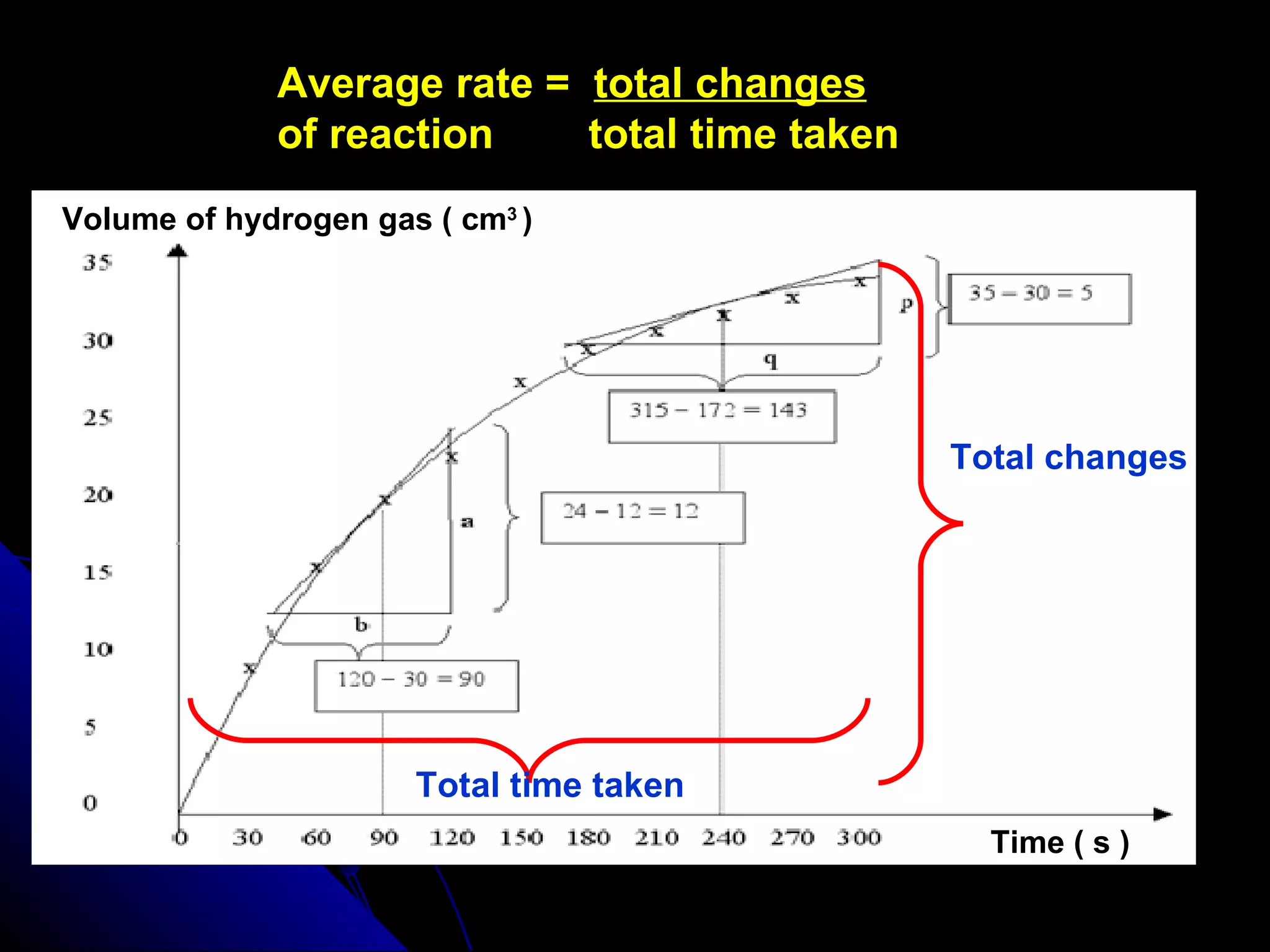
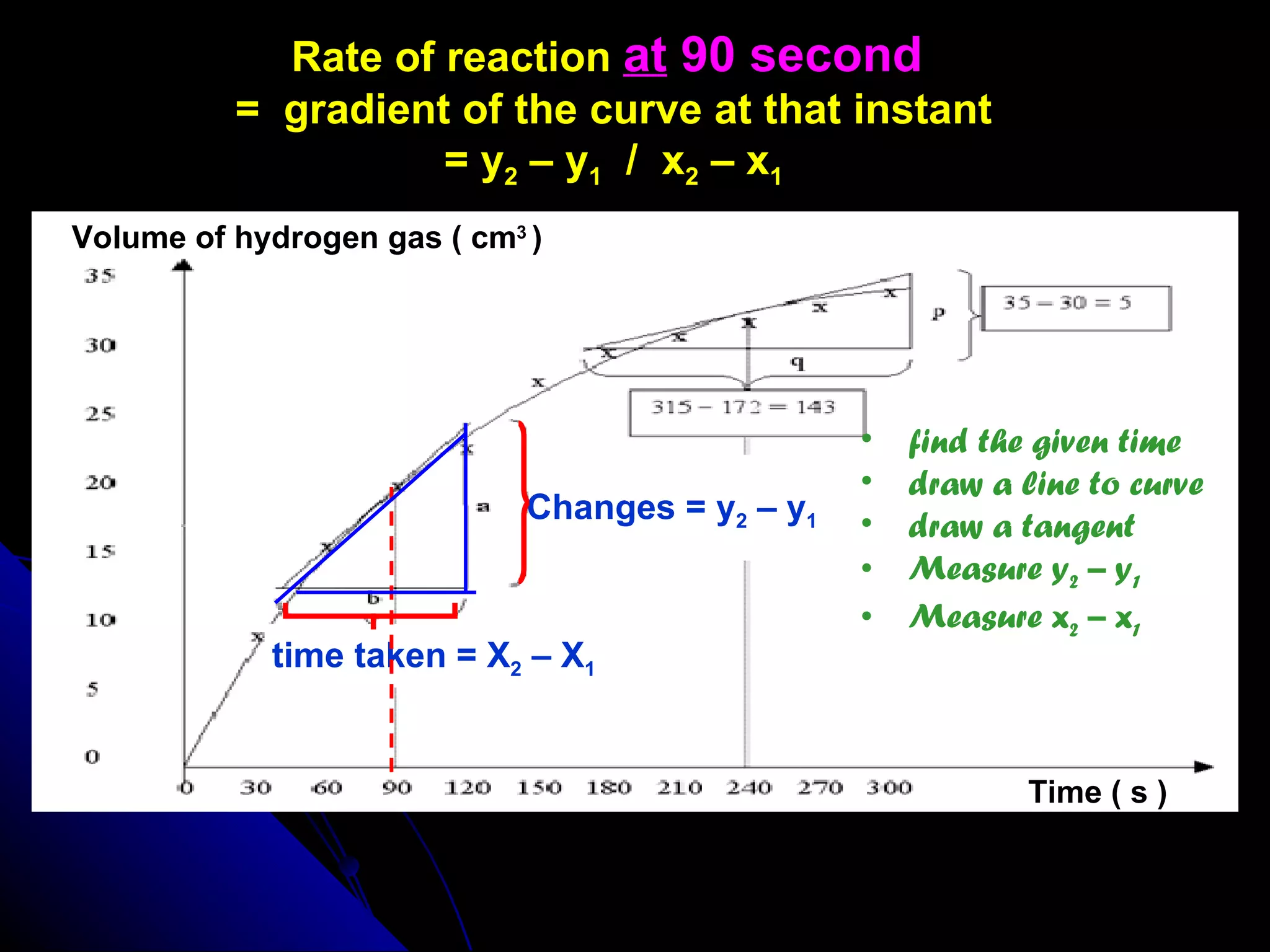
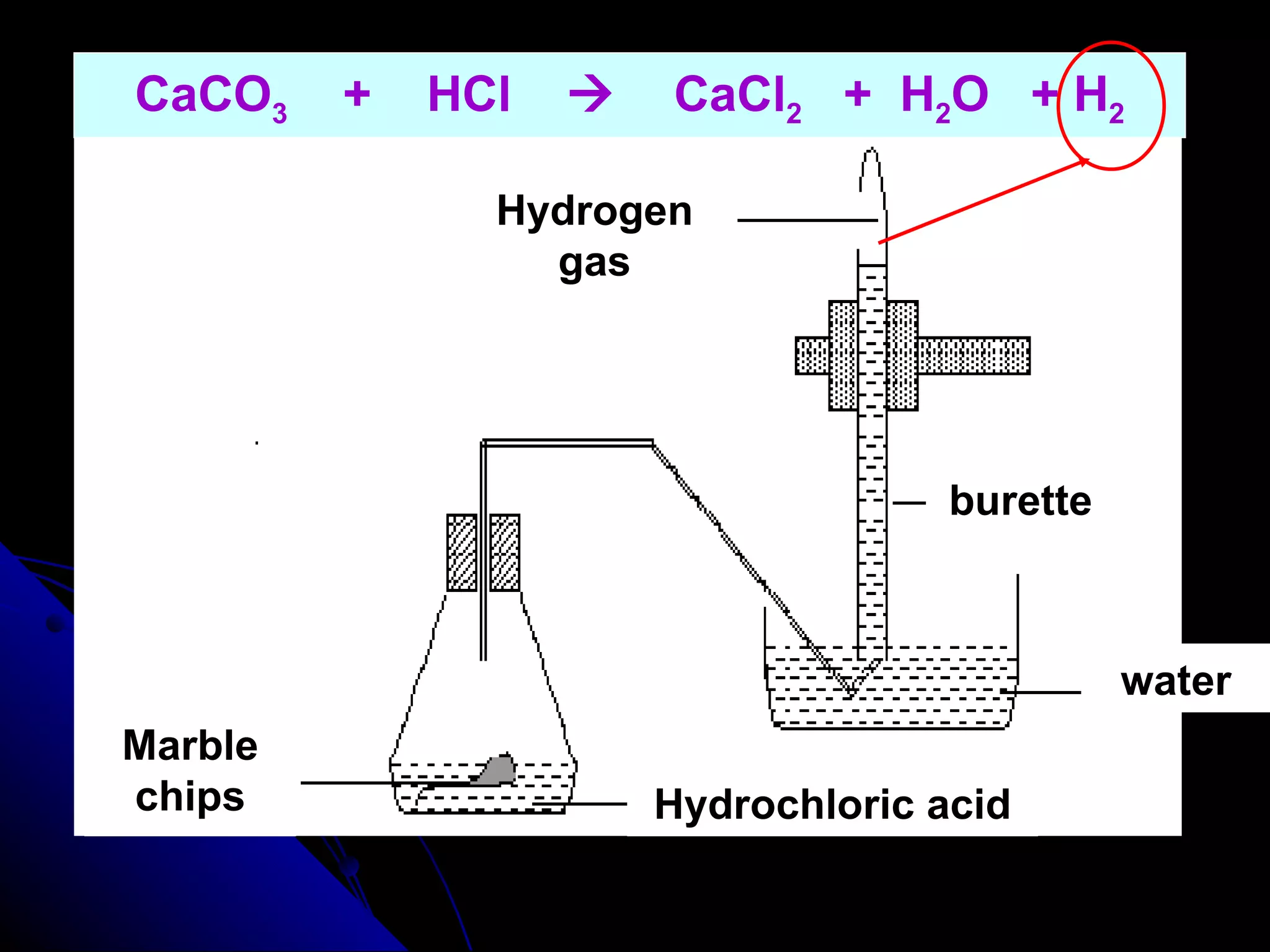
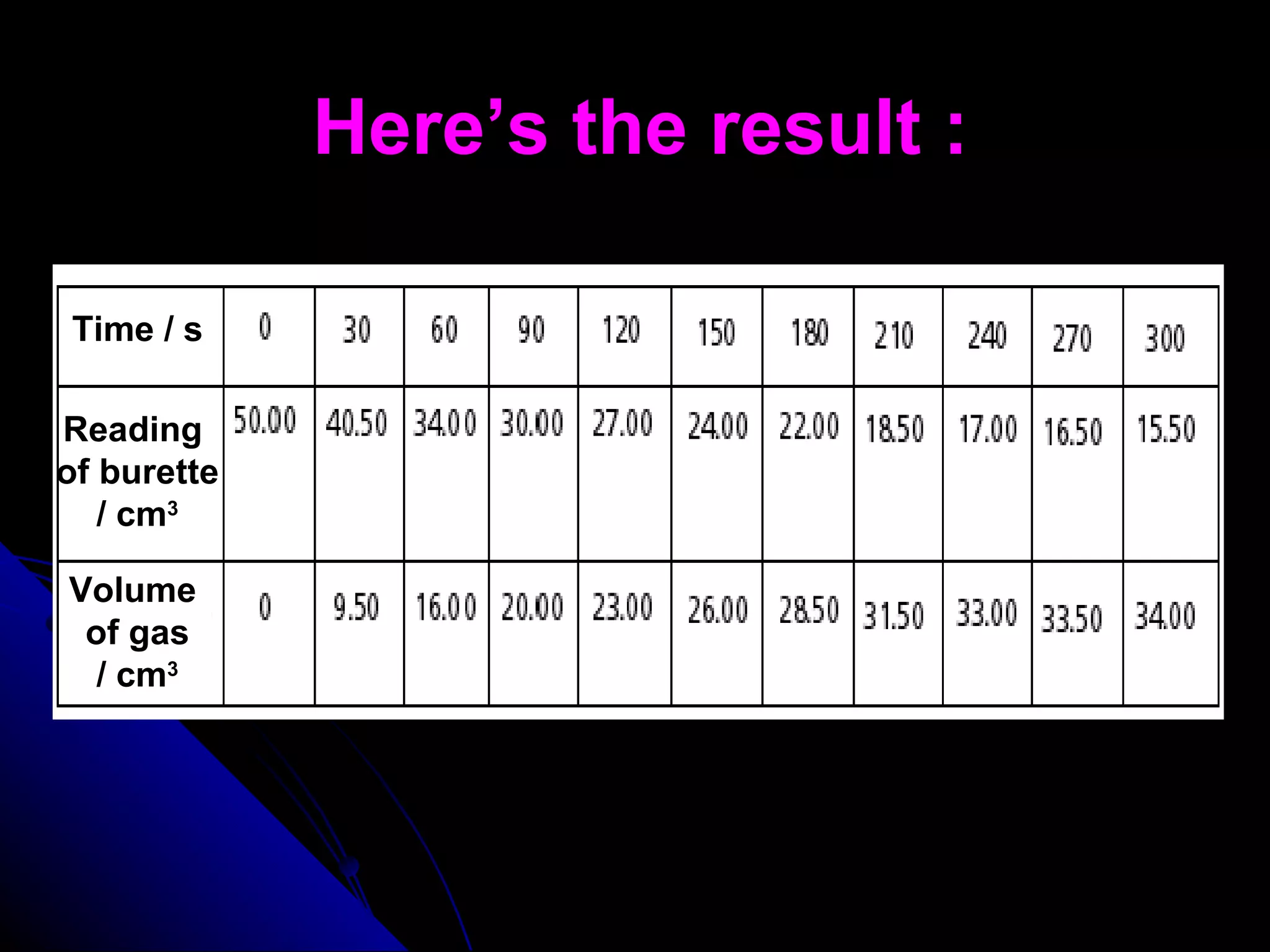
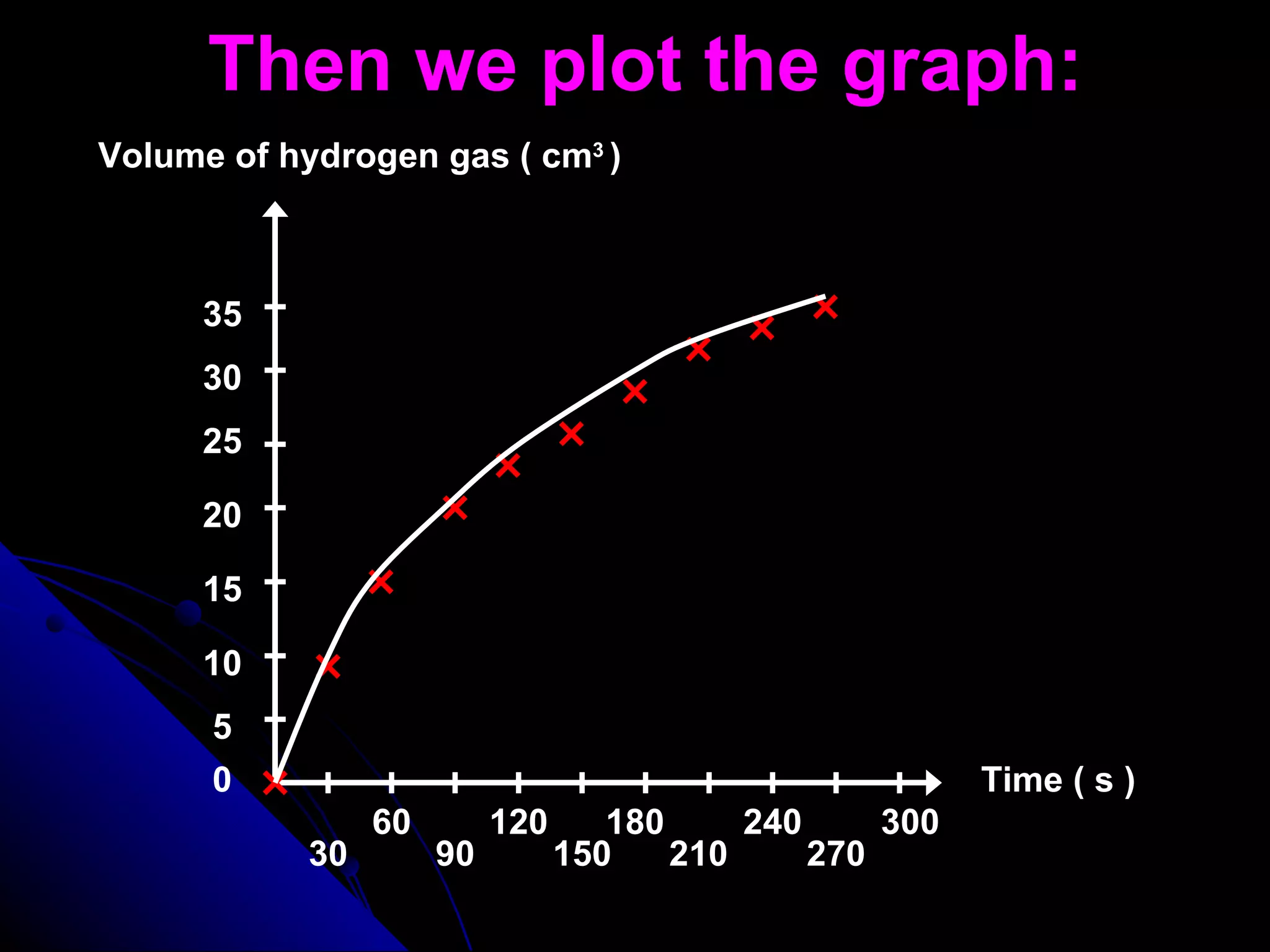
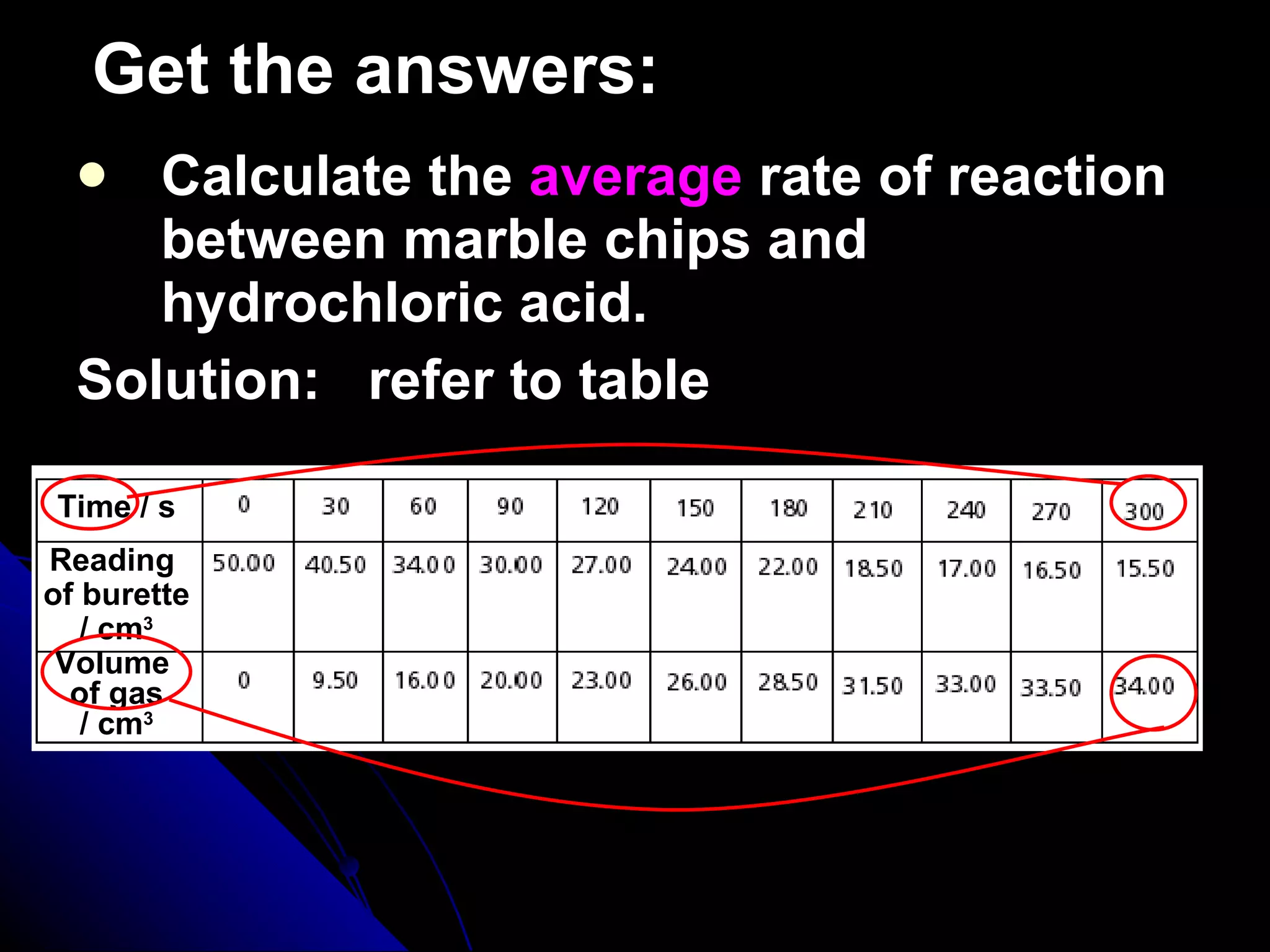
