periodic classification notes of chap 5.pptx
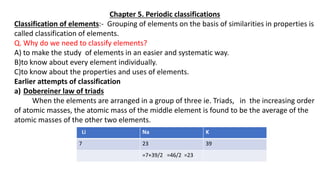
- 1. Chapter 5. Periodic classifications Classification of elements:- Grouping of elements on the basis of similarities in properties is called classification of elements. Q. Why do we need to classify elements? A) to make the study of elements in an easier and systematic way. B)to know about every element individually. C)to know about the properties and uses of elements. Earlier attempts of classification a) Dobereiner law of triads When the elements are arranged in a group of three ie. Triads, in the increasing order of atomic masses, the atomic mass of the middle element is found to be the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements. Li Na K 7 23 39 =7+39/2 =46/2 =23
- 2. Limitations a) He could arrange only lighter elements. b) Only three triads he arranged. c) Dissimilar elements were classified in triads. Cl Br I 35.5 80 127 =35.5+127/2 =162.5/2 =81.5 Ca Sr Ba 40 88 137 =40+137/2 =177/2 =88.5
- 3. Newlands law of octaves Newland arranged elements in the increasing order of atomic mass. He found that the properties of the first element is the repetition of the properties of the eighth element like the notes of music(octaves). Limitations a) It is valid only for elements till calcium. b) No space is allotted for noble gases when they were discovered. c) All elements discovered at that time could not be arranged in octaves. d) Newland used some incorrect atomic masses while placing them with similar 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 sa re ga ma pa dha Ni do re me fa So la ti H Li Be B C N O F Na Mg Al Si P S Cl K Ca Cr Fe Co,Ni
- 4. e) Co and Ni were placed in the same slot below fluorine and chlorine which has entirely different property. f) Iron was kept in a different position eventhough it shows similarity with cobalt and nickel. Mendelev’s Periodic Table *1869, DMITRI IVANOVICH MENDELEV *He arranged the then known 63 elements in the form of table. *He arranged in the order of atomic masses Mendelev’s Periodic law “The physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic masses”.(law of chemical periodicity) On the basis of periodic law, Mendelev arranged the then known 63 elements in the increasing order of atomic mass. Features • He arranged the then known 63 elements on the basis of atomic mass. • His periodic table contains 8 vertical coloumns of elements called groups and 6 horizontal rows called periods. • Each group has two subgroups A and B. • Groups from I to VII have been divided into two subgroups while group VIII is meant for three elements. • Two general formula one for oxide and second for hydride have been given for elements of each group at the top in the periodic table. • Periodic reccurance of elements with similar physical and chemical properties can be observed.
- 5. R2O RO R2O3 RO2 R2O5 RO3 R2O7 RO4 RH RH2 RH3 RH4 RH3 RH2 RH
- 6. Advantages of Mendelev’s Periodic Table a)He could classify all the 63 elements discovered at that time on the basis of similarities in properties. b) He left gaps for yet to be discovered c)He predicted the properties of the undiscovered elements and thus helped in the discovery o these elements later on. d) He named some elements by prefixing Sanskrit numeral eka boron, eka-aluminium, eka-silic etc. to the name of the preceding similar element in the same group. All these elements were discovered later and did have the properties similar to those predicted Mendelev. Later Eka –boron was named as Scandium and Eka-Aluminium as Gallium and Eka- silicon as Germanium. Properties Eka -Alumininium Gallium At. Mass 63 69.7 Formula of oxide E2O3 Ga2O3 Formula of chloride ECl3 GaCl2
- 7. e) It helped in the correction of atomic masses of certain elements on the basis of their position in the periodic table. f) After the discovery of noble gases , they were placed in separate group called zero group after group VIII without disturbing the position of any other elements. Limitations of Mendelev’s Periodic Table a) Position of hydrogen Position of hydrogen was placed in group I although its properties resembled Group I (alkali metals) and Group VII elements (halogens). b)Mendelev placed elements according to their similarities in properties and not in the increasing order of their atomic masses, while some dissimilar elements were grouped together. *Co (58.9)was placed before Ni(58.6) *Cu and Hg are similar in their properties but placed separately. *Tellurium(127.6) is placed before I (126.9) c) Isotopes have not been given separate places in the periodic table. d)Lanthanides and Actinides were not given proper places in the Mendelev’s table. e) Mendelev’s table was unable to explain the cause of periodicity among elements.
