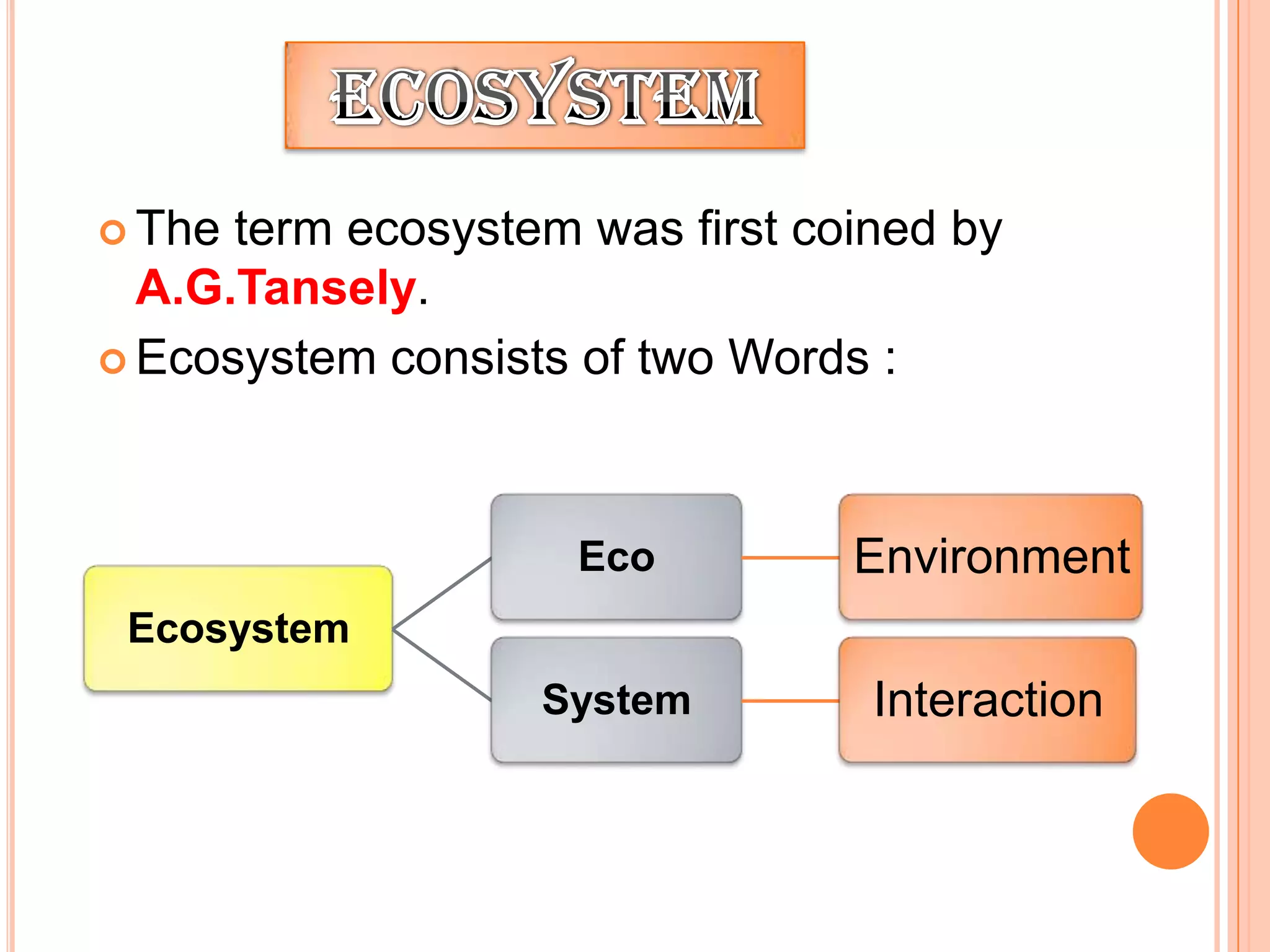
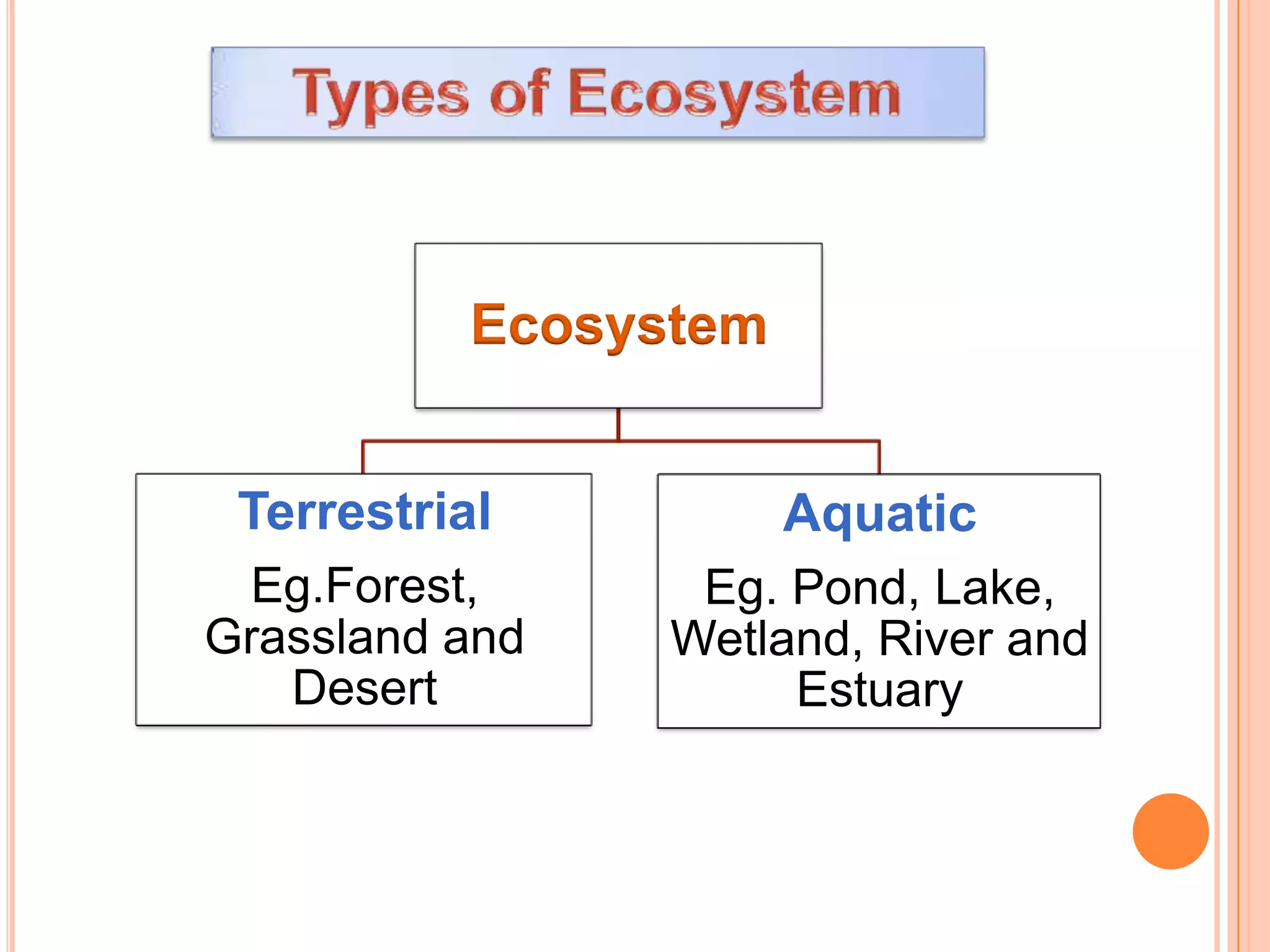