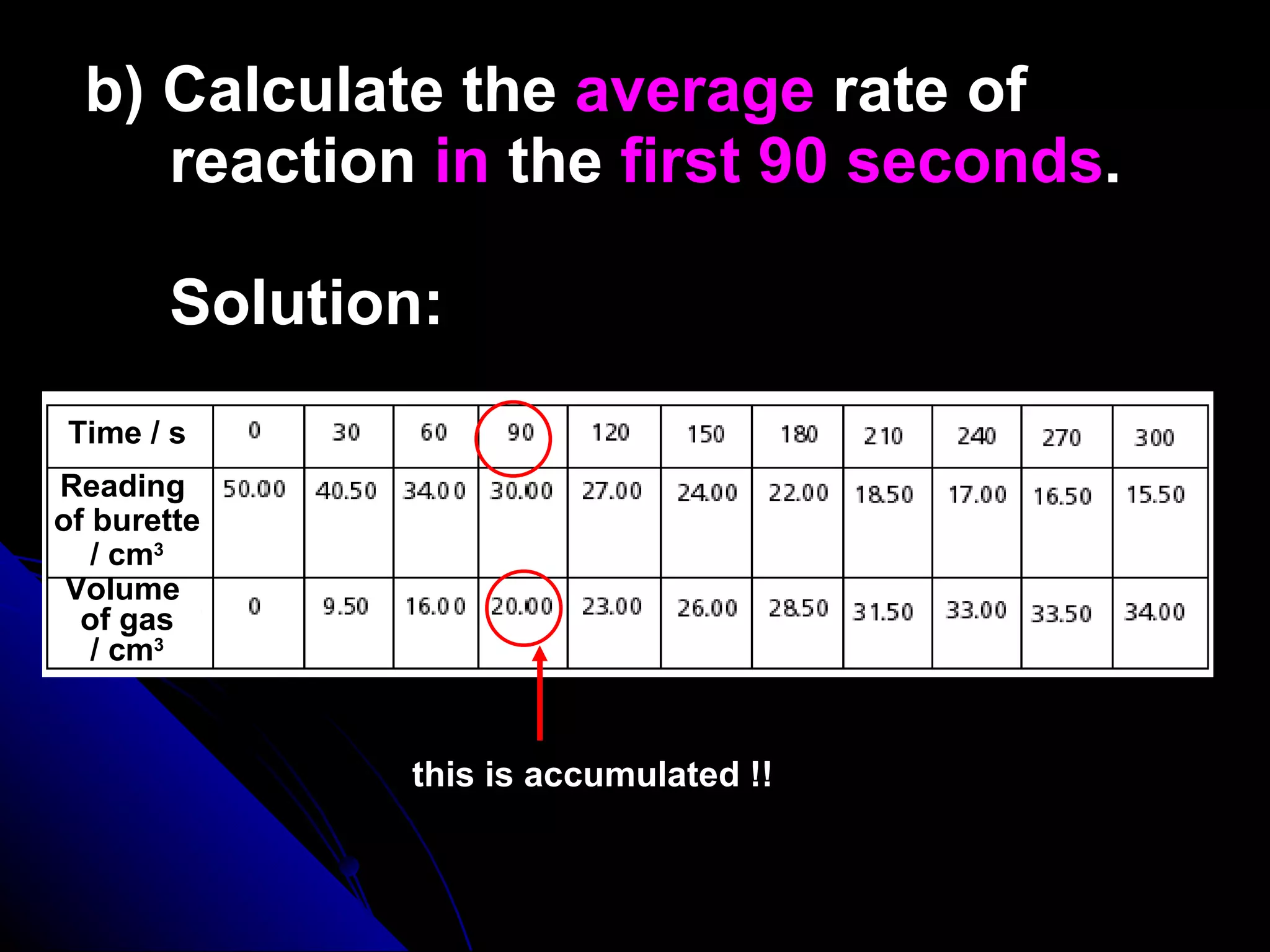
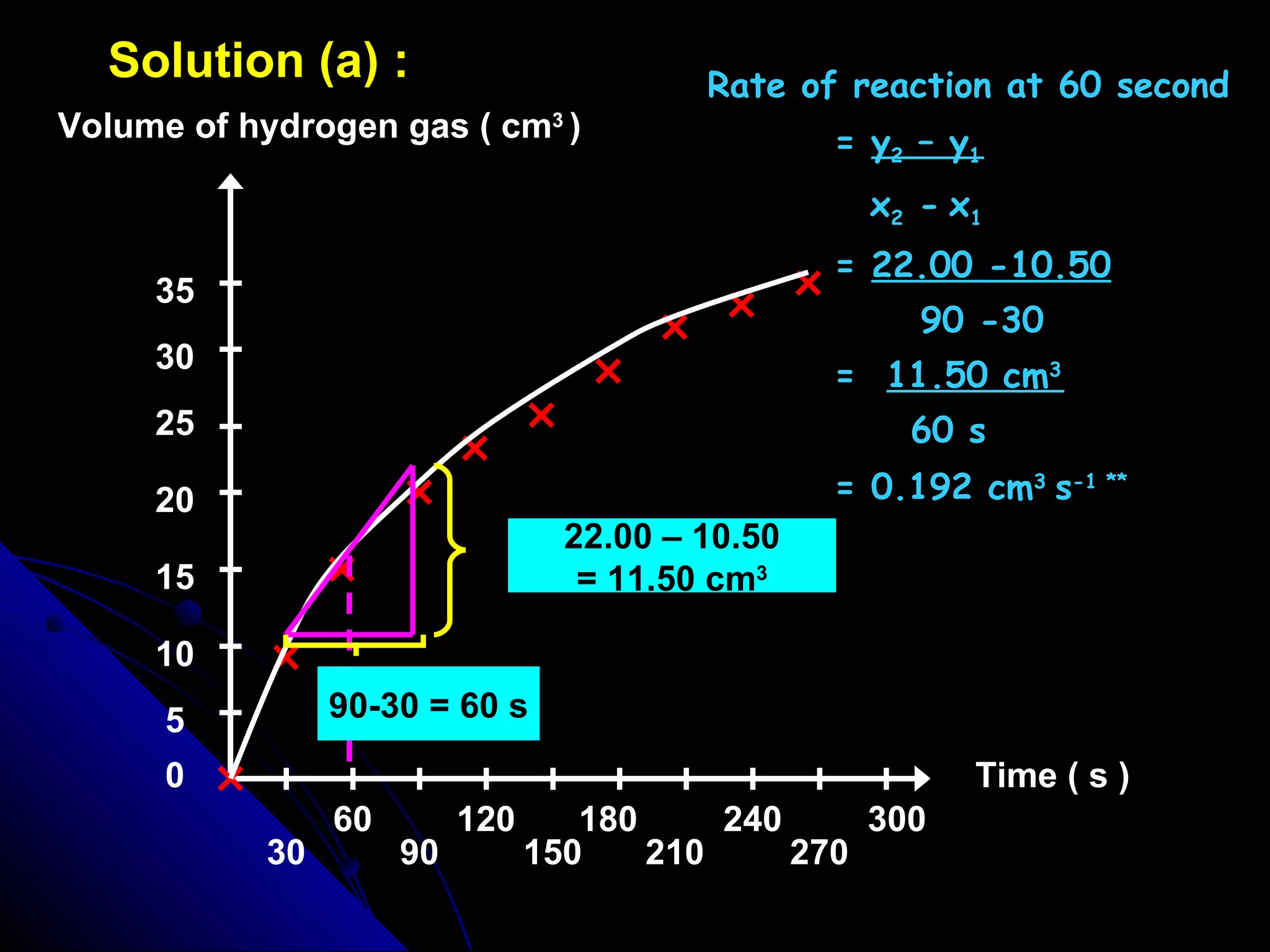
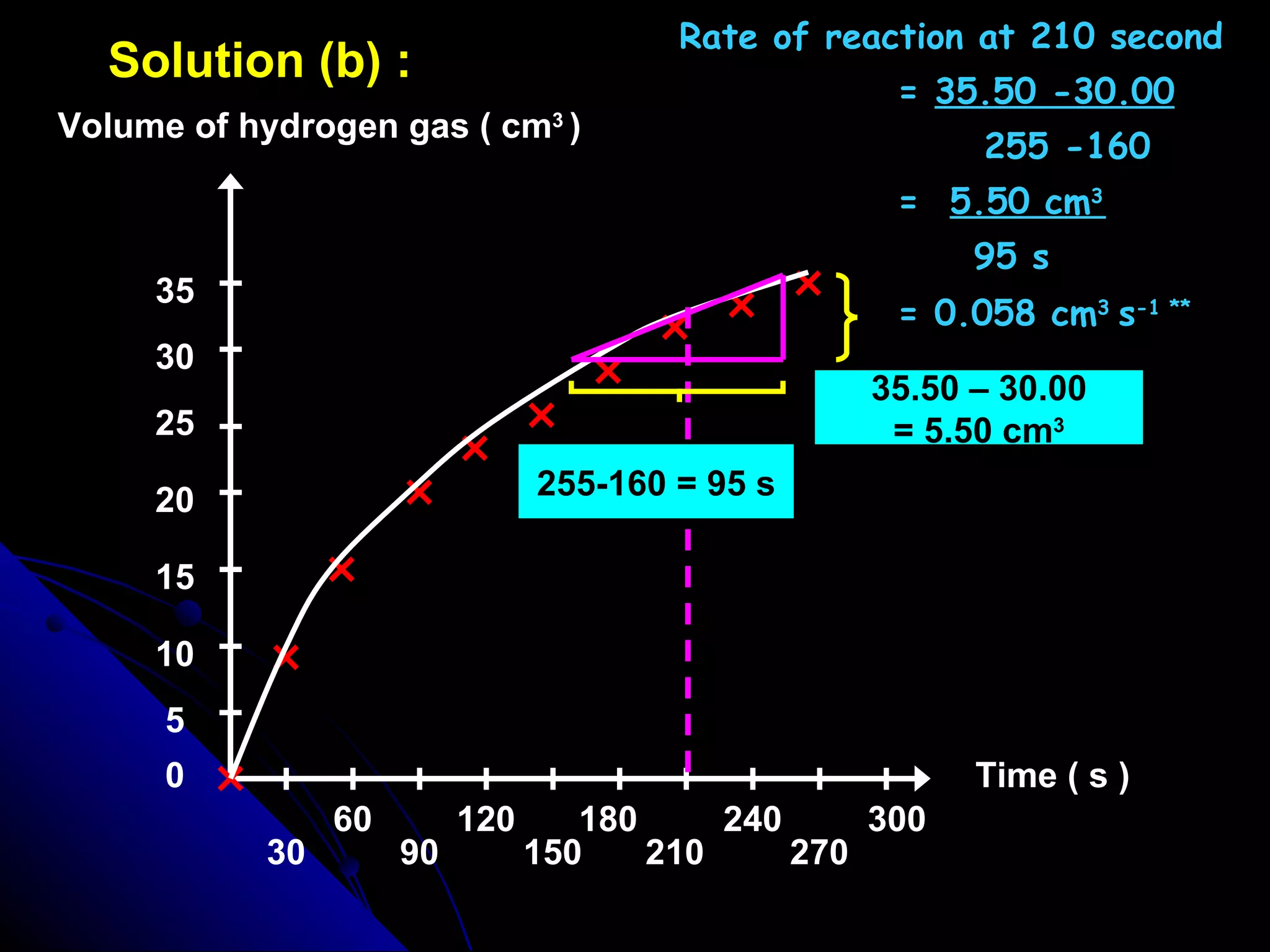
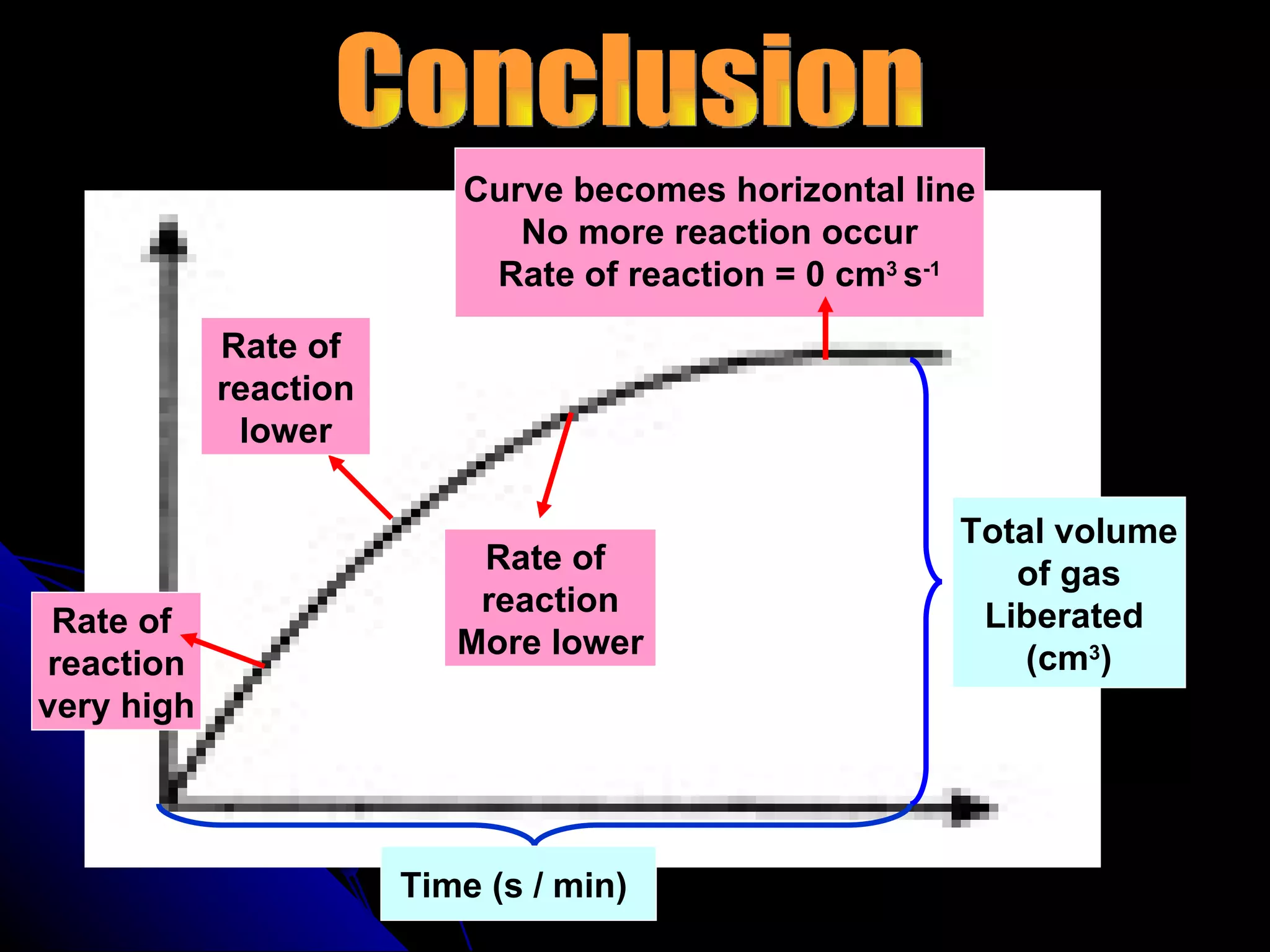
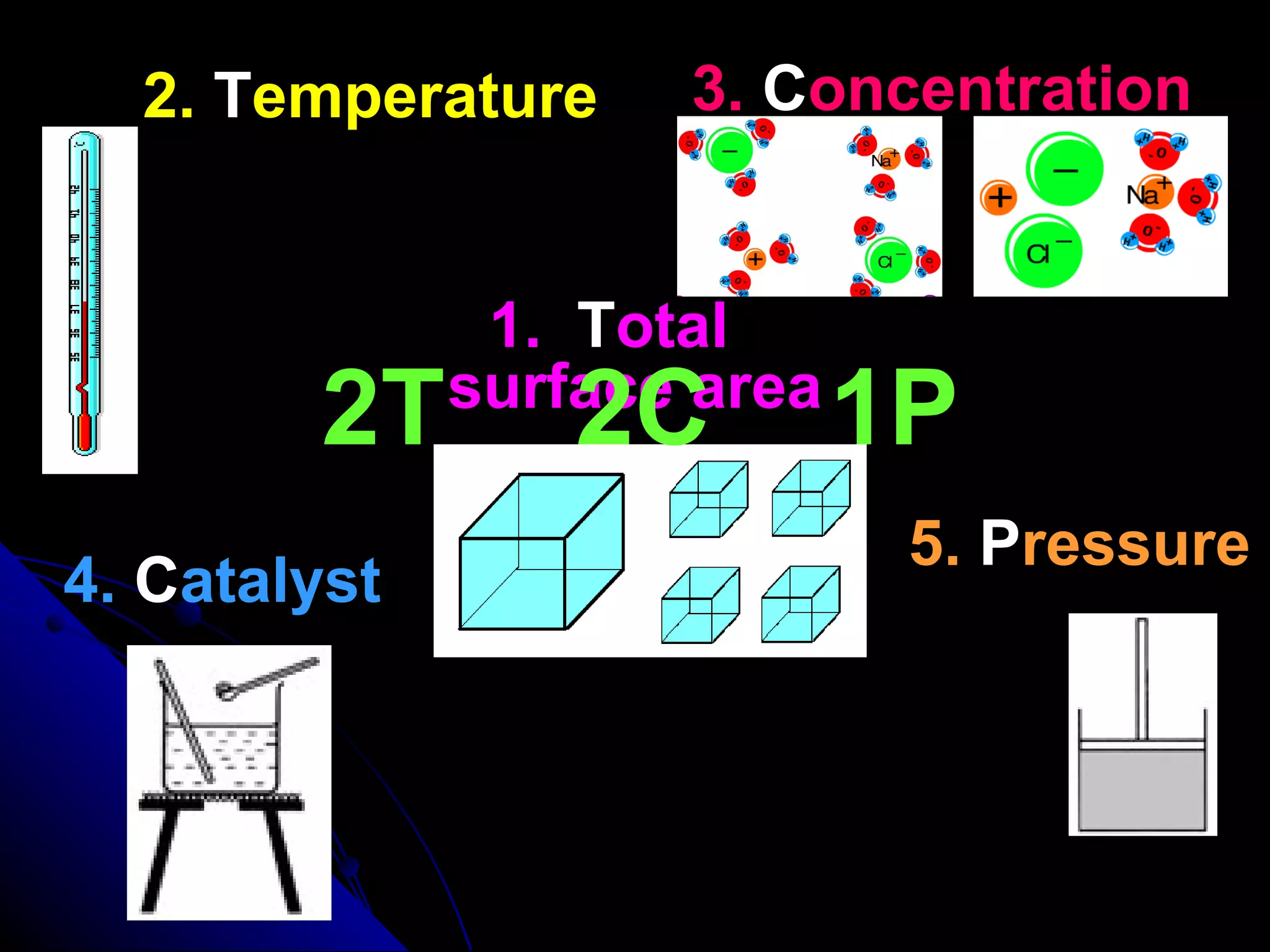
