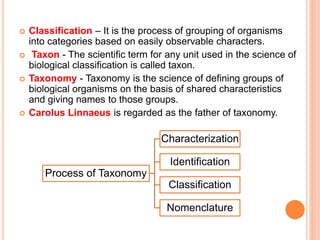
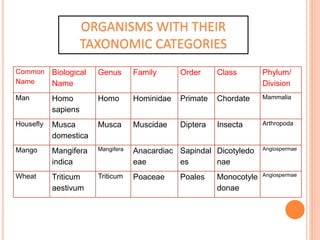
The document discusses the key characteristics of living things such as growth, reproduction, metabolism, and response to stimuli. It also covers the basics of biology, taxonomy, and classification. The levels of taxonomic classification from lowest to highest are species, genus, family, order, class, phylum/division, and kingdom. Herbaria, botanical gardens, museums, zoological parks, and keys are described as important taxonomic aids.