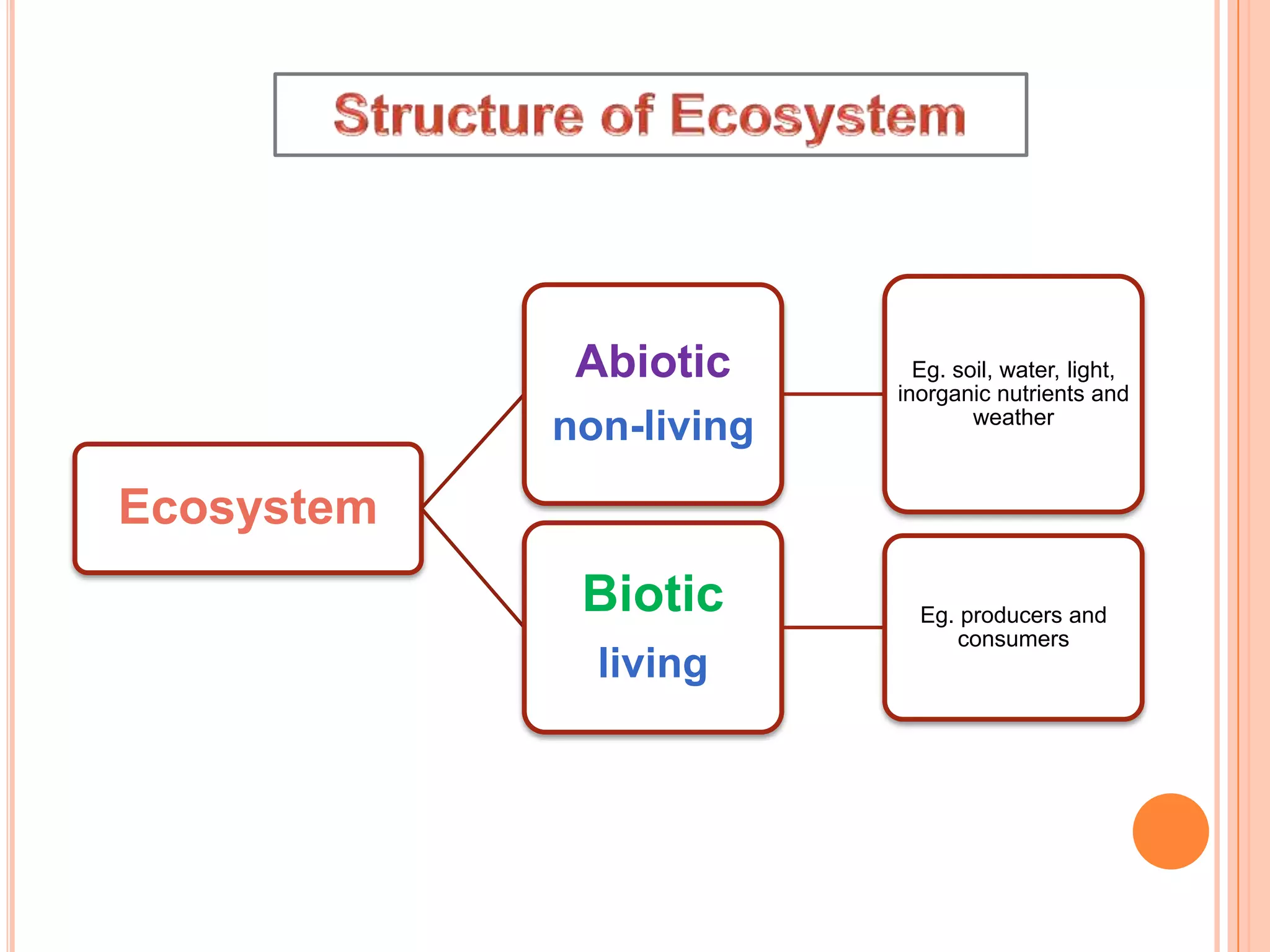
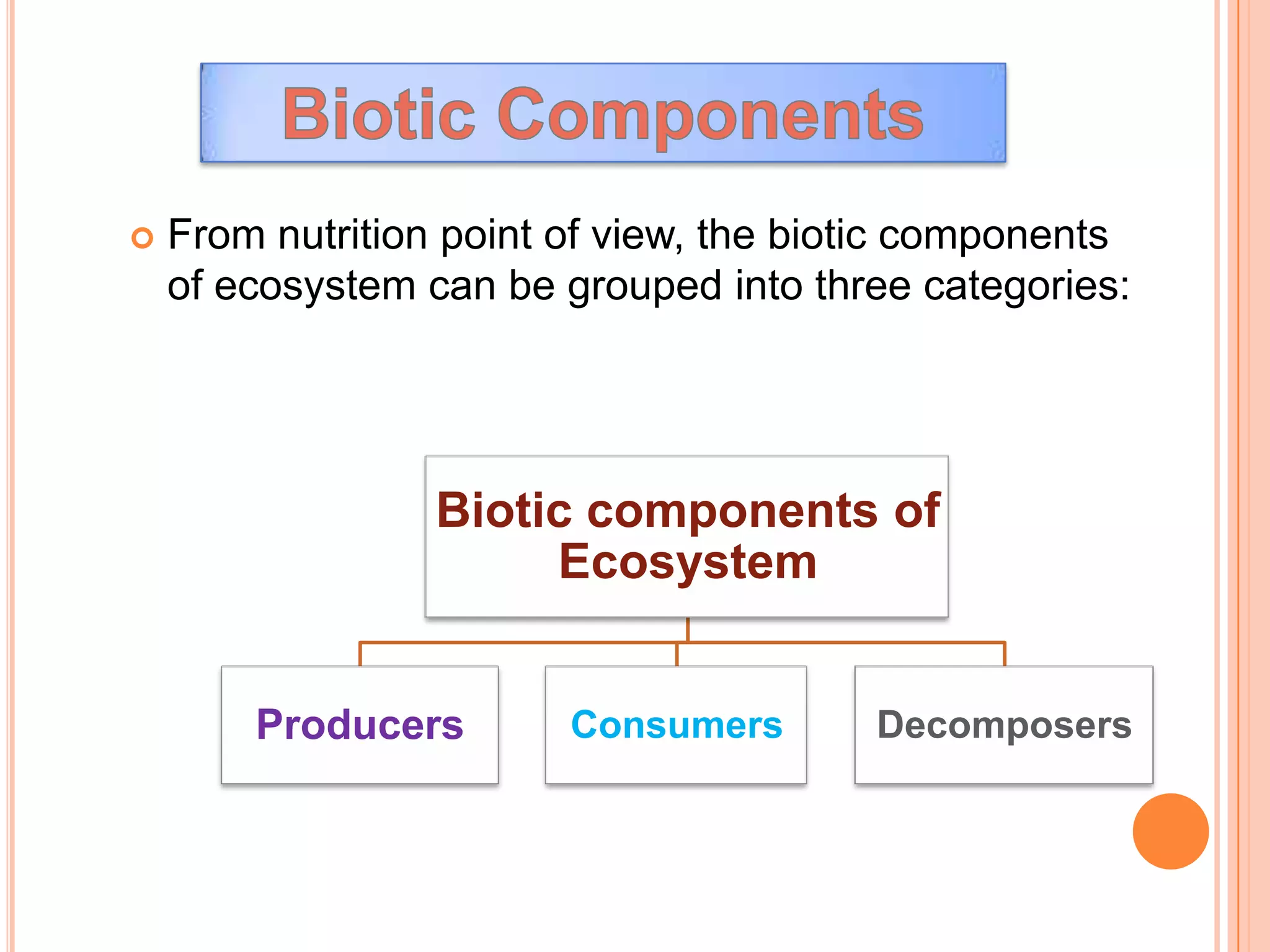