- 8. Modern Periodic Table In 1913, Henry Moseley found that atomic number was the fundamental property of an element and not the atomic mass for classification of elements. Modern Periodic Law “The physical and chemical properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic number”. According to the periodic law, elements were arranged according to the increase in atomic number and the modern periodic table was devised and it is also known as Long form of the periodic table or Extended form of the Periodic Table. Features of Long Form of the Periodic Table a) Elements were arranged in 18 vertical coloumns called groups. b) There are 7 horizontal rows known as periods. c) Elements having similar outer electronic configuration have been placed in same groups.
- 9. d)Modern periodic table has 18 vertical columns known as groups arranged from left to right in the order IA,IIA,IIIB,IVB,VB,VIB,VIIB,VIII(3 coloumn),IB,IIB,III A,IVA, VA,VIA,VII A and zero. Old Notation New Notation IA Group 1(Alkali metals) II A 2 (Alkaline earth metals) III B 3 IVB 4 VB 5 VIB 6 VII B 7 VIII 8,9,10 IB 11 IIB 12 IIIA 13 (Boron family) IVA 14(Carbon family) VA 15(Nitrogen family) VIA 16(Oxygen family) VII A 17(Halogen family)
- 10. Group I(Alkali metals) They form strong alkalies with water. They are very good reducing agents. They are electropositive ions. They are monovalent ions. Group II (Alkaline earth metals) They form weaker alkalies as compared to group I elements. They form divalent cations. Group I and Group II elements are called s-block elements as they fill inner subshell S. Group 13 elements(Boron family) They are having 3 electrons in its outermost shell. Boron is the first member of this group. Group 14 elements(Carbon family) Carbon is the first member having 4 electrons. They are tetravalent in nature. Group 15 elements(Nitrogen family) Nitrogen is the first member having 5 valence electrons. The valency is found to be 3. Group 16 elements (Oxygen family) Oxygen family is having 6 electrons in its outermost shell. The valency is found to be 2. They are also known as chalcogens.(Ore forming)
- 11. Group 17( Halogens) Halogens are having 1 valence electrons and the valency is found to be one. They usually form salts. • Elements of group 13 to 17 are called p- block elements • Elements of group 1,2,13,15,17 are known as main group elements/Representative elements/Normal elements. • Elements of group 3 to 12 are known as transition metals ie show variable valency. Their two outermost shell are found to be incomplete.( D- block elements) • Elements of group 18 are known as noble / Inert/Rare gases or 18th group elements. They are having a stable electronic configuration(duplet /octect configuration. They are non-reactive elements.
- 12. Periods • 7 horizontal rows known as periods are present in the modern periodic table. • The no, of shells present in an element determine its period. • Elements of period I have one shell and elements of period II have two shells and so on. • First period contains two elements – shortest period • Second and third period contains 8 elements- short period • Third period elements –Na, Mg,Al, Si, P, S, Cl,Ar are called typical elements. • Fourth and fifth period contain 18 elements – Long periods • Sixth period contain 32 elements- Longest period • Seventh period is incomplete. • In group 3 of sixth period a set of 14 elements with atomic number 57-71 are called lanthanides. • In group 3 of seventh period a set of 14 element with atomic number 89- 103 are known as Actinides. • Lanthanides and Actinides are otherwise known as F- block elements.
- 13. A L K A L I M E A L K A L I N E TRANSITION METALS OR D-BLOCK ELEMENTS B O R O N F A M C A R B O N F A N I T R O G E N O X Y G E N O R H A L O G E N S I N E R T G A S TYPICAL ELEMENTS S-BLOCK P-BLOCK D-BLOCK REPRESENTATIVE ELEMENTS F-block elements Lanthanides and Actinides
- 14. The periodic table is divided into four blocks. a)s- block elements -Group 1 and 2 elements are called s- block elements. b) p- block elements- Group 13 to 18 are called p- block elements. c) d- block elements- Group 3 to 12 are called d- block elements. d) f- block elements – The elements placed at the bottom of the periodic table are known as f-block elements. The fourteen elements called Lanthanides (58 to 71) And Fourteen elements called Actinides (90 to 103) PERIODICITY The properties that appear at regular intervals are called periodic properties. They are having similar electronic configuration. VALENCY The combining capacity of an atom of an element.It is determined by the number of valence electrons present in the outermost shell of an element. Down a group: Valency remains same down a group, as the number of electrons in the outermost shell remains the same. ACROSS A PERIOD: Valency first increases then decreases. Across a period , increases from 1 to 4 and decreases from 3 to 0.
