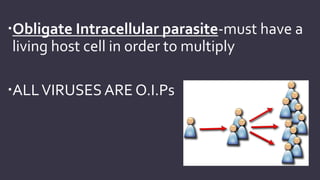
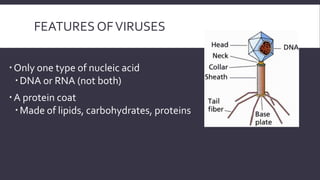
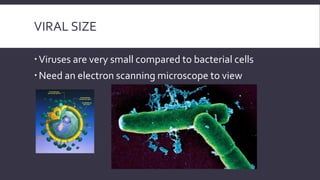
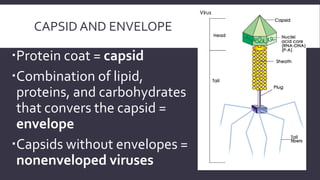
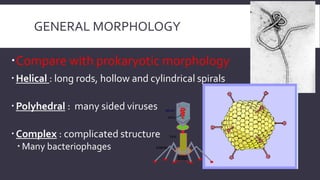
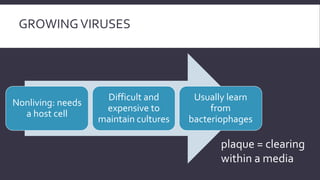
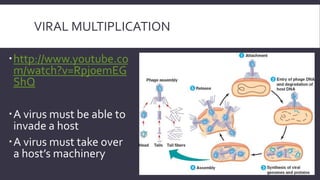
Viruses are obligate intracellular parasites that can only multiply within host cells. They contain either DNA or RNA, and have a protein coat called a capsid that may be surrounded by an envelope. To replicate, a virus must invade a host cell, take over its machinery, and use it to produce new viral particles, which then go on to infect more cells. While viruses use living cells to multiply, they are not themselves considered living things.