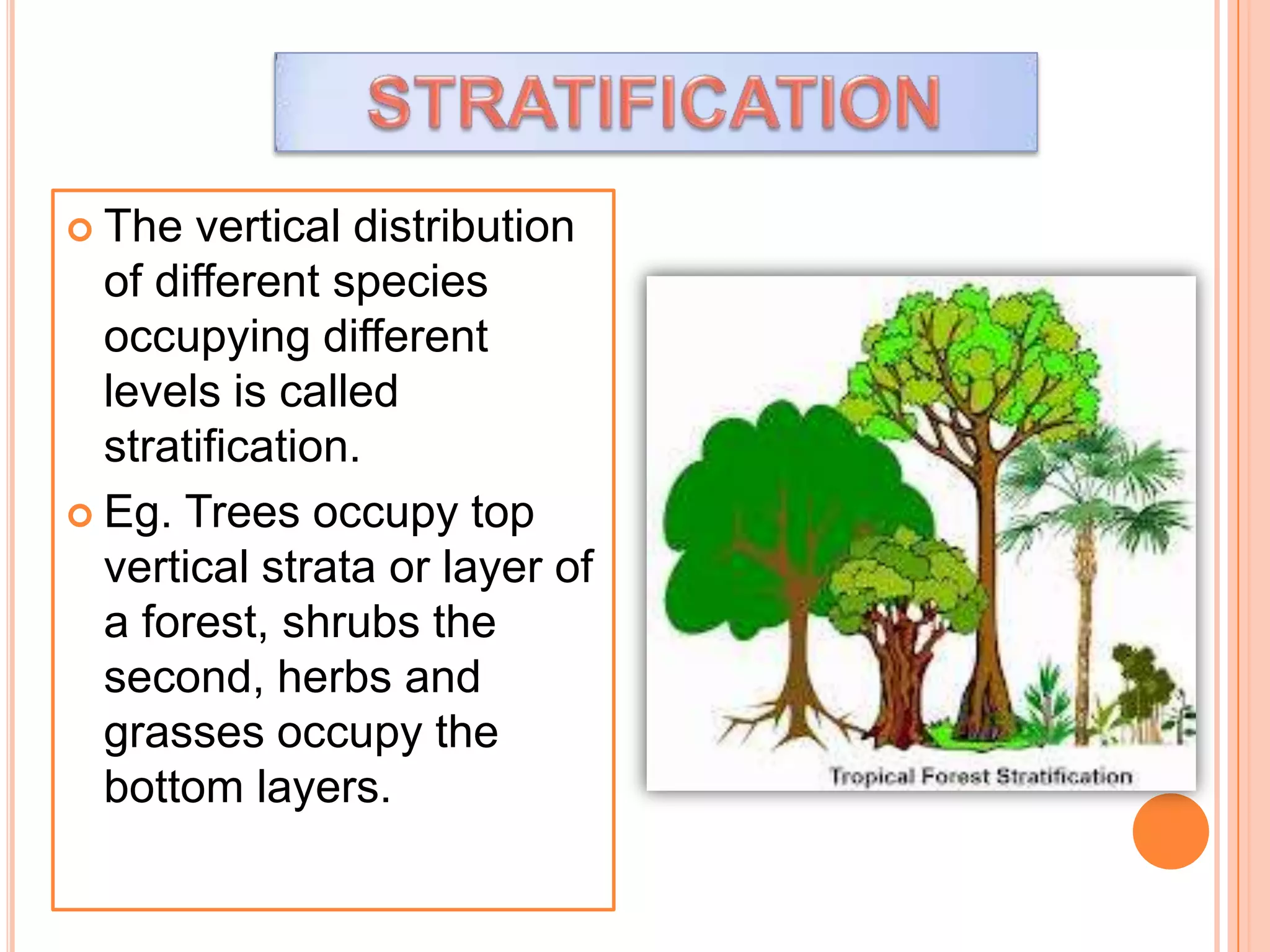
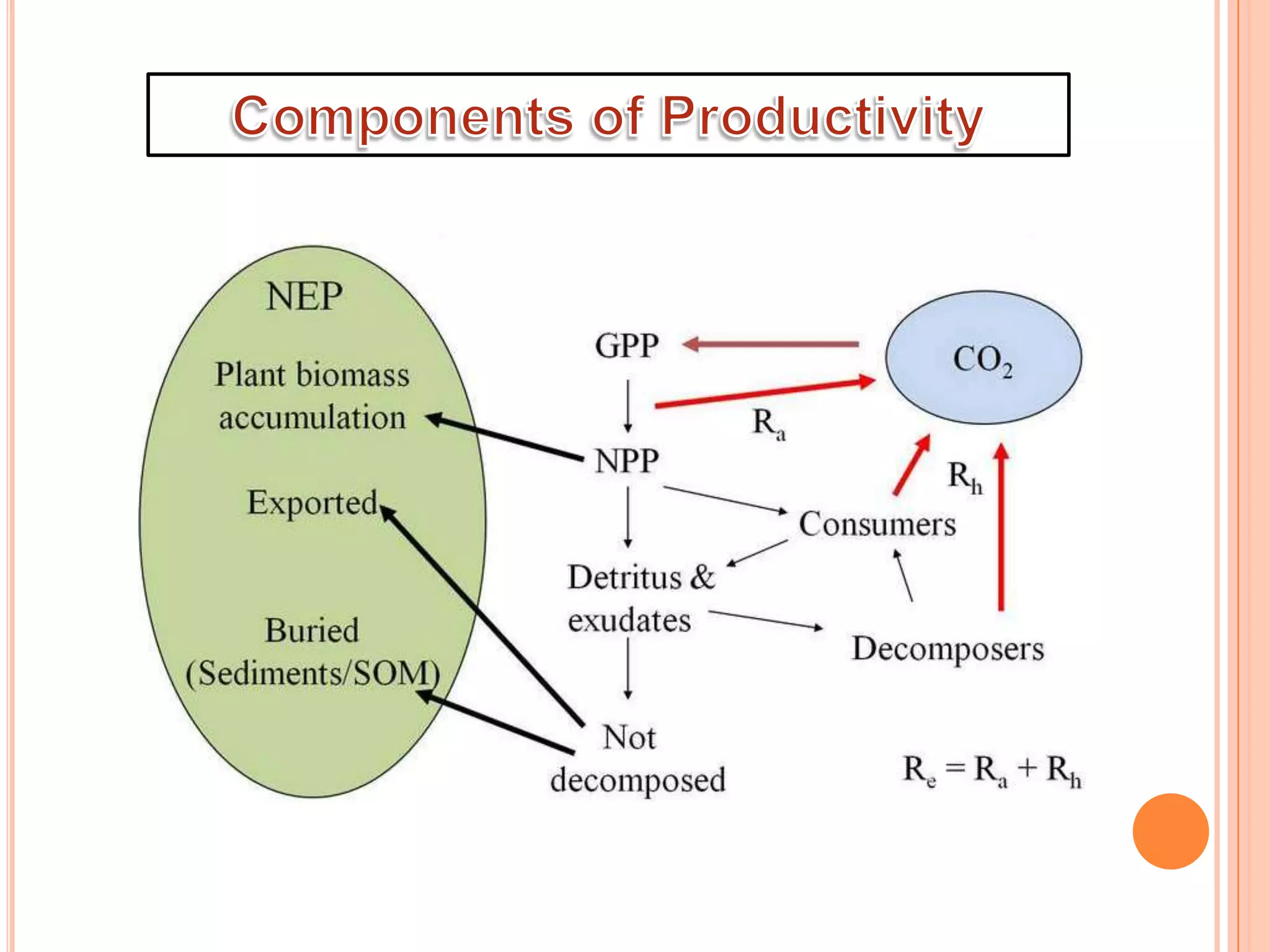
