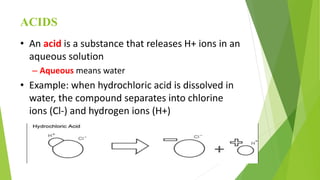
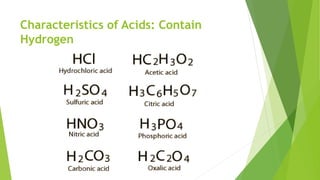
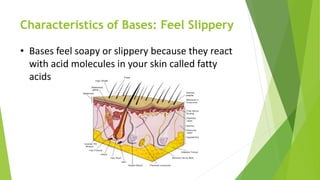
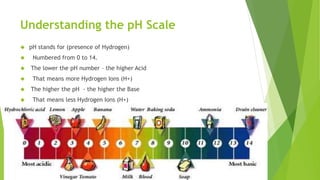
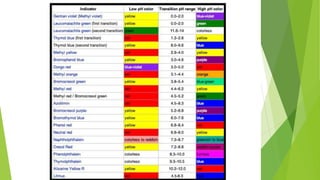
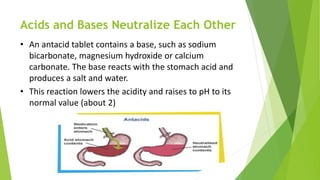
Acids and bases are defined by their properties in aqueous solutions. Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) and have a sour taste, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-) and feel slippery. The pH scale measures acidity and basicity, with values from 0-14 and neutral substances having a pH of 7. Acid-base indicators change color with pH and can test whether a solution is acidic or basic. When acids and bases are mixed, a neutralization reaction occurs where they cancel out each other's properties and form a salt and water.