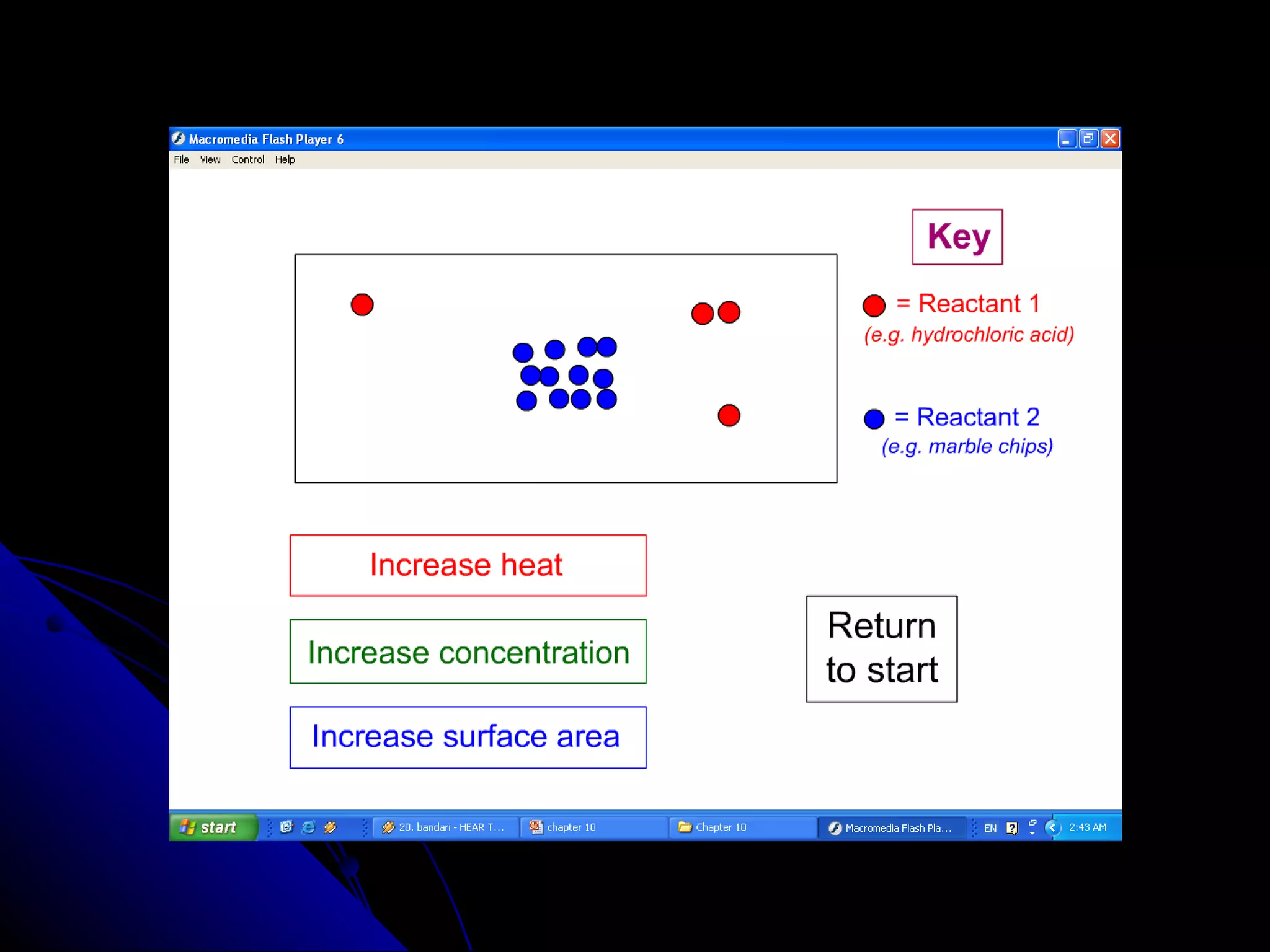
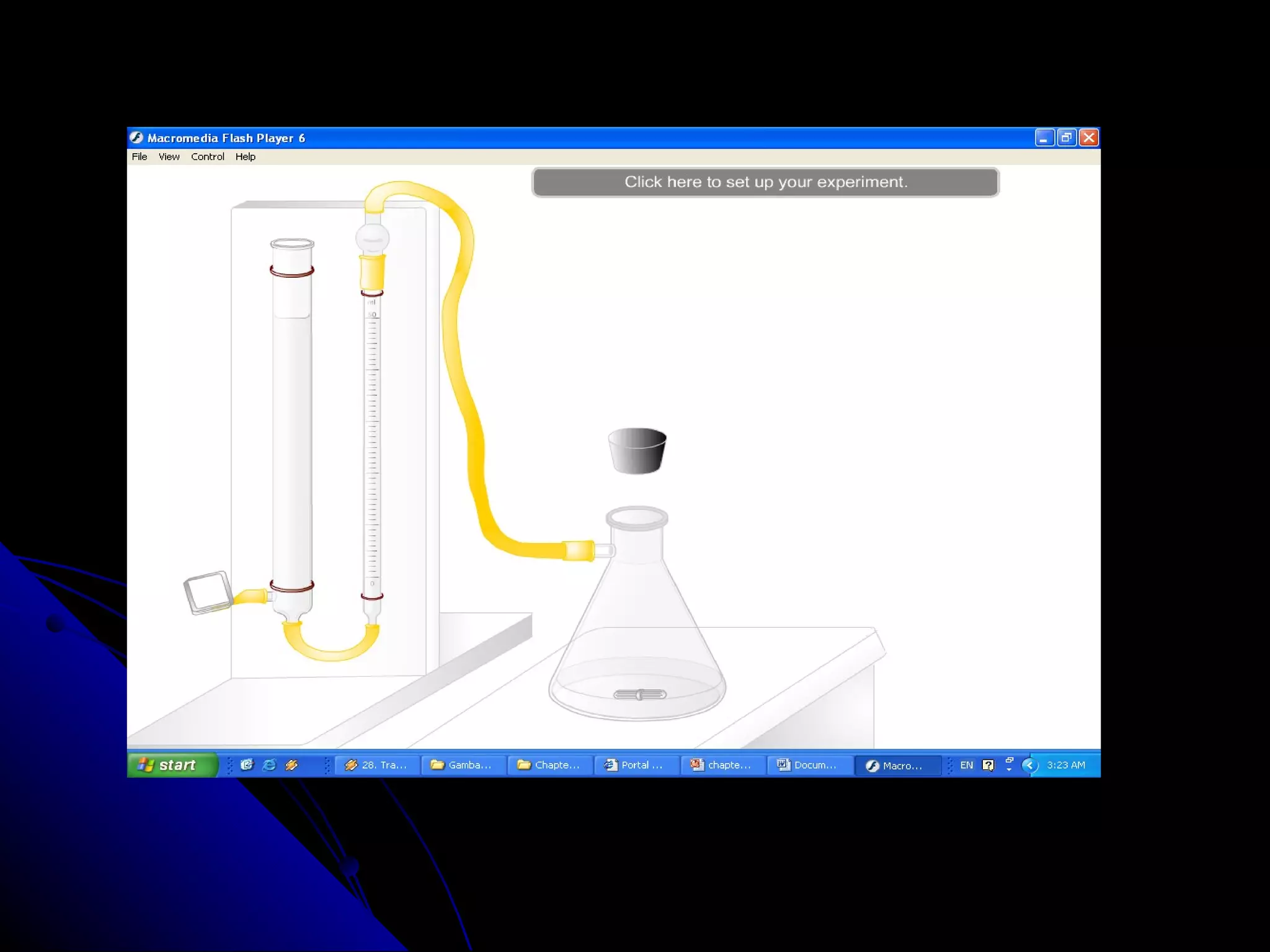
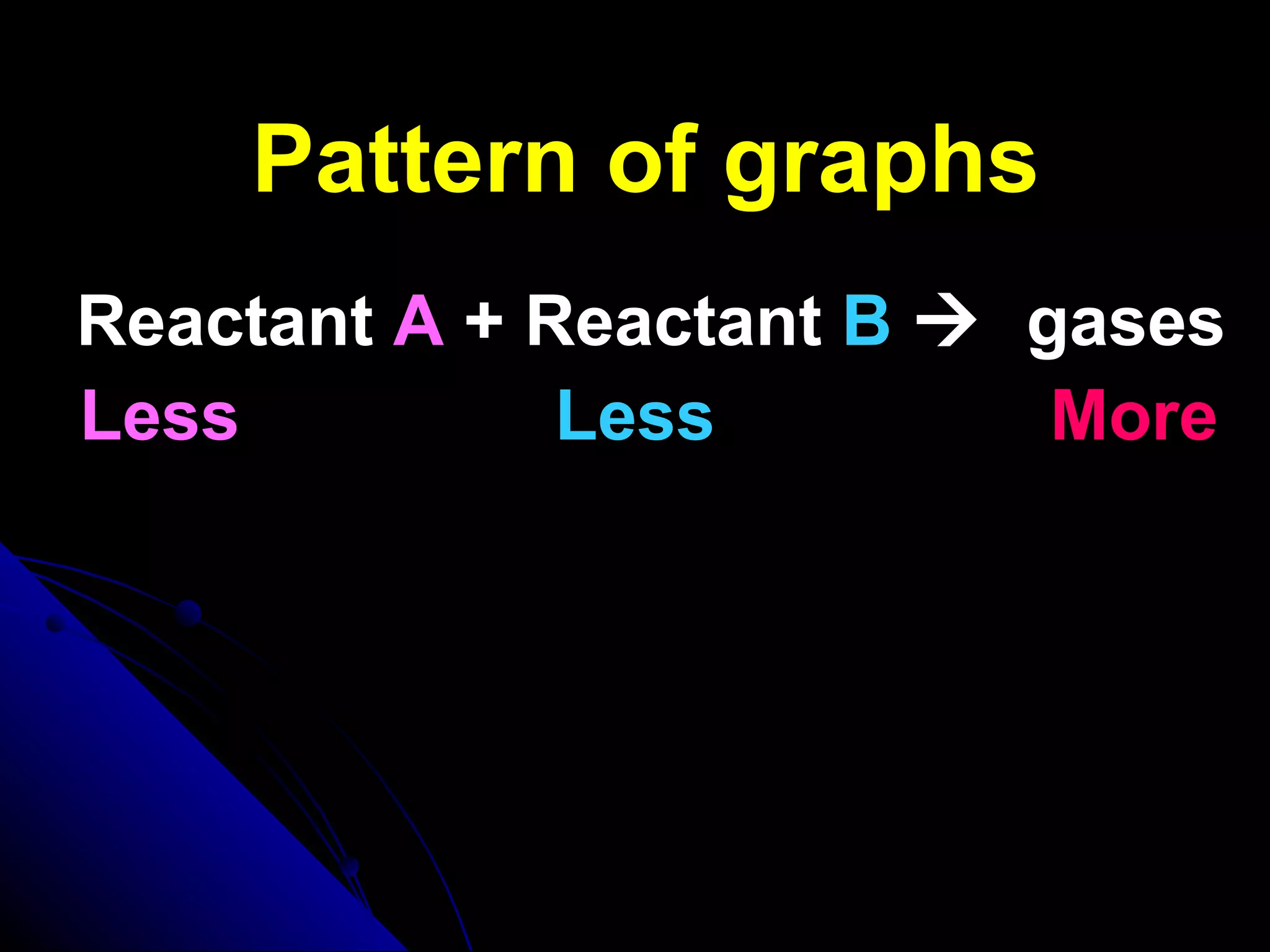
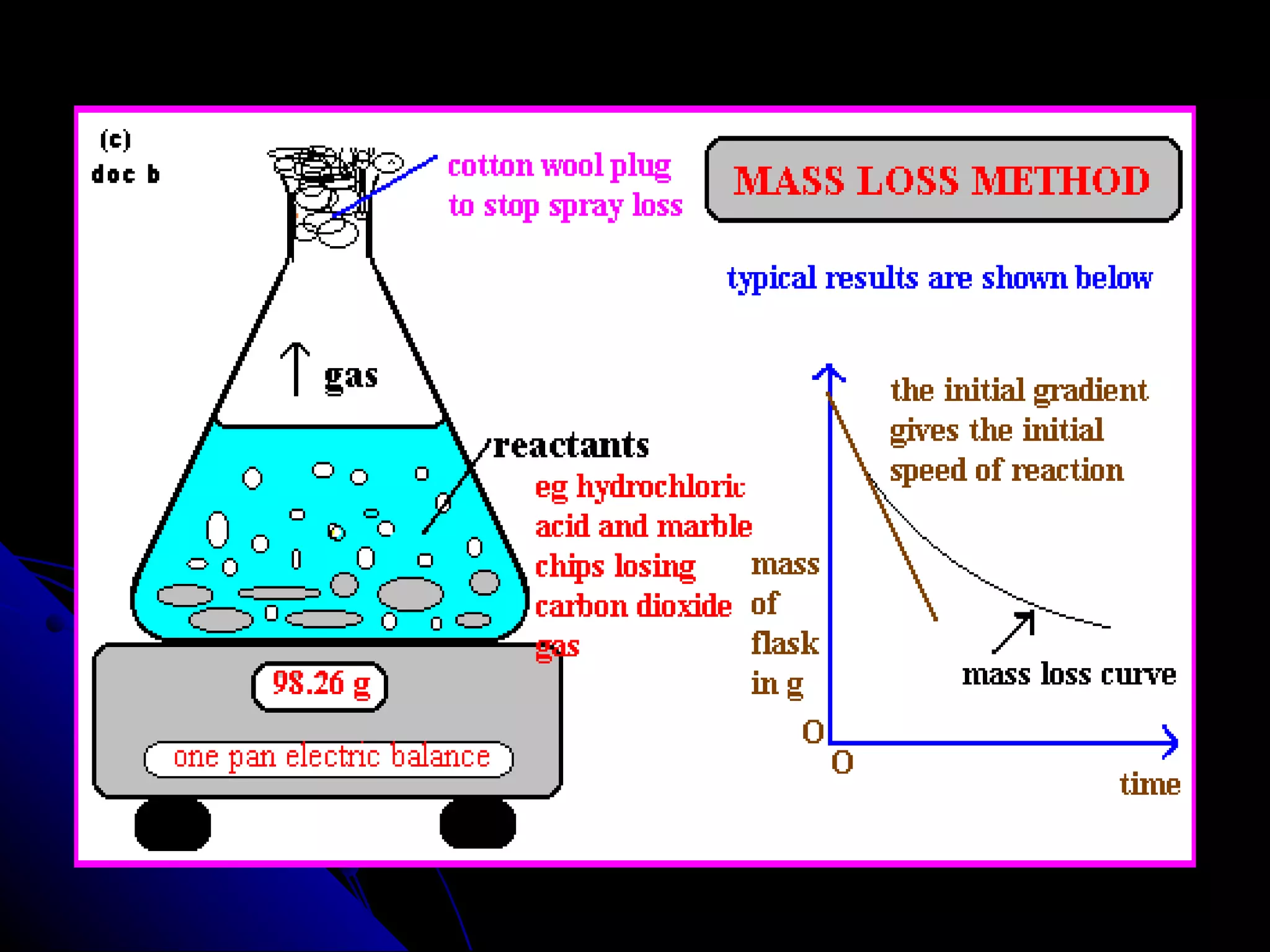
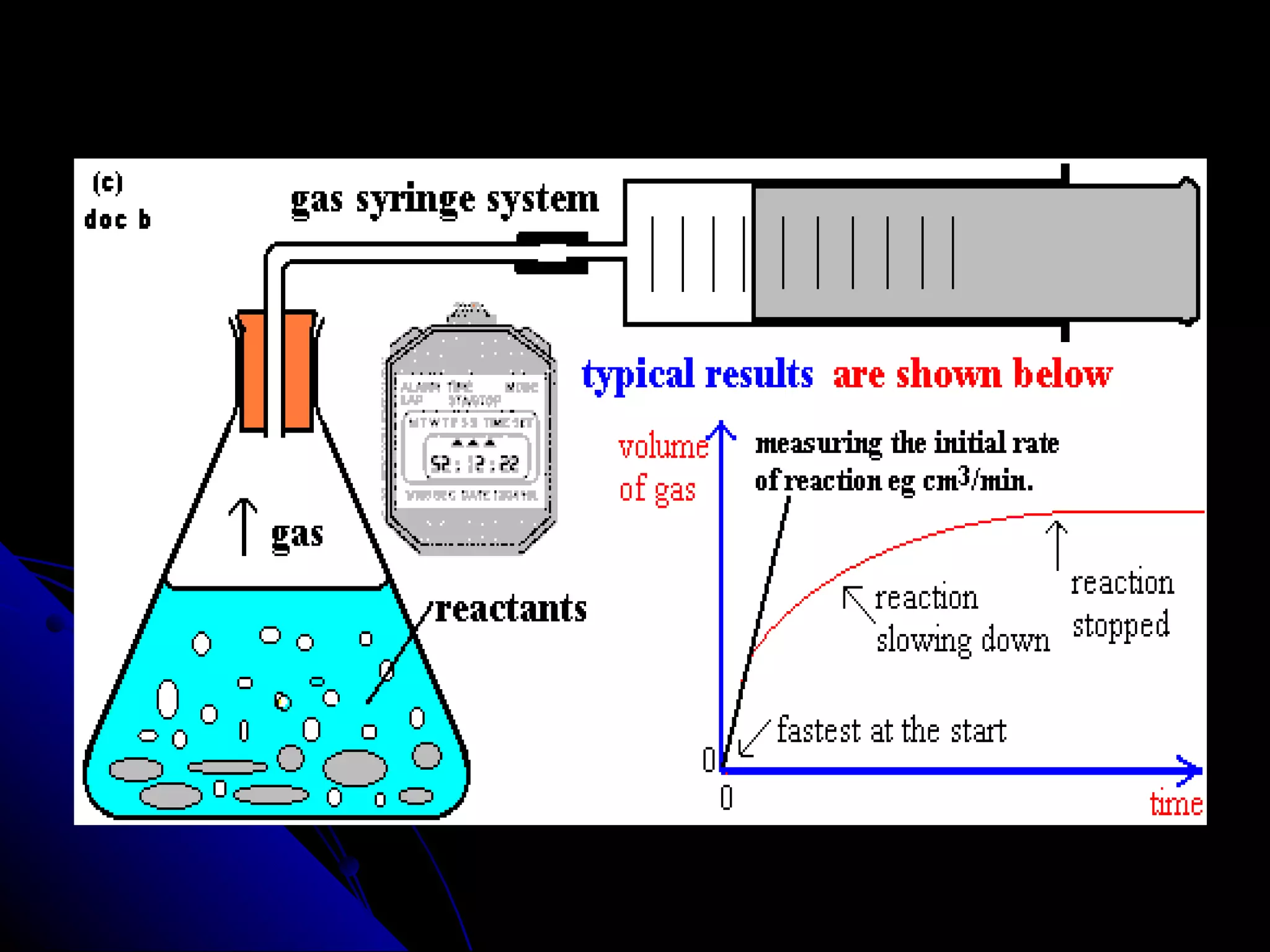
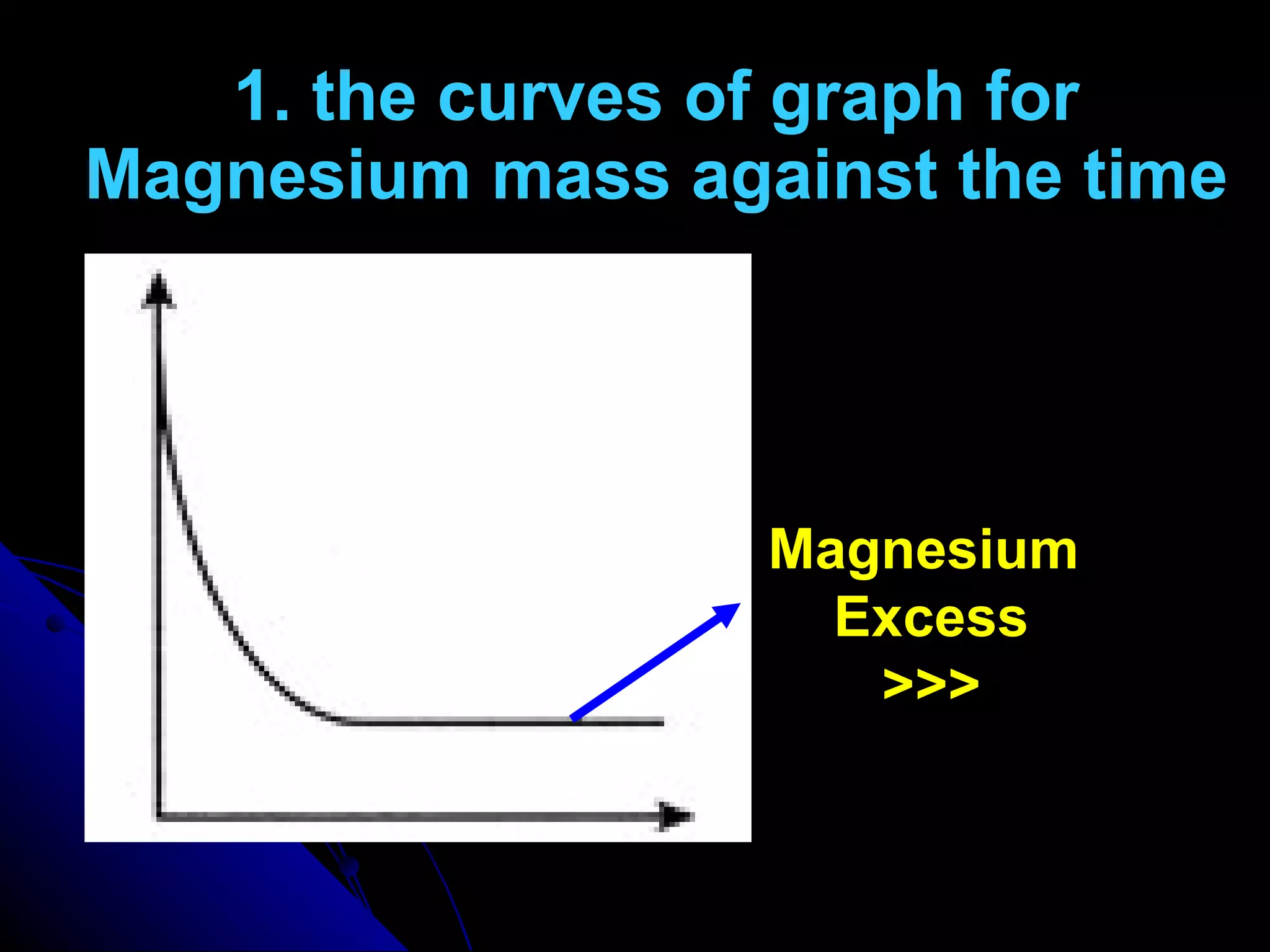
