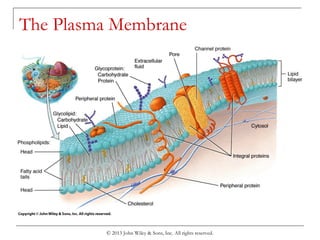
The document summarizes key components and functions of cells. It describes that cells have three main regions: the nucleus, cytoplasm, and plasma membrane. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable and transports substances via passive diffusion, facilitated diffusion, osmosis, and active transport. The cytoplasm contains organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex and ribosomes that synthesize proteins. Transport across the membrane and protein synthesis in the cell are essential cellular functions.













![Transport Across the Plasma
Membrane – Vesicular Transport
Transport in vesicles includes both endocytosis
(phagocytosis and bulk-phase endocytosis [pinocytosis])
and exocytosis. Phagocytosis is the ingestion of solid
particles. It is an important process used by some white blood
cells to destroy bacteria that enter the body. Bulk-phase
endocytosis is the ingestion of extracellular fluid. Exocytosis
involves movement of secretory or waste products out of a
cell by fusion of vesicles within the cell with the plasma
membrane.
© 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3cells-150812173534-lva1-app6892/85/Chapter-3-cells-15-320.jpg)

























































