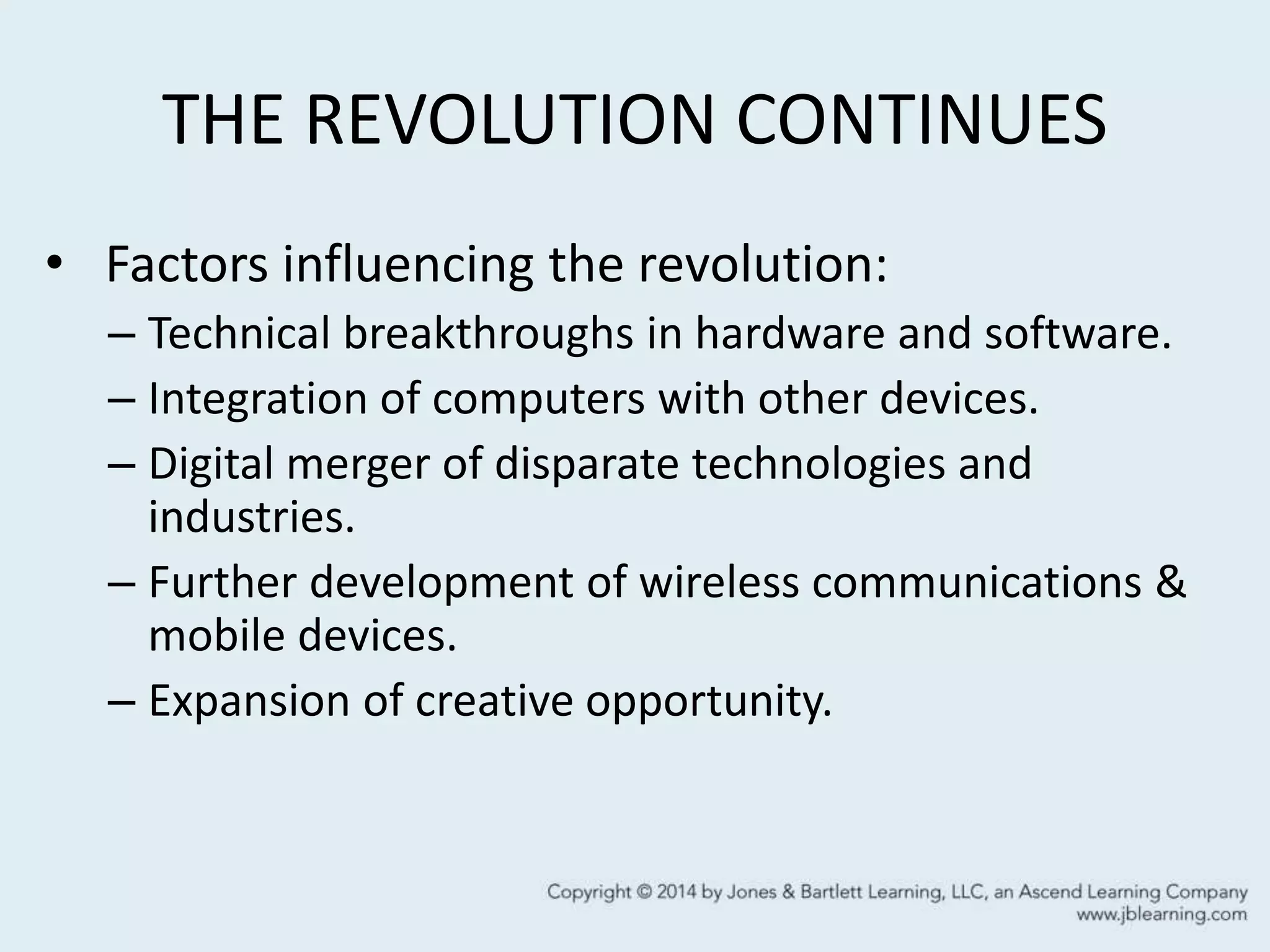
This chapter discusses the multimedia revolution and its key visionaries. It defines multimedia as the development, integration, and delivery of any combination of text, graphics, animation, sound or video through a digital processing device. Multimedia can be non-interactive, where the user passively observes information, or interactive, where the user participates in the flow of information. The chapter profiles several pioneers in multimedia, including Vannevar Bush and his proposed Memex machines, Alan Turing's concept of the universal Turing machine, Douglas Engelbart's innovations for human-computer interactivity, and Tim Berners-Lee's invention of the World Wide Web. It concludes that ongoing technical breakthroughs and the integration of computers with