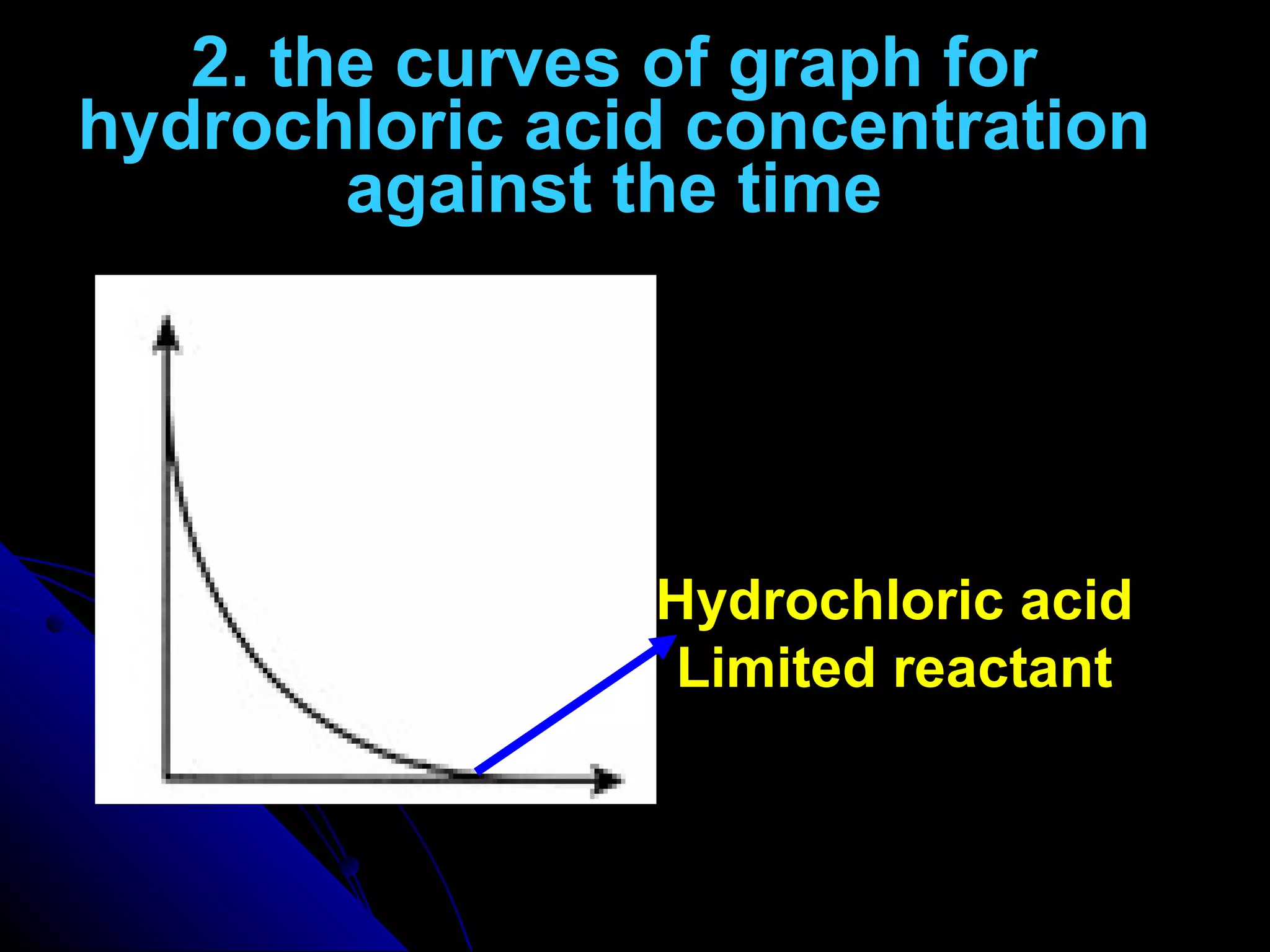
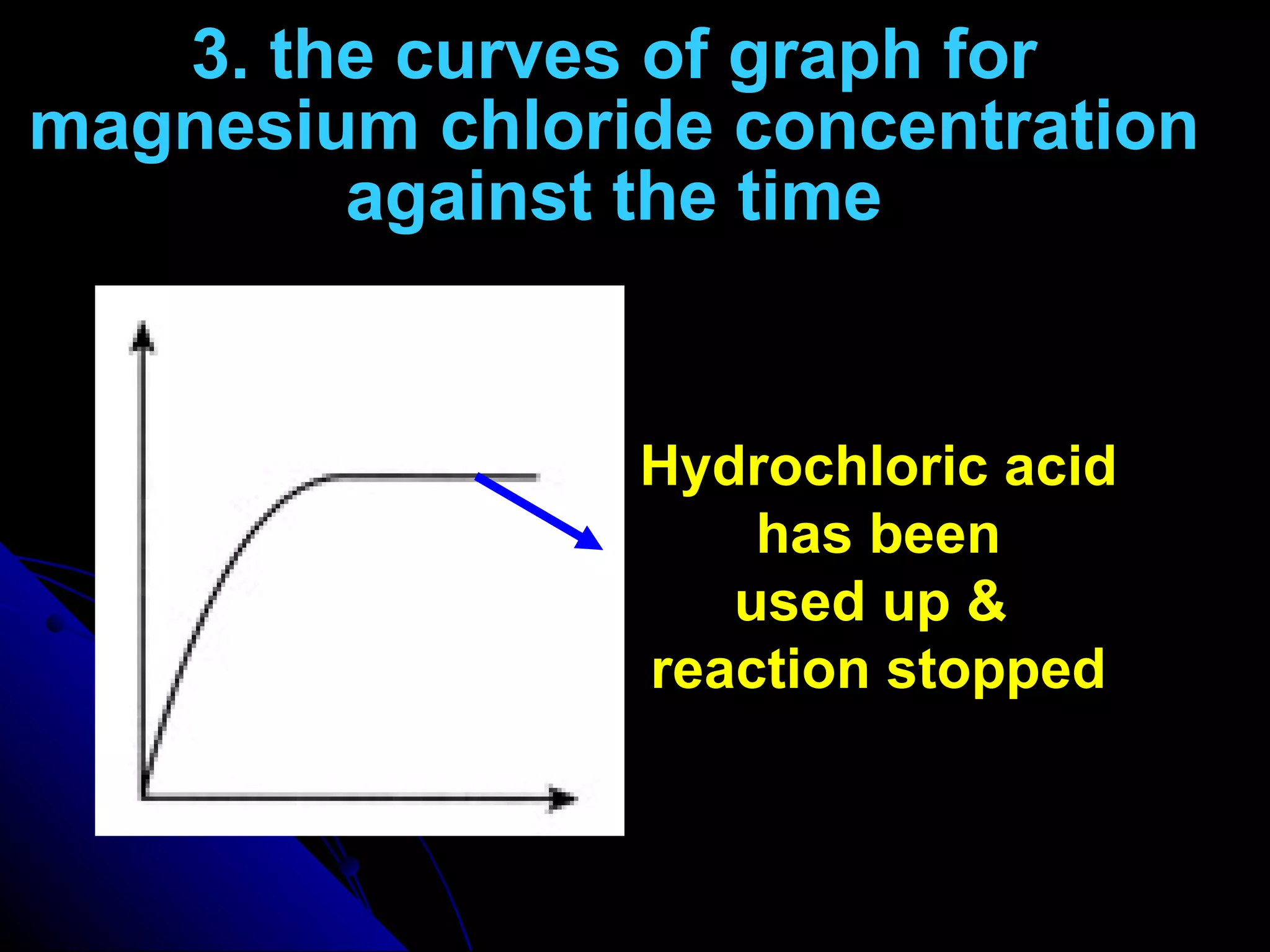
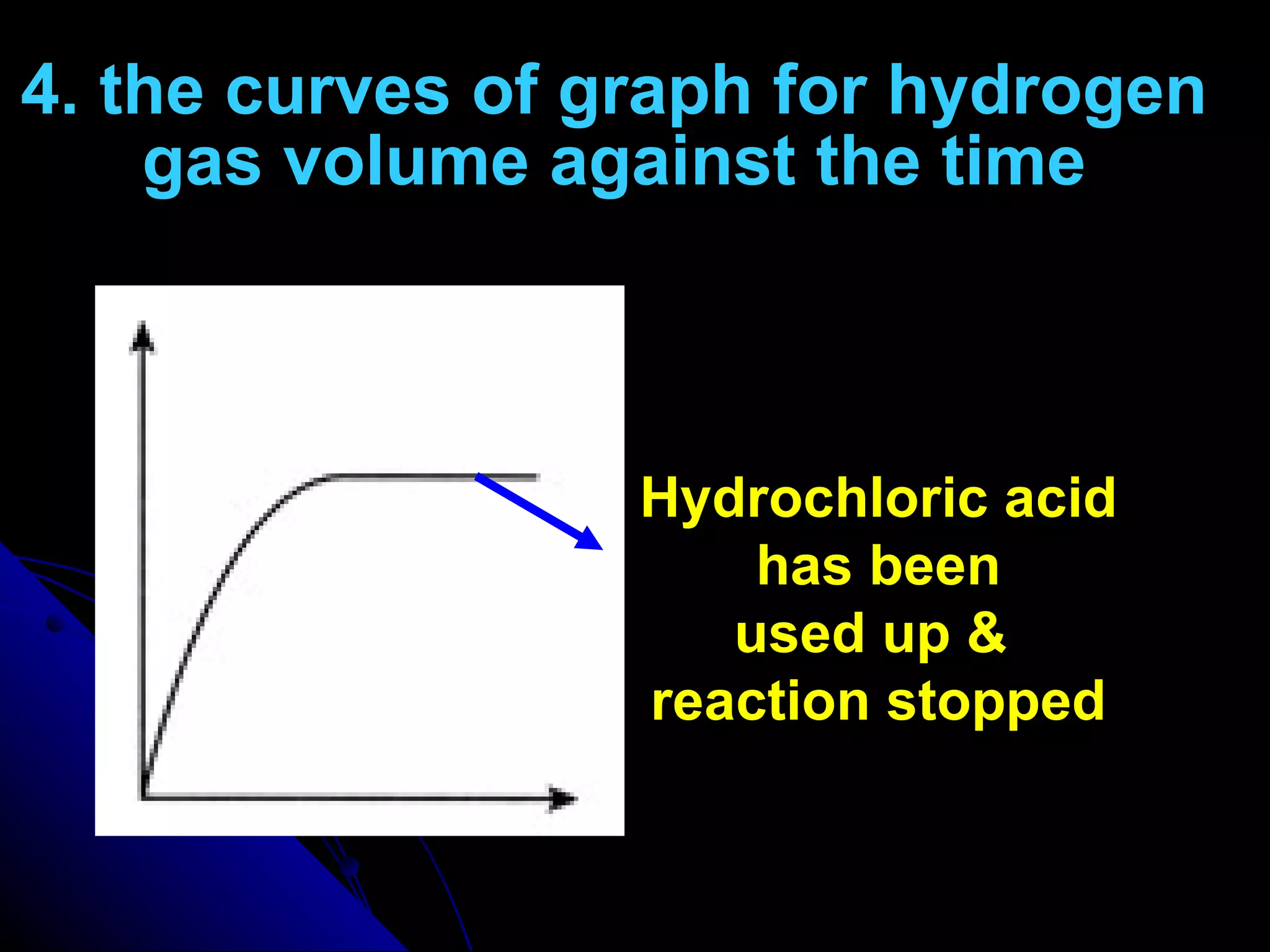
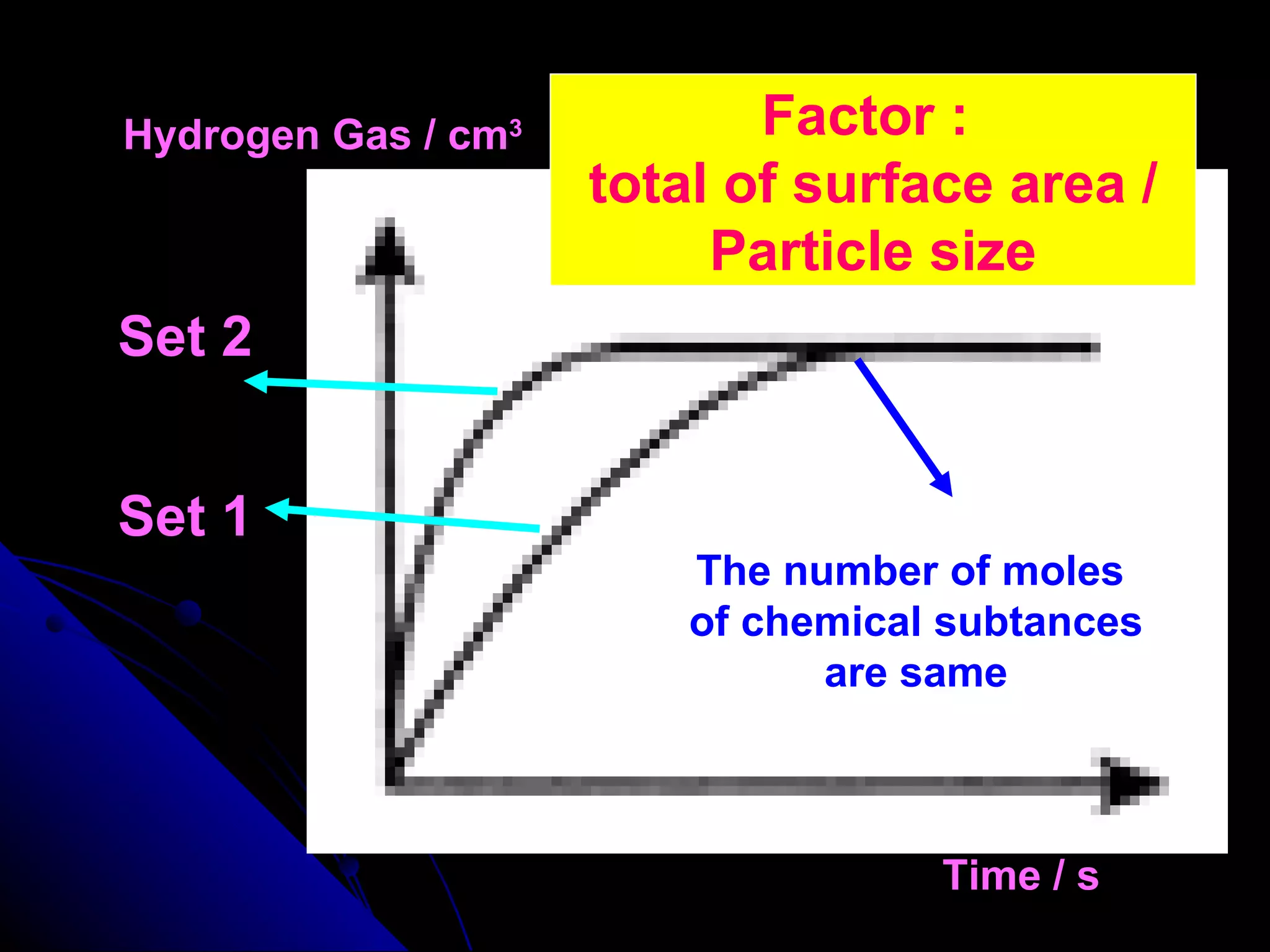
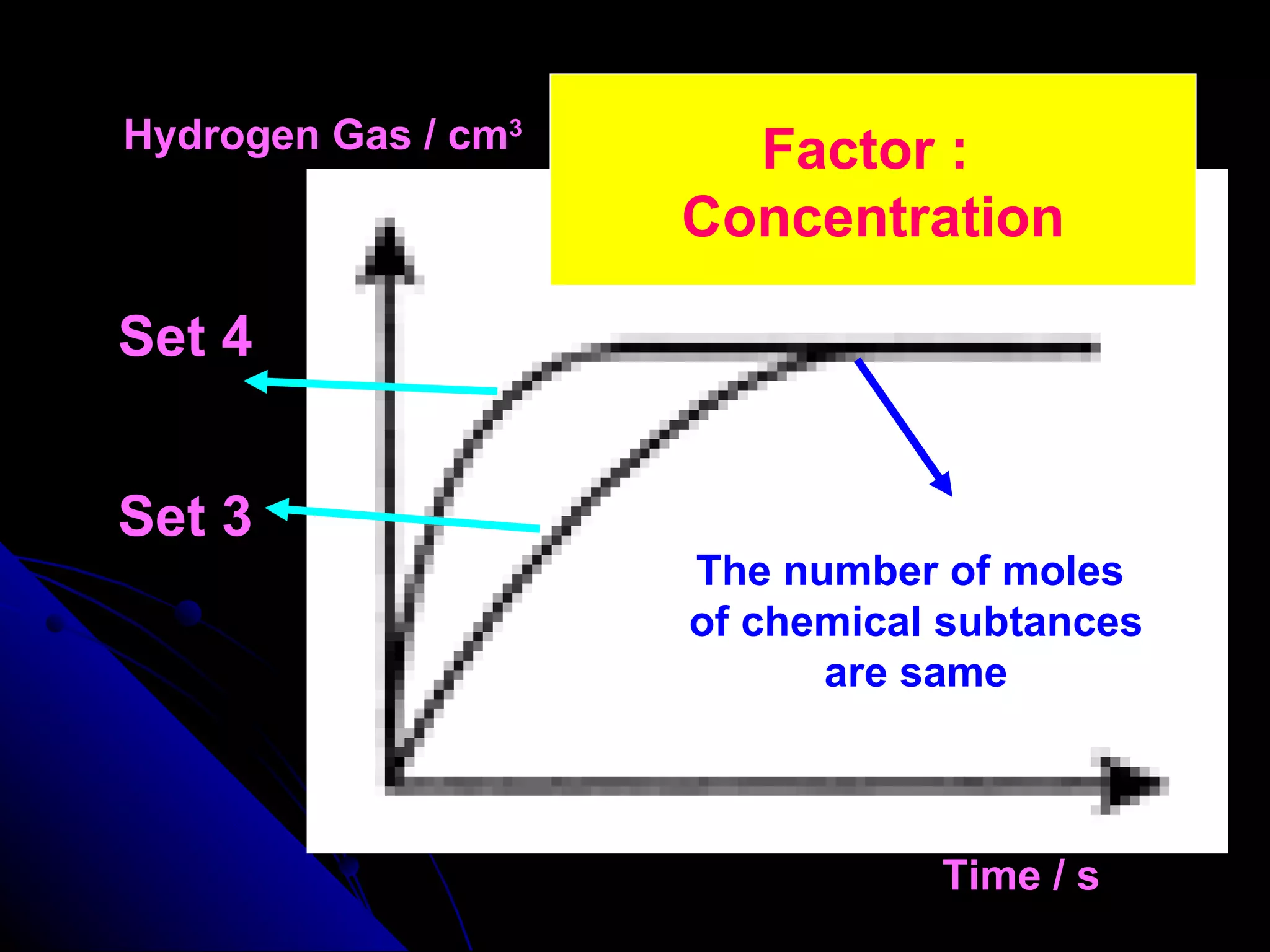
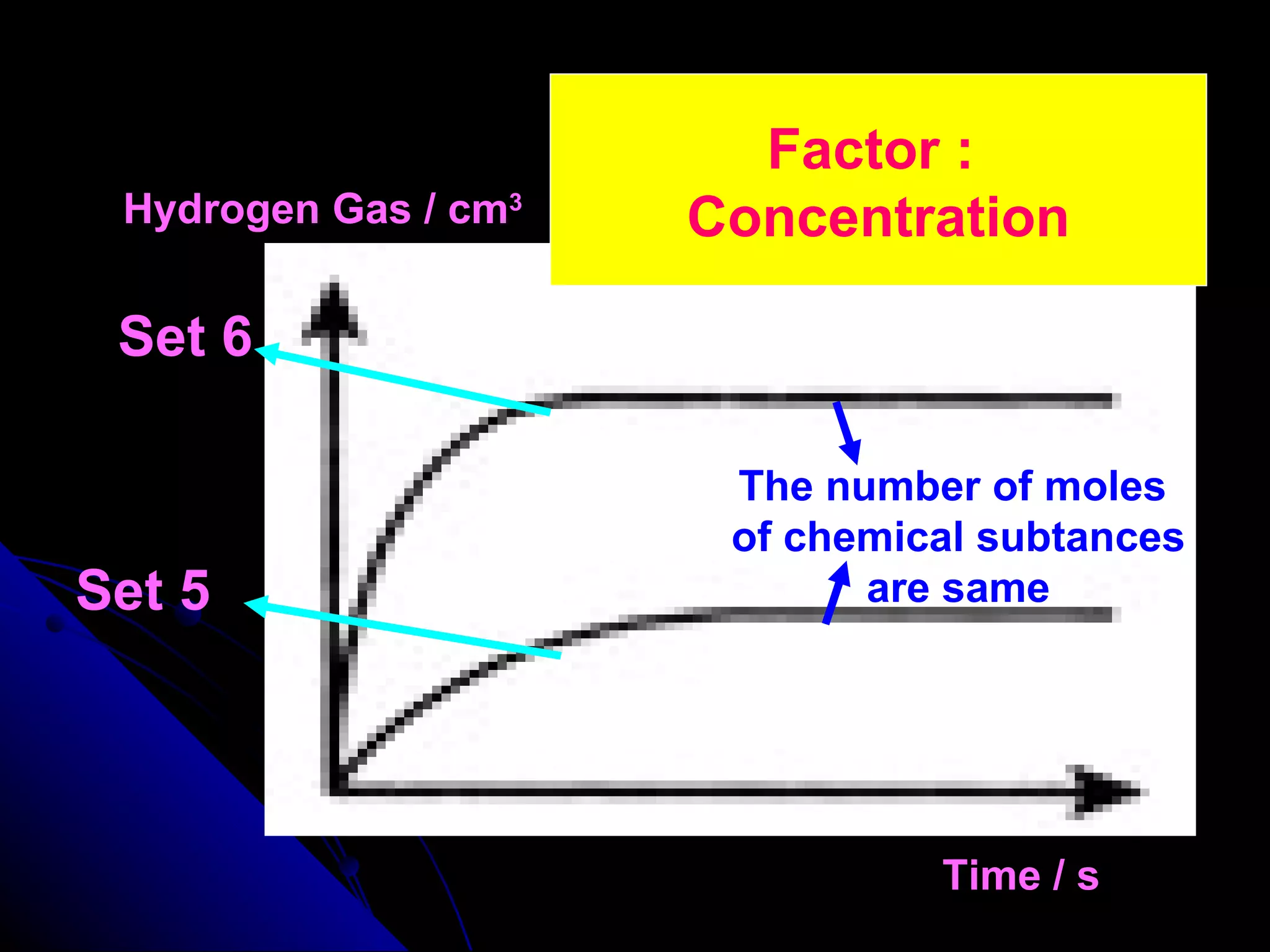
