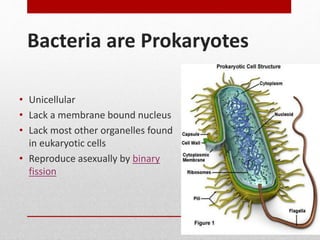
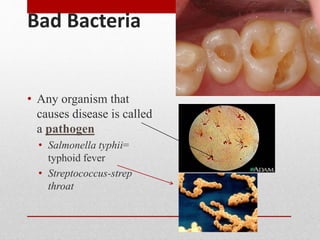
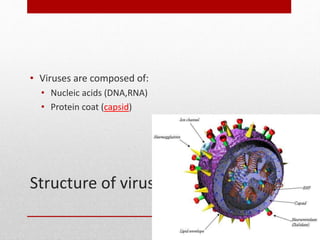
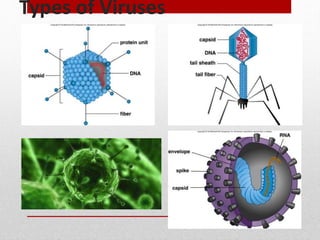
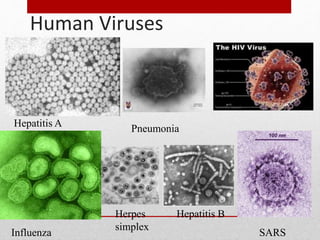
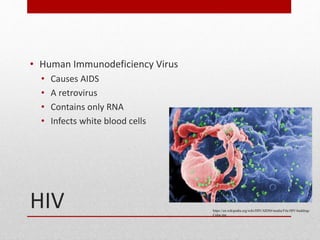
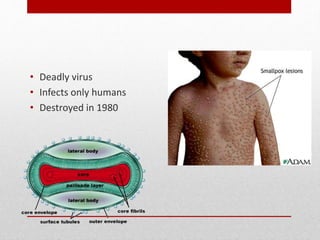
This document discusses viruses and bacteria. It defines bacteria as unicellular prokaryotes that lack organelles like a nucleus. Viruses are described as non-living particles that need a host to reproduce and are smaller than bacteria. The document lists some common human viruses including hepatitis A, influenza, herpes, and HIV. It explains that antibiotics only work on bacteria, not viruses, and how the immune system develops immunity through memory cells, helper T cells, and killer T cells to fight diseases. Vaccination is highlighted as the best way to build immunity against viruses.