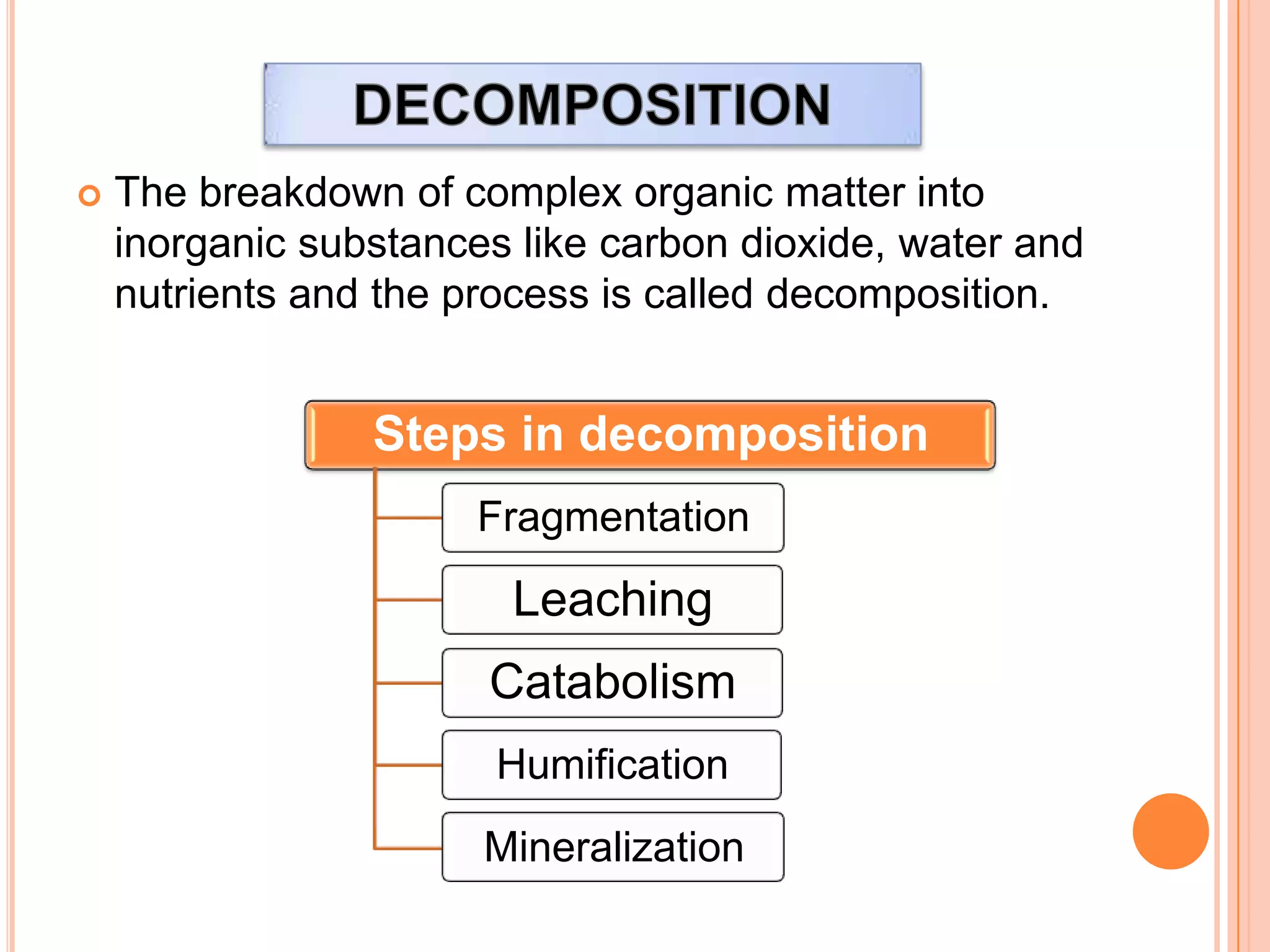
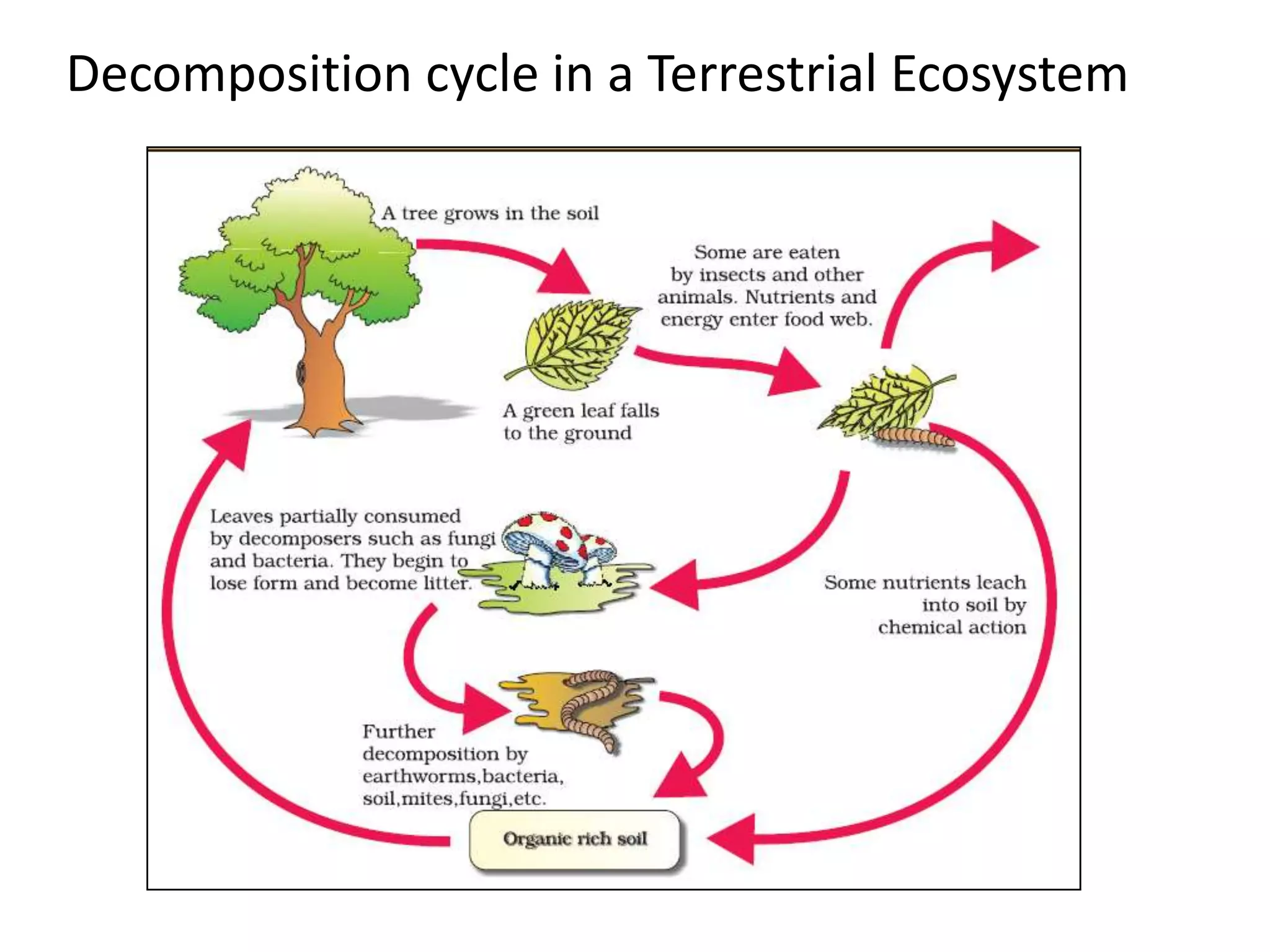
