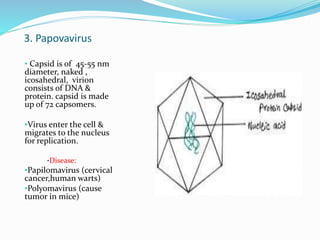
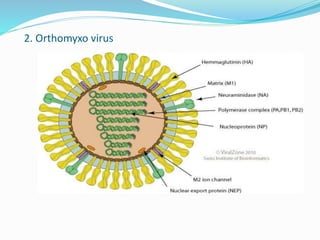
Animal viruses are intracellular parasites that depend on host cells for replication, classified into seven groups based on their nucleic acid and transcription methods. Examples include dsDNA viruses like adenoviruses and herpes viruses, which can cause various diseases such as respiratory illness and chickenpox. Other virus groups include ssDNA, (+) ssRNA, (−) ssRNA, dsRNA, and reverse-transcribing viruses, each associated with specific viral characteristics and diseases.