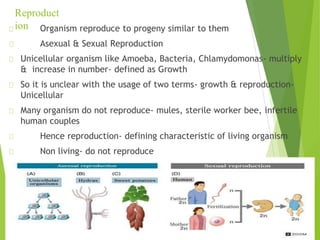
The document discusses the characteristics of living organisms, including growth, reproduction, metabolism, and consciousness, establishing these as defining features of life. It also elaborates on biodiversity and the necessity for classification, which is achieved through systematic nomenclature and taxonomy, providing a structured hierarchy for understanding the relationships among various organisms. Key terminology and principles of classification, such as binomial nomenclature and taxonomic hierarchy, are explained to emphasize the organization of living entities into their respective categories.