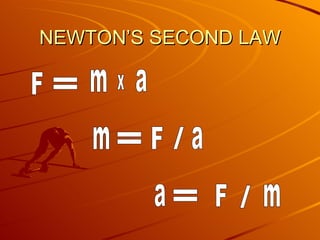Embed presentation
Downloaded 14 times





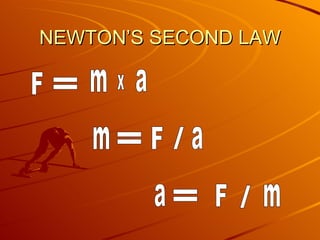


Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it, in the direction of the force. The greater the net force, the greater the acceleration, and if the net force is zero, the acceleration will be zero, though the object may still be moving at a constant speed. An object's mass also affects its acceleration, as greater mass means it takes more force to accelerate the object.