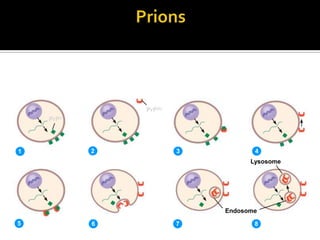
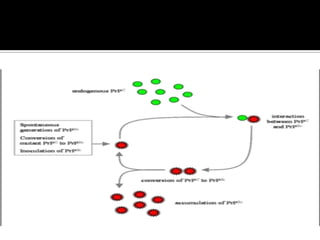
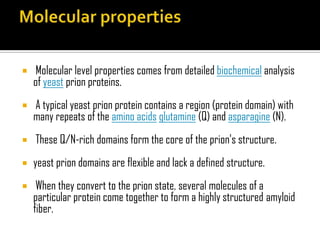
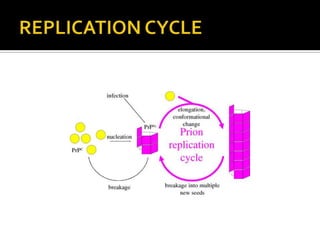
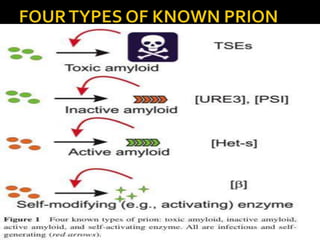
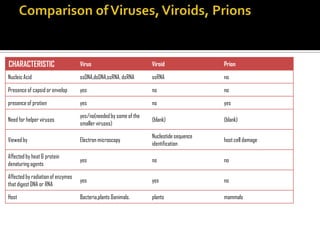
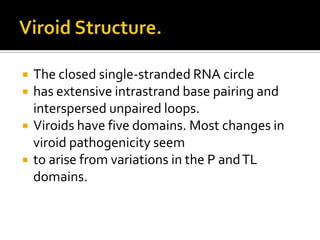
Prions are infectious proteins that can cause neurodegenerative diseases such as mad cow disease and CJD in humans. Prions lack nucleic acids and are composed solely of abnormal versions of host-encoded proteins. They propagate by converting normal protein molecules into the abnormal prion form. This causes disease by disrupting normal protein folding in the brain. While prion diseases are generally untreatable and fatal, research on yeast prions has provided insights into prion transmission and conversion mechanisms at the molecular level.