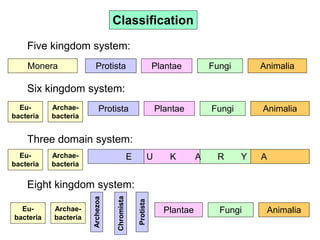
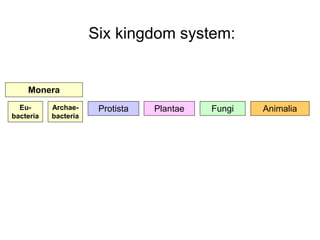
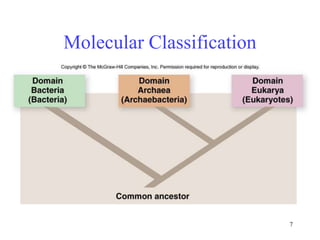
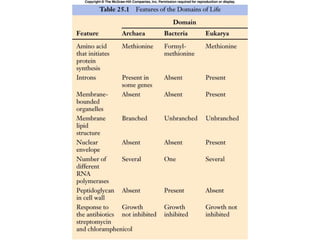
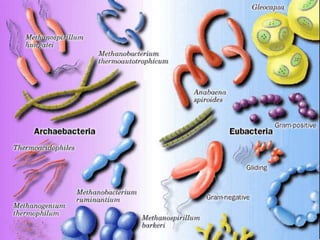
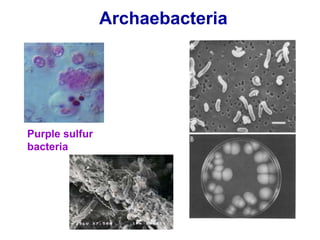
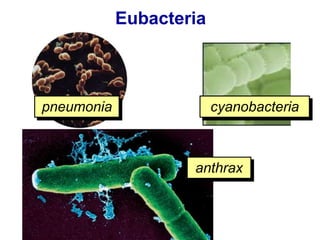
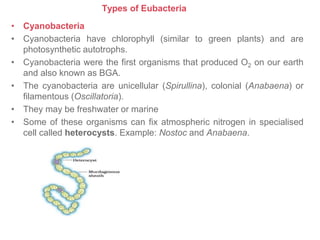
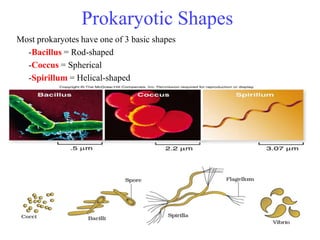
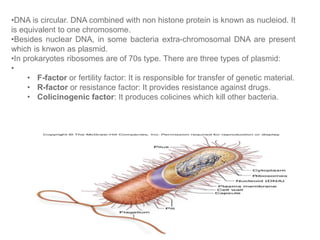
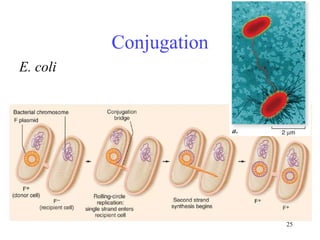
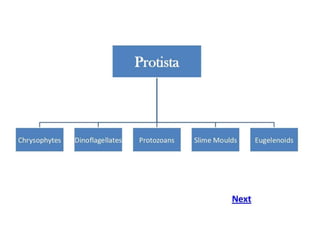
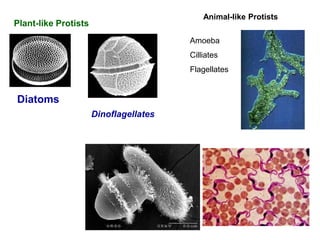
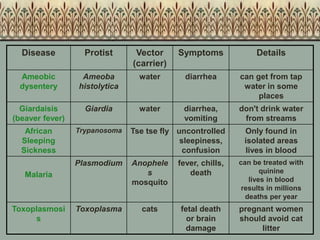
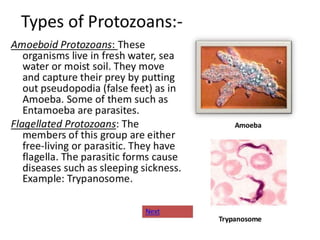
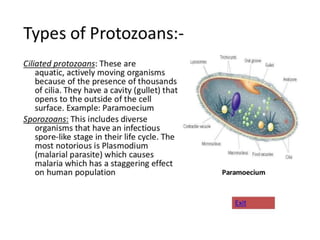
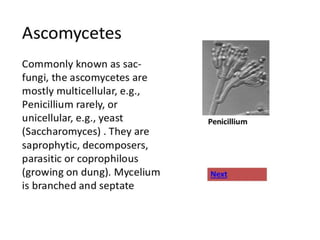
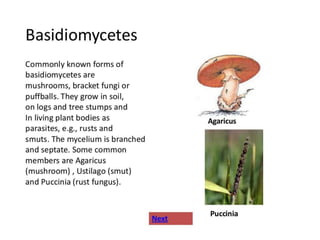
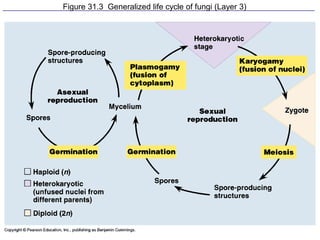
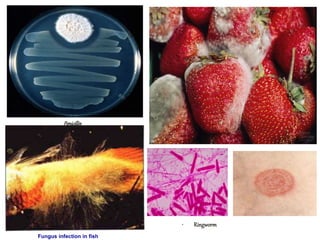
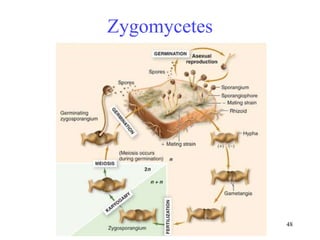
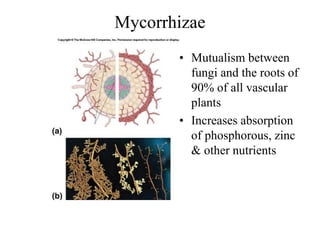
Biological classification involves the study and organization of organisms into a hierarchy of groups and taxa based on their evolutionary relationships and distinguishing characteristics. The main goals are to identify all organisms and determine their evolutionary history. Carl Linnaeus developed the binomial naming system in the 1700s that is still used today. There are several systems that have been proposed to classify life, with newer systems incorporating molecular evidence to revise the evolutionary relationships between domains, kingdoms, and taxa. Prokaryotes like bacteria and archaea are classified based on characteristics like shape, metabolism, and environment. Eukaryotes like protists, fungi, plants and animals are organized into domains, kingdoms and smaller taxa.