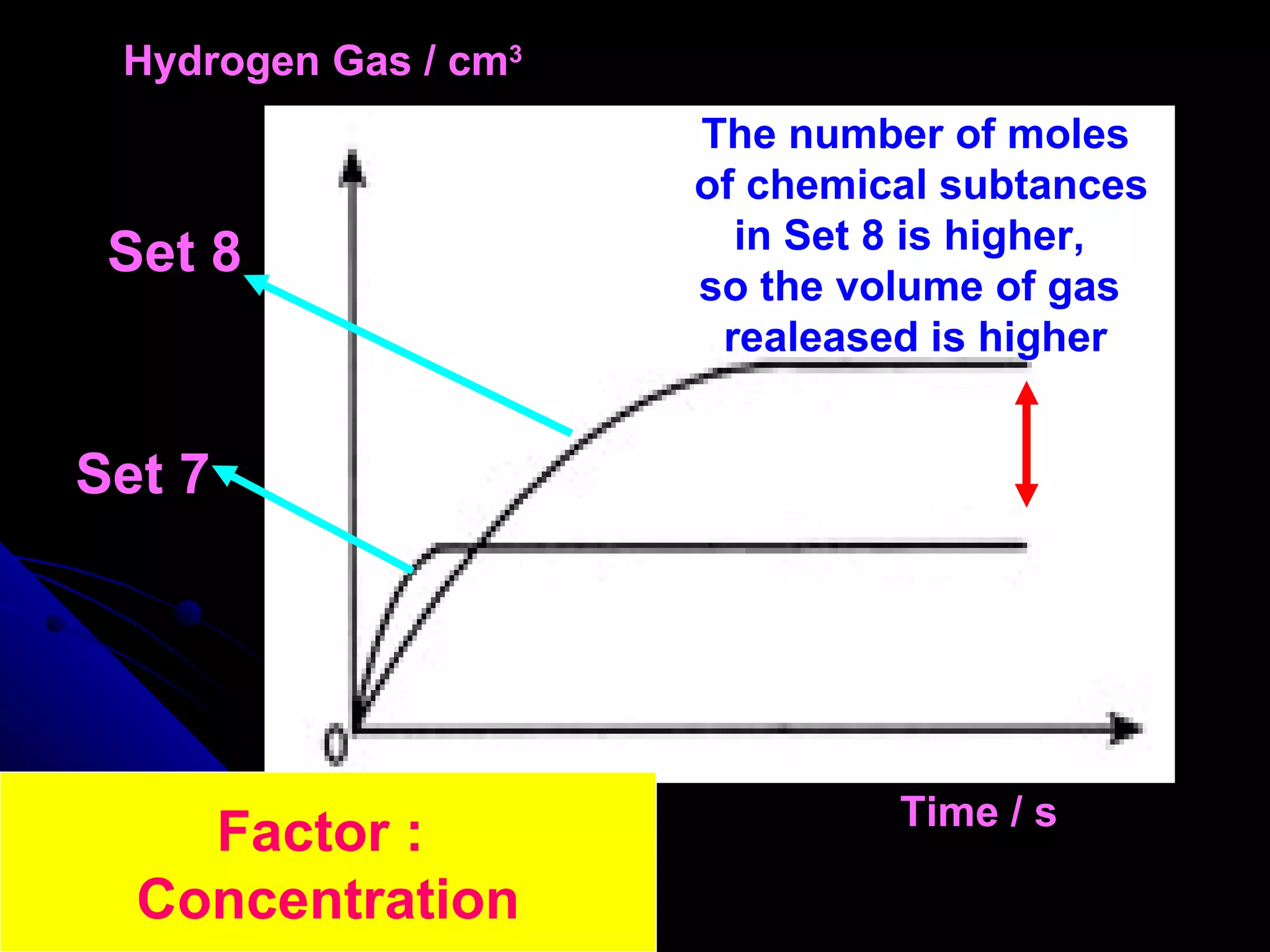
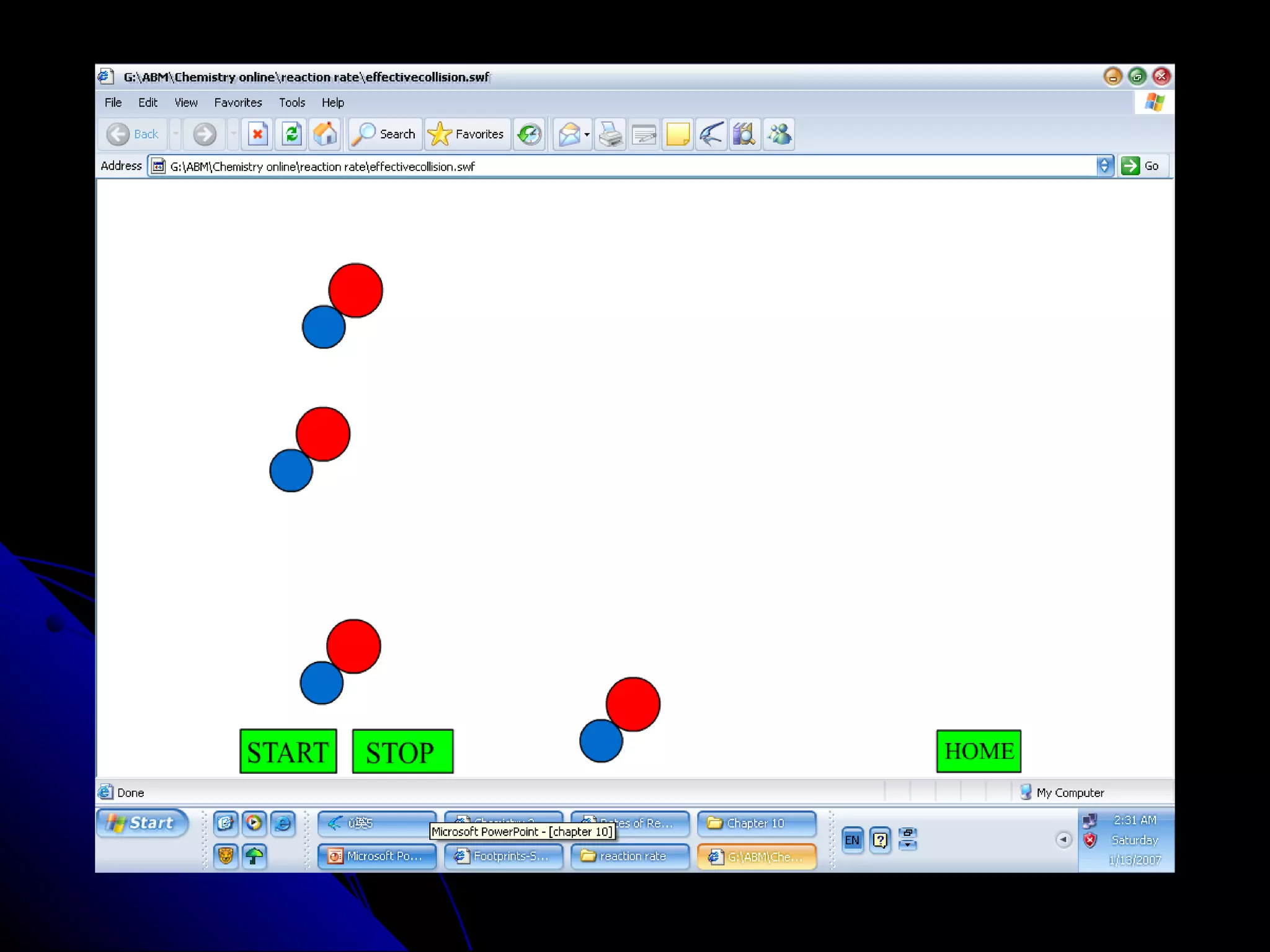
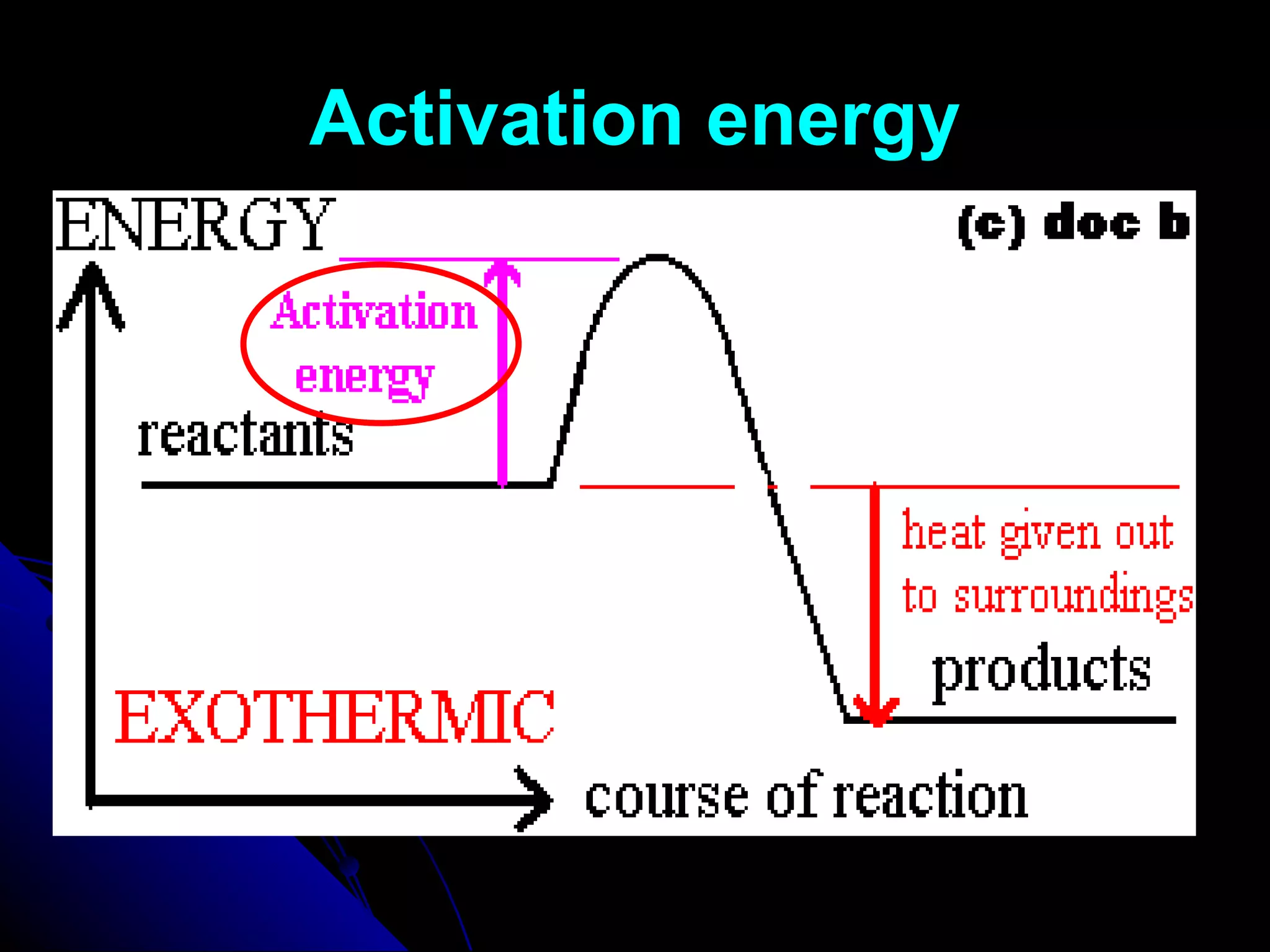
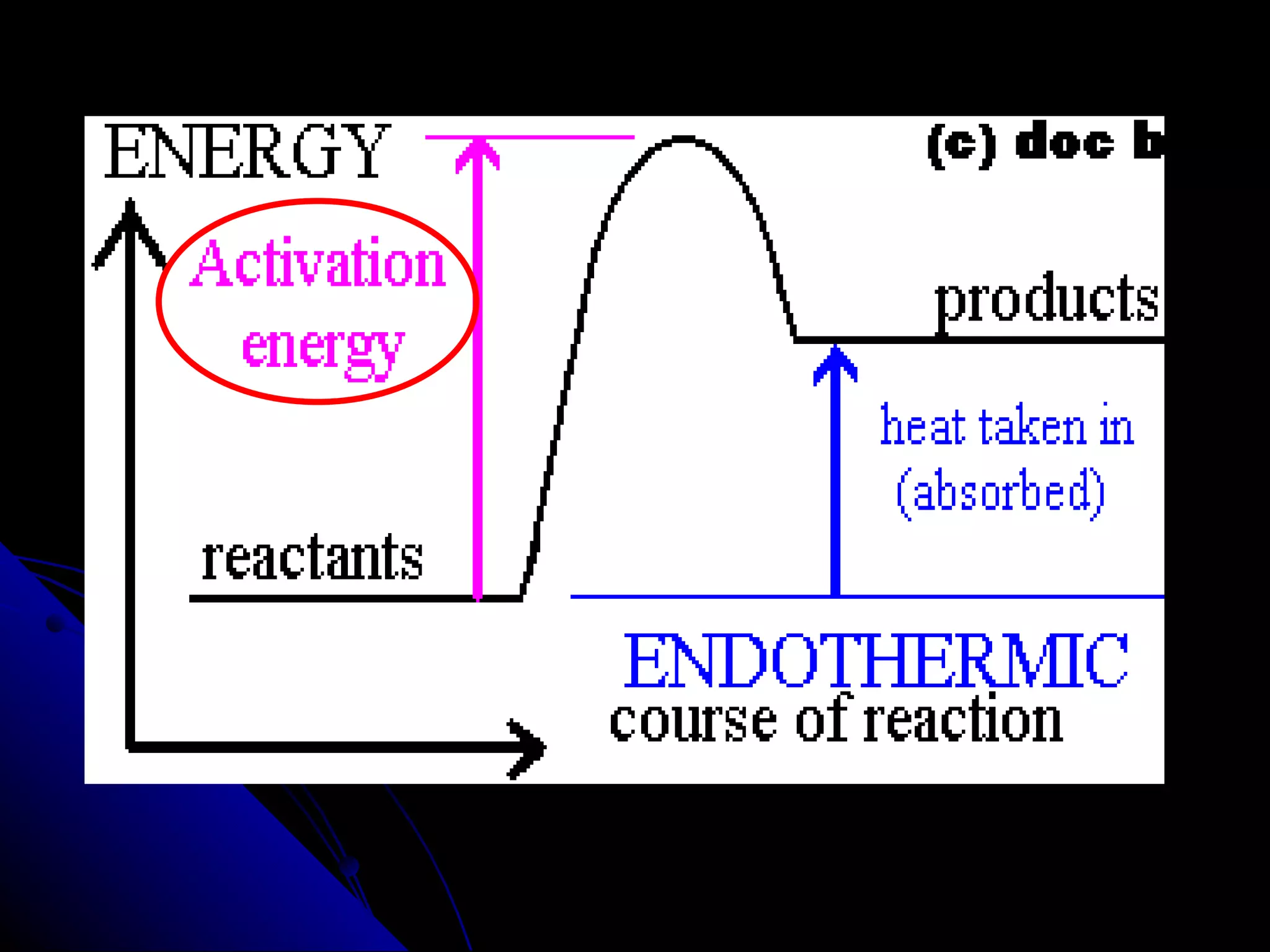
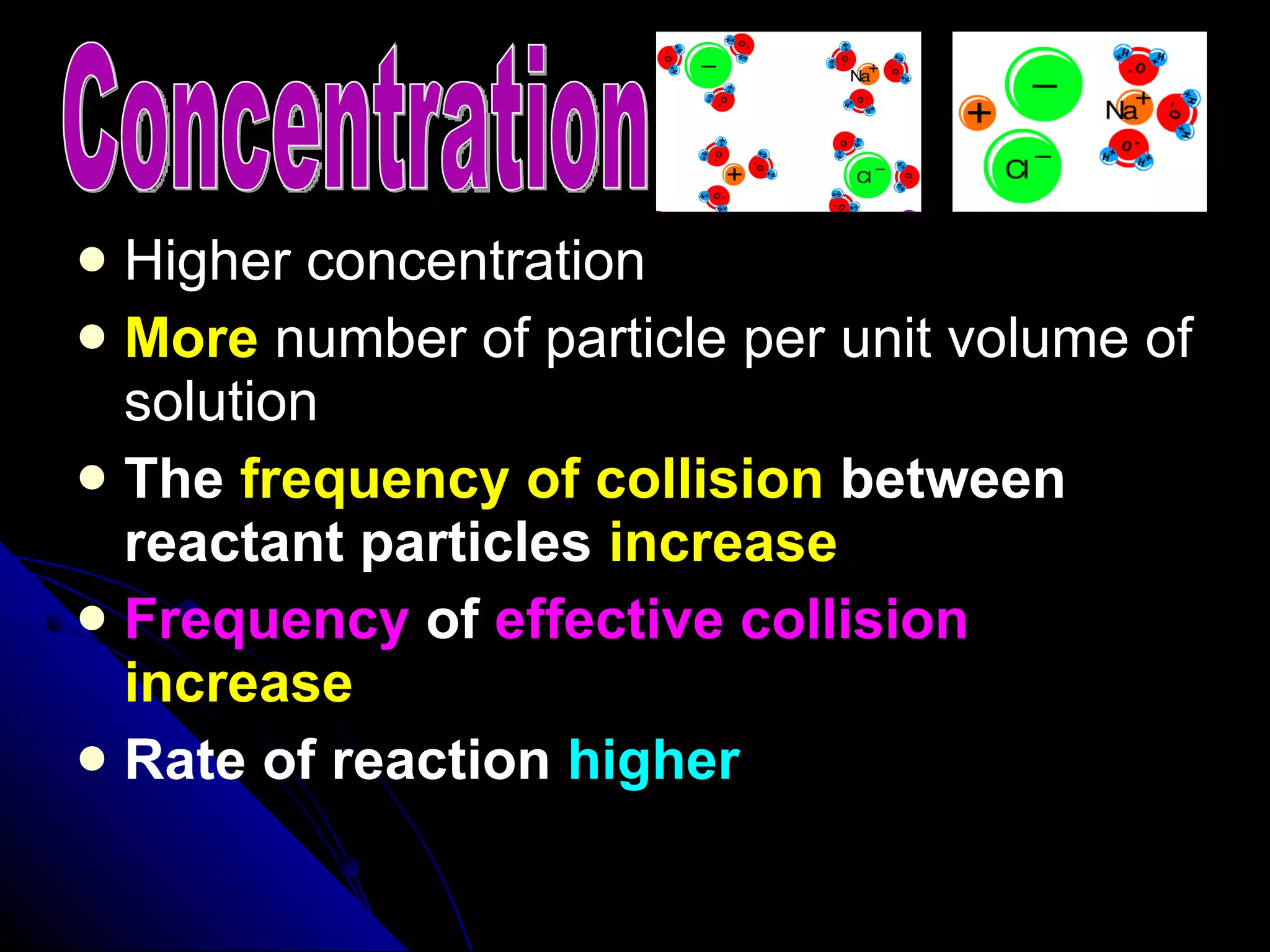