- 15. Atomic size It is the distance between the centree of the nucleus of an atom and its outermost shell.It is the radius of an atom. Atomic size vary according to the nuclear charge. IN A GROUP: Atomic size increases from top to bottom in a group. It is due to the addition of a new shell.ie no. of shell go on increasing. Li- 2,1 133pm Na – 2,8,1 154pm K -2,8,8,1 201 pm Rb - 2, 8,18,8,1 216 pm F< Cl< Br< I<As ACROSS A PERIOD: Atomic size go on decreasing along a period from left to right. Reason: It is due to the increase in the nuclear charge which pulls the electrons towards it ie, the force of attraction between nucleus and valence electrons increases, therefore atomic size decreases. Na>Mg>Al>Si> P> S>Cl Li Be B C N O F Ne 133 89 80 77 70 66 64 Li Na K Rb Cs Fr
- 16. Metallic character The elements that have a tendency to lose electrons and form +ve ion are considered as metals. Metallic character depends on 1)Atomic size 2)Nuclear charge 1)Atomic size: Greater the atomic size, farther the outermost shell, lesser the nuclear pull. As a result, electrons can be removed easily from the outermost orbit thus making elements more metallic. 2) Nuclear charge:- Greater the nuclear charge, greater force exerted by the nucleus on the outermost shell. This makes it difficult to remove the electrons from the outermost shell.Therefore metallic character decreases. DOWN A GROUP: Down a group atomic size increases, nuclear charge increases, metallic character increases. Metals are having a very good tendency to lose electrons. Therefore they are very good reducing agents also. ACROSS A PERIOD:- On moving across a period, nuclear pull increases, atomic size decreases, elements cannot lose electrons, they only gain electrons. Therefore metallic character decreases across a period from left to right.
- 17. Non- metallic character Those elements which have a tendency to gain electrons are called non- metals. IN a GROUP:- Atomic size increases, non- metallic character decreases down a group. ACROSS A PERIOD:- Atomic size decreases, non-metallic character increases from left to right. IONISATION ENERGY:- It is the energy required to remove an electron from the outermost shell of an atom in its isolated gaseous state, thereby converting it into positively charged ion. Na ------------- Na+ + 1e (496 KJ /mol energy) Cs ------------- Cs+ +1 e (376 KJ /mol energy) Metals are having low ionisation energy. Inert gases have maximum ionisation energy. DOWN A GROUP:- I.E decreases down a group.
- 18. Electron Affinity:- It is the energy released on adding an electron to the outermost shell of an atom in its isolated gaseous state, thereby converting it into an anion. Cl+ 1e ---------- Cl- Inert gases have zero electron affinity. Non-metals have high electron affinity. Halogens have maximum electron affinity in their respective periods. ELECTRONEGATIVITY: It is the tendency of an atom to attract the shared pair of electrons towards its side when combined in a compound. Fluorine is the most electronegative element. (3.9) Eg: H—Cl
- 19. • Inert gases are having complete octet or stable configuration He -2 Ne -2,8 Ar -2,8,8 Kr -2,8,18,8 The features of alkali metals are • Highly electropositive in nature • Good reducing agents • Valency 1 • They have low ionisation energy • They form metallic hallides. • Good conductors of electricity. • They have larget atomic size in their periods. • They react vigourously with dilute acids and coldwater to liberate
- 20. The features of halogens are • Highly electronegative in nature. • Valency -1 • Good oxidising agents. • They have high electron affinity. • They undergo ionic bond formation with metals. • Poor conductors of electricity. • They have smallest size in their period. • They do not react with dilute acids. • Text back questions. 1. Did the Dobereiner’s triads also exist in the column of Newlands Octaves? Compare Only one triad exist in the coloumn of Newlands Octaves. The triad formed by elements Li, Na and K of Dobereiners triad also occurred in the coloumn of Newlands octaves.
- 21. 2. Use Mendelevs PT to predict the formula for the oxides of the following elements: K, C, Al, Si, Ba. K- group 1 K2O C- group 4 CO2 Al – Group 3 Al2O3 Si group 4 - SiO2 Ba - Group 2 - Ba O 3. Besides Gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendelev in his Periodic Table. Scandium and Germanium. 4. How could the Modern Periodic Table remove the various anomalies of Mendelev’s Periodic Table? Mendelev was unable to give a fixed position to hydrogen and isotopes in the periodic table. Mendelevs periodic table couldn’t arrange all the then known elements in the increasing order of atomic masses according to the similarities in the properties.
- 22. But long form periodic table could arrange elements in the increasing order of atomic number according to the similarities in properties. 5. Name two elements that show similar chemical properties as that of magnesium. Mg- 2, 8,2 Ca -2,8,2 Sr -2, 8, 18, 2 Compare and contrast Mendelev and Modern Periodic Table. Mendelevs PT Modern PT Elements are arranged according to their atomic masses Elements are arranged according to their atomic number. 8 groups and 6 periods 18 groups and 7 periods Elements having similar properties have been arranged one after another Elements having same valence shell are present in the same period and elements having same valence electrons are arranged in the same group.