Bacteria and viruses share some characteristics:
- They can both reproduce rapidly and mutate. However, bacteria are cellular and prokaryotic while viruses are non-cellular and require a host cell to reproduce.
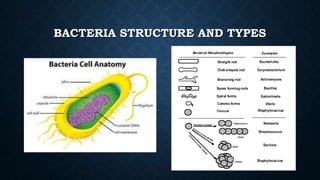
- Bacteria come in many types including autotrophs that produce their own food and heterotrophs that feed on organic material. They have cell walls and circular DNA.
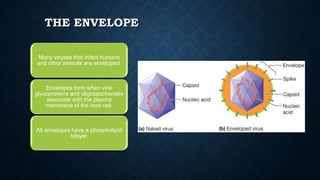
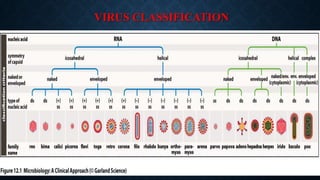
- Viruses have either DNA or RNA inside a protein coat and some have an additional envelope. They reproduce by taking over the machinery of living host cells. While viruses cause disease, some bacteria are useful in food webs, nitrogen fixation, and producing antibiotics.