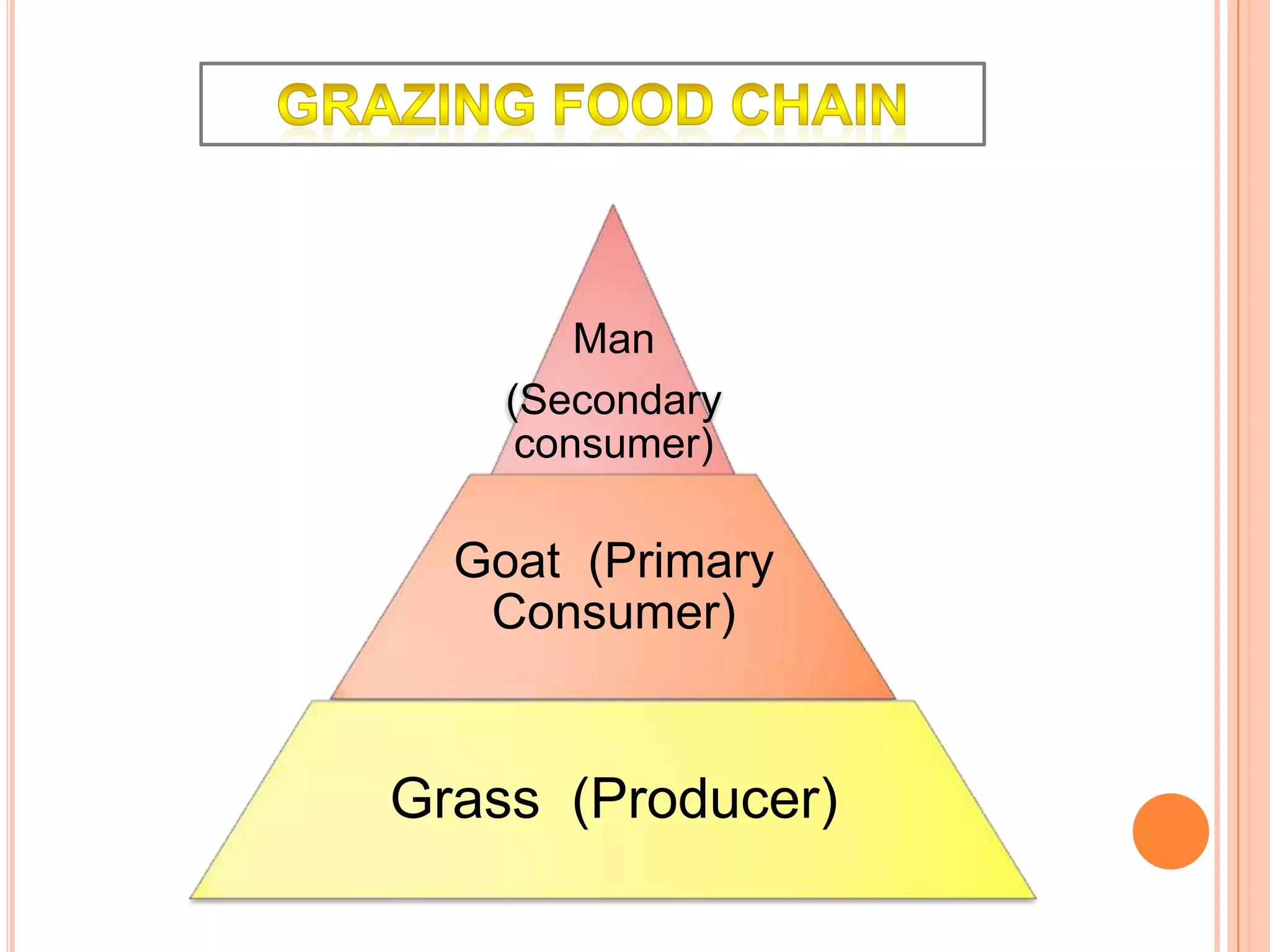
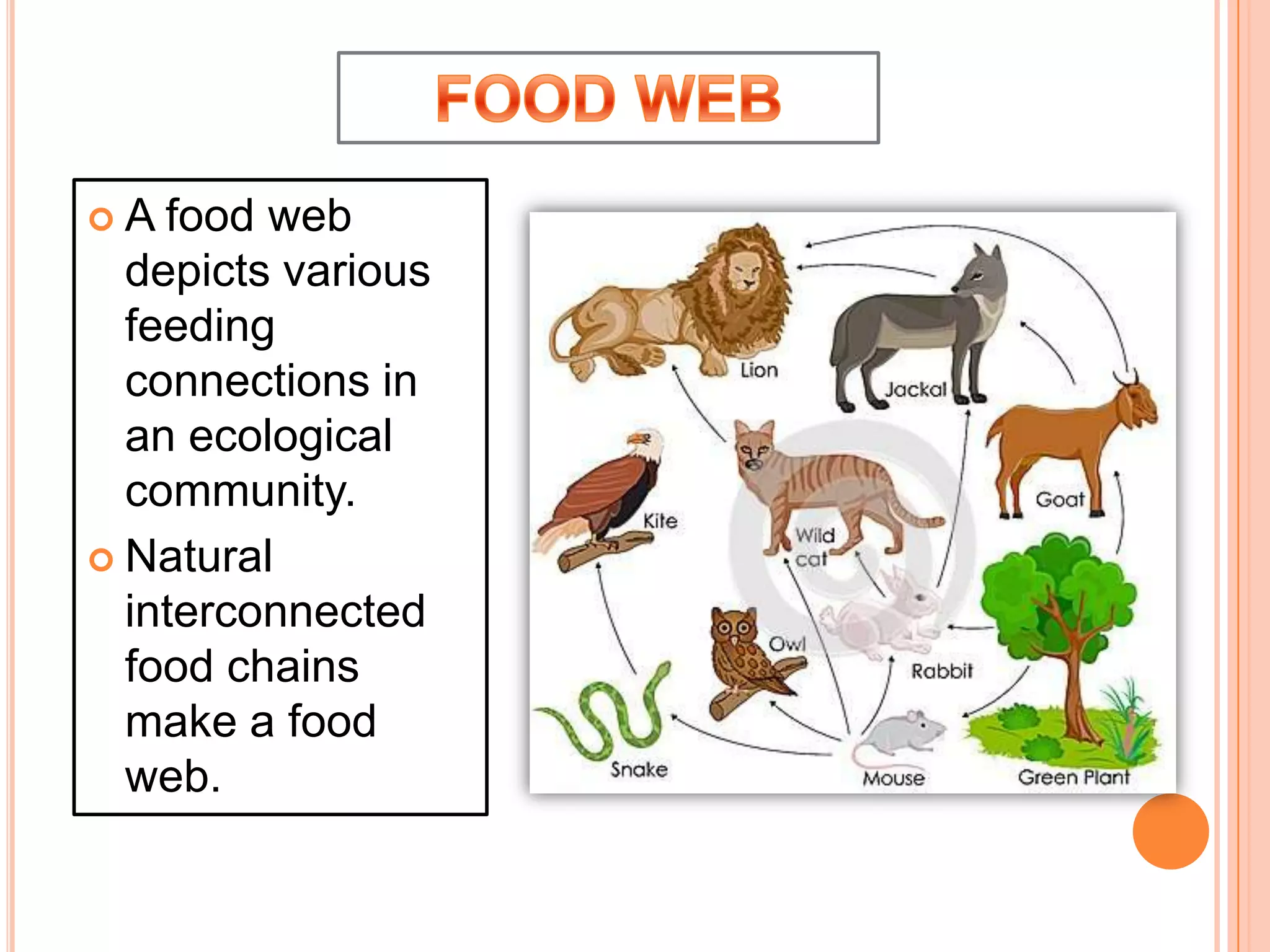
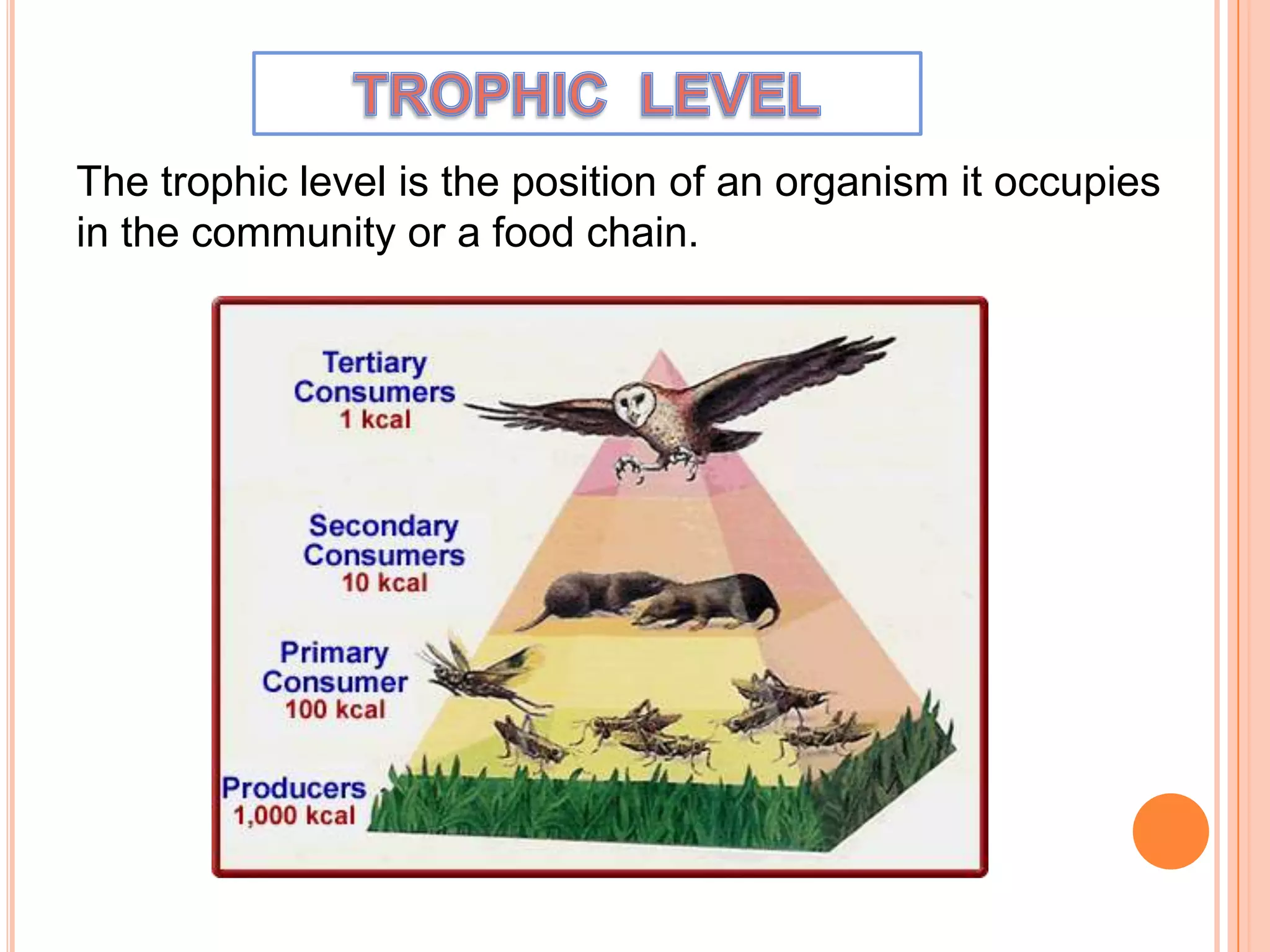
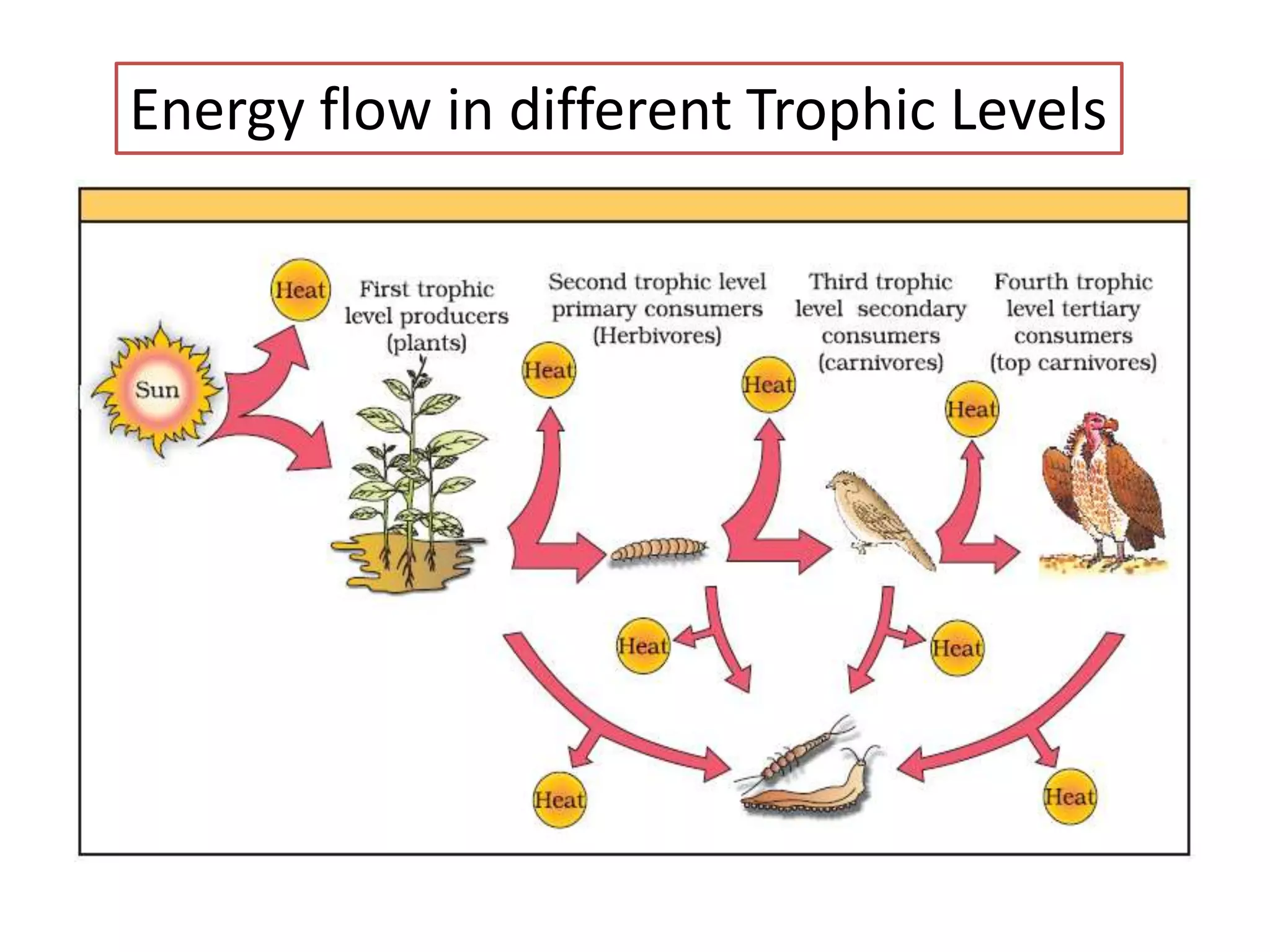
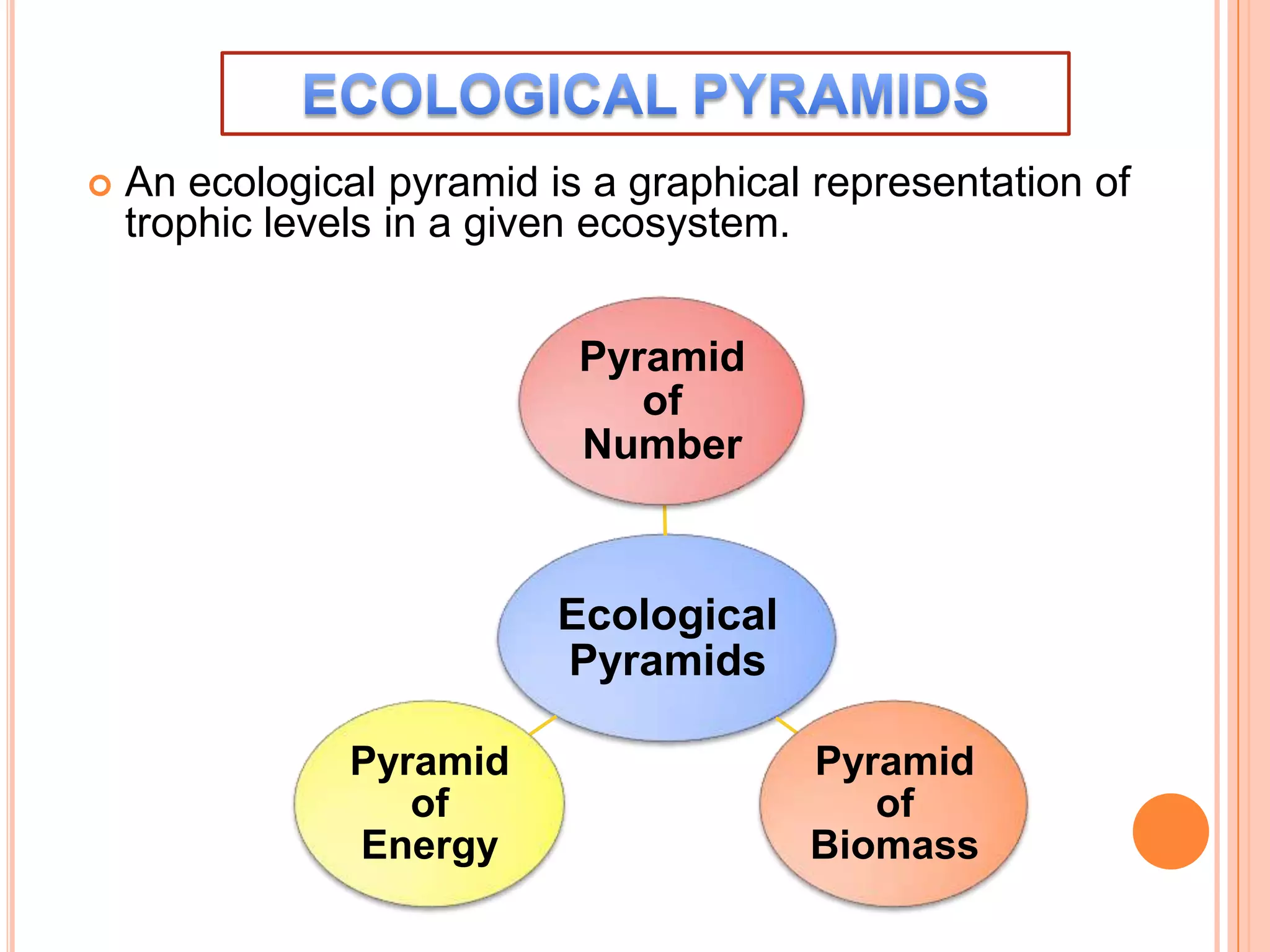
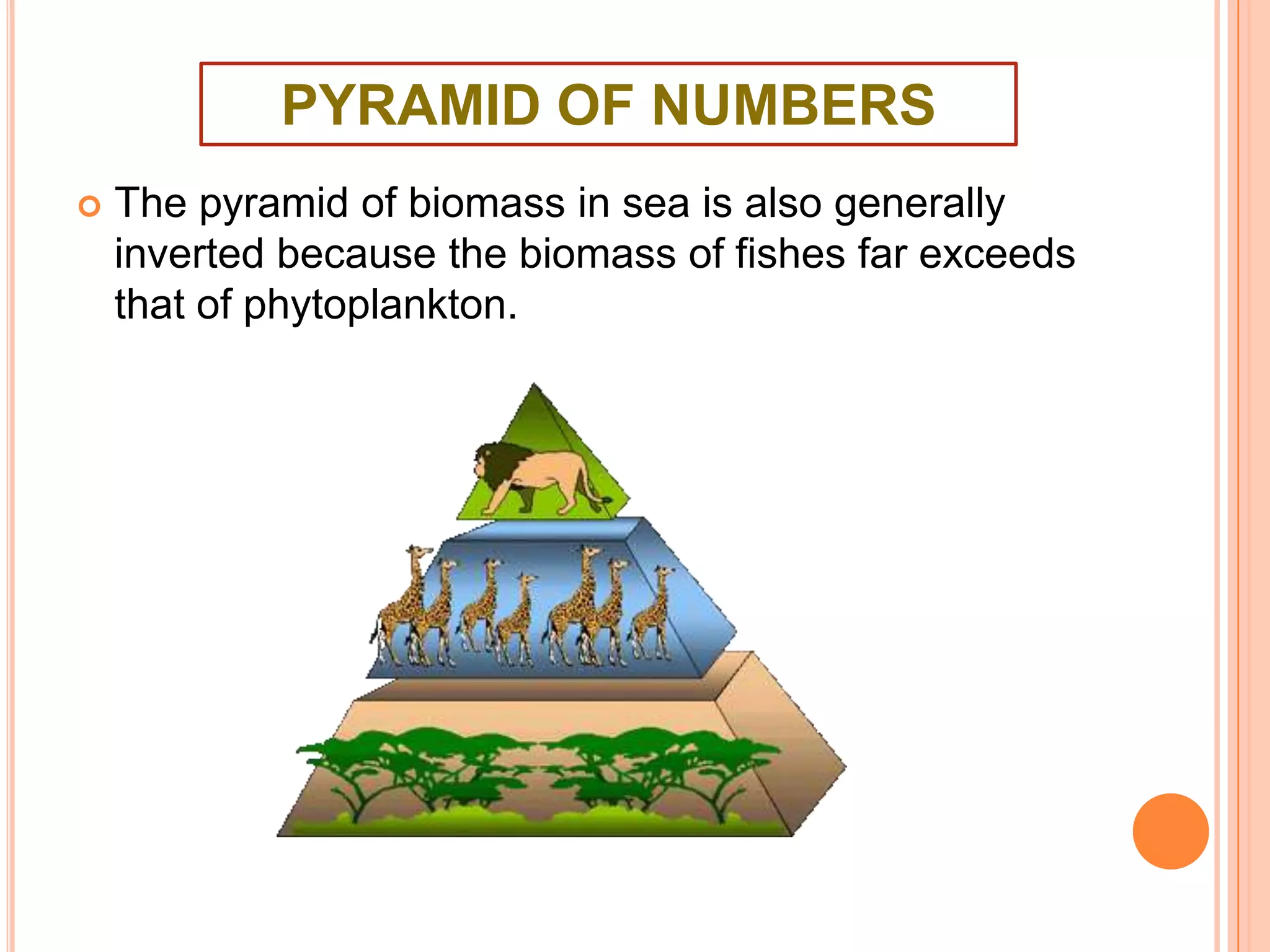
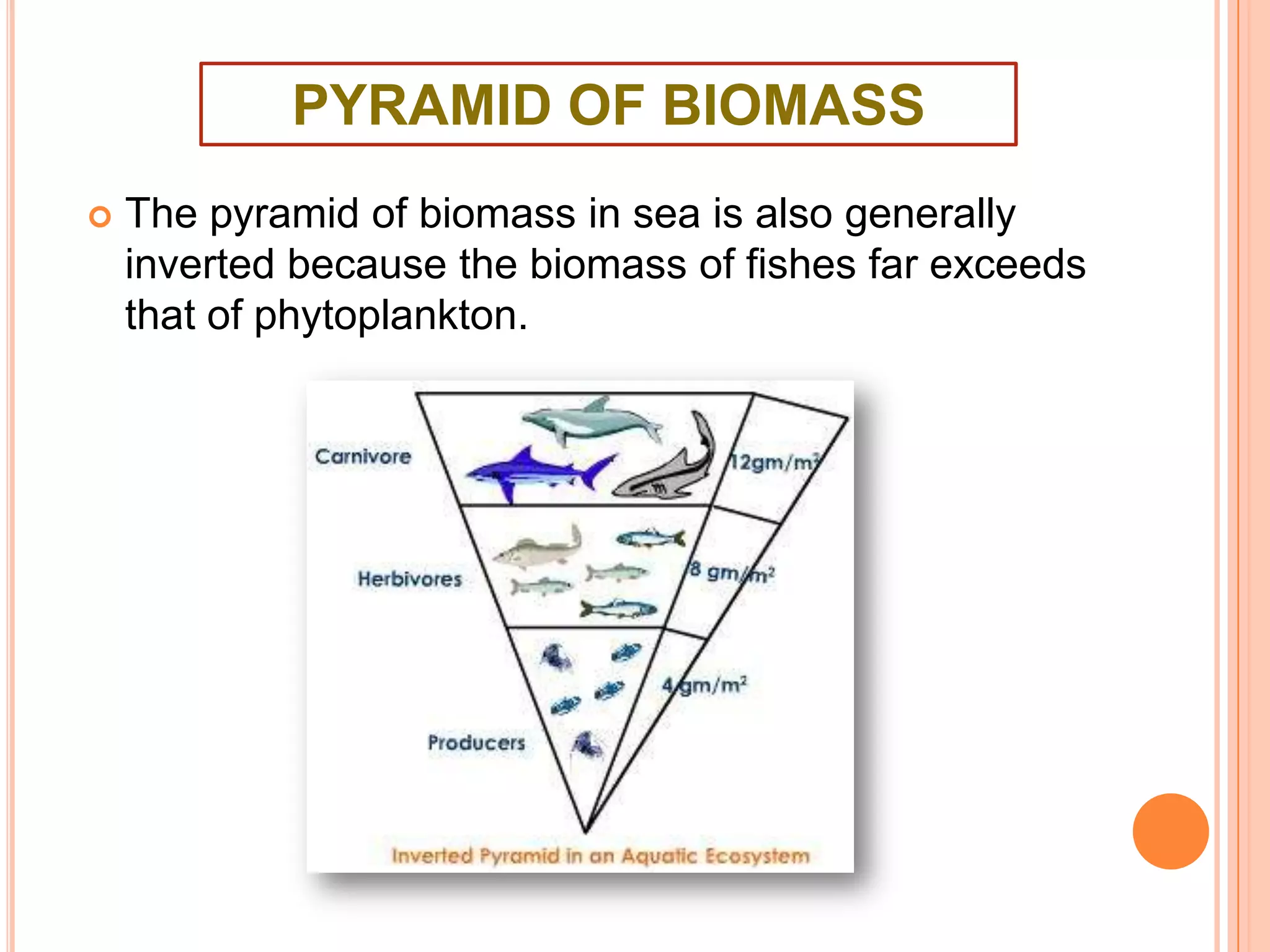