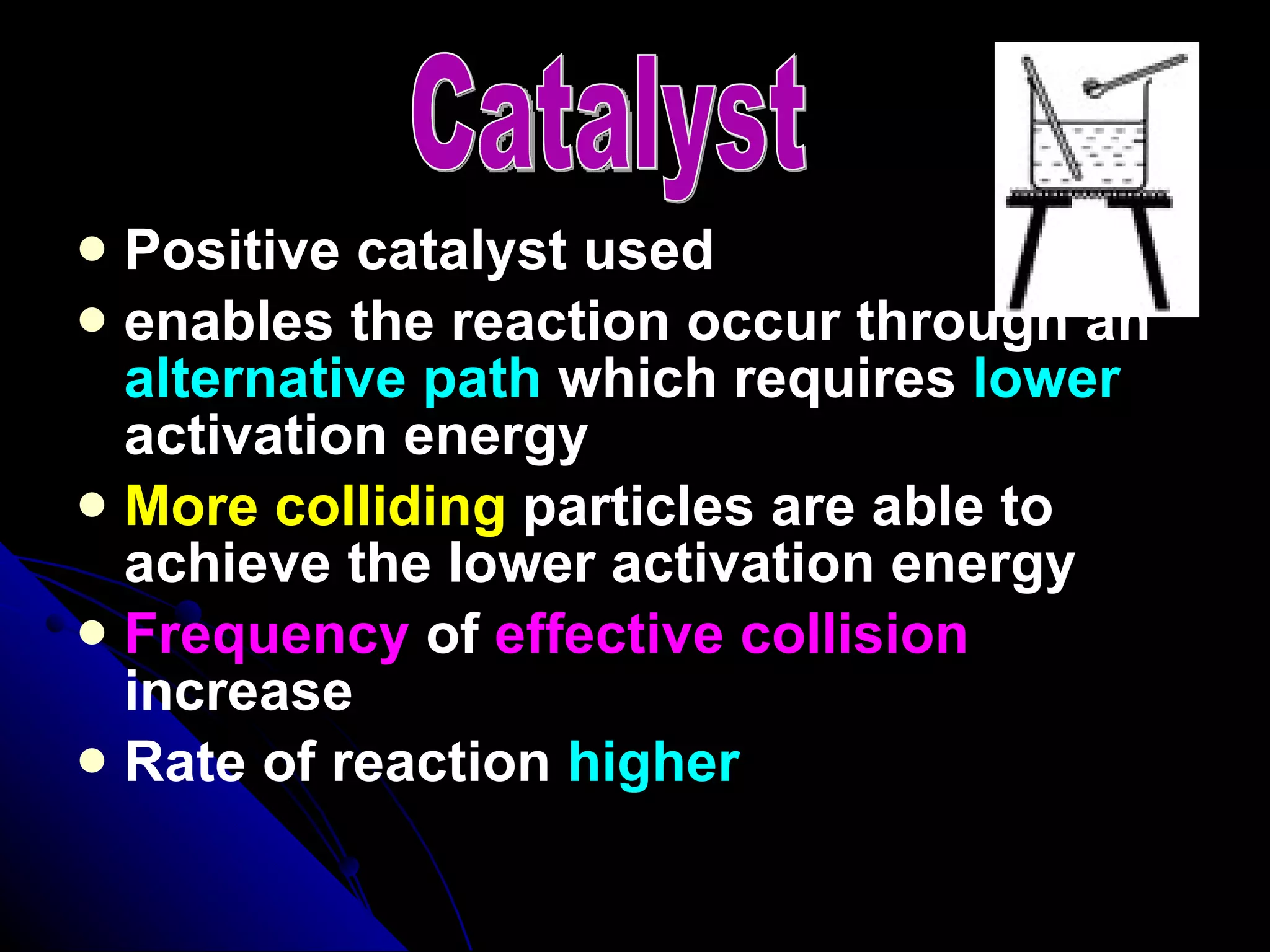
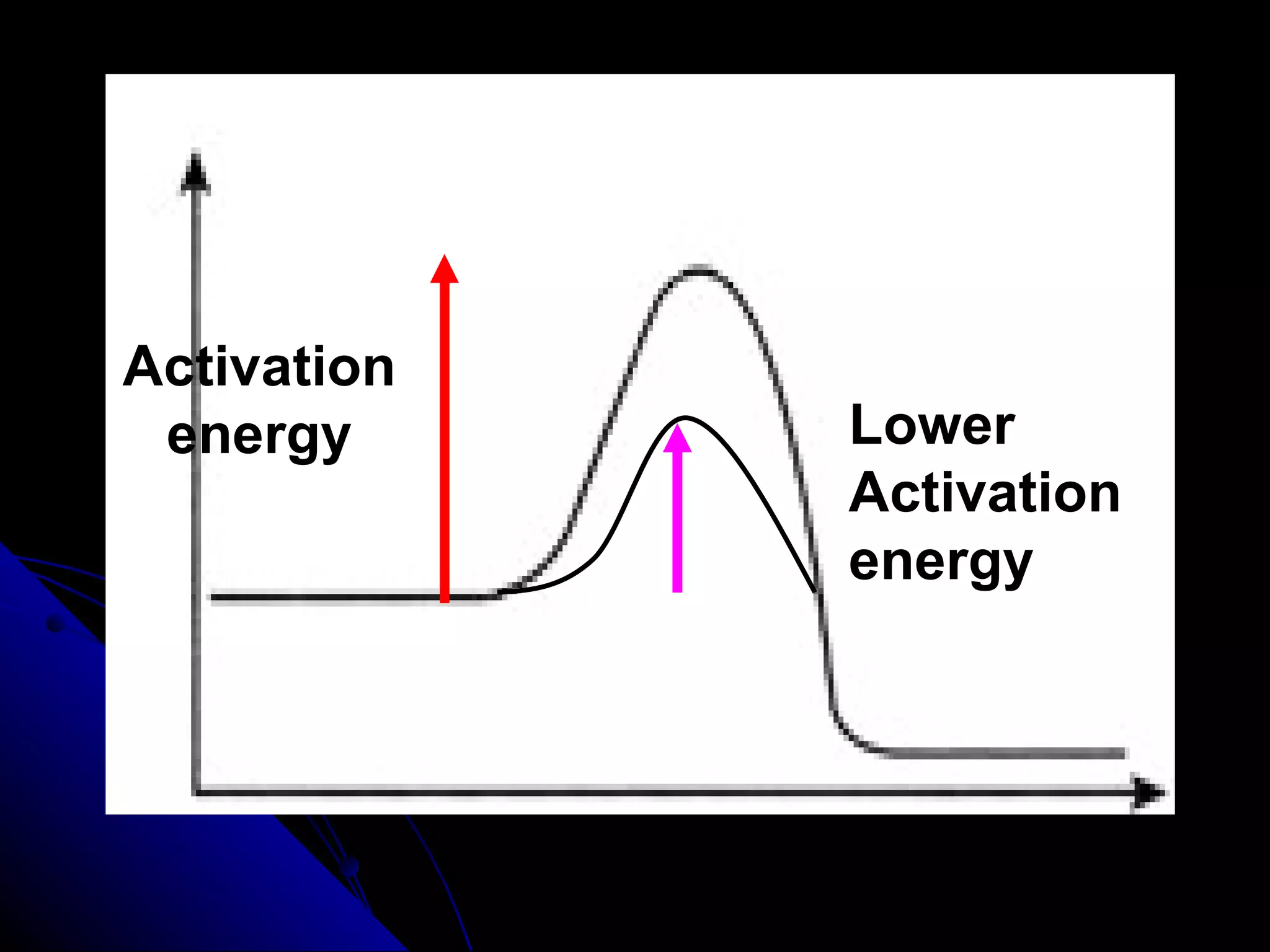
The document discusses the rate of chemical reactions and factors that affect it. It provides examples of reactions that occur at different rates and how rate is calculated. The average rate and instantaneous rate are defined. Experiments are described to determine the effect of surface area, concentration, temperature, catalyst, and pressure on the reaction rate. The concept of effective collision is introduced, where particles must collide with sufficient energy and correct orientation for a reaction to occur. Factors that increase collision frequency or lower activation energy can increase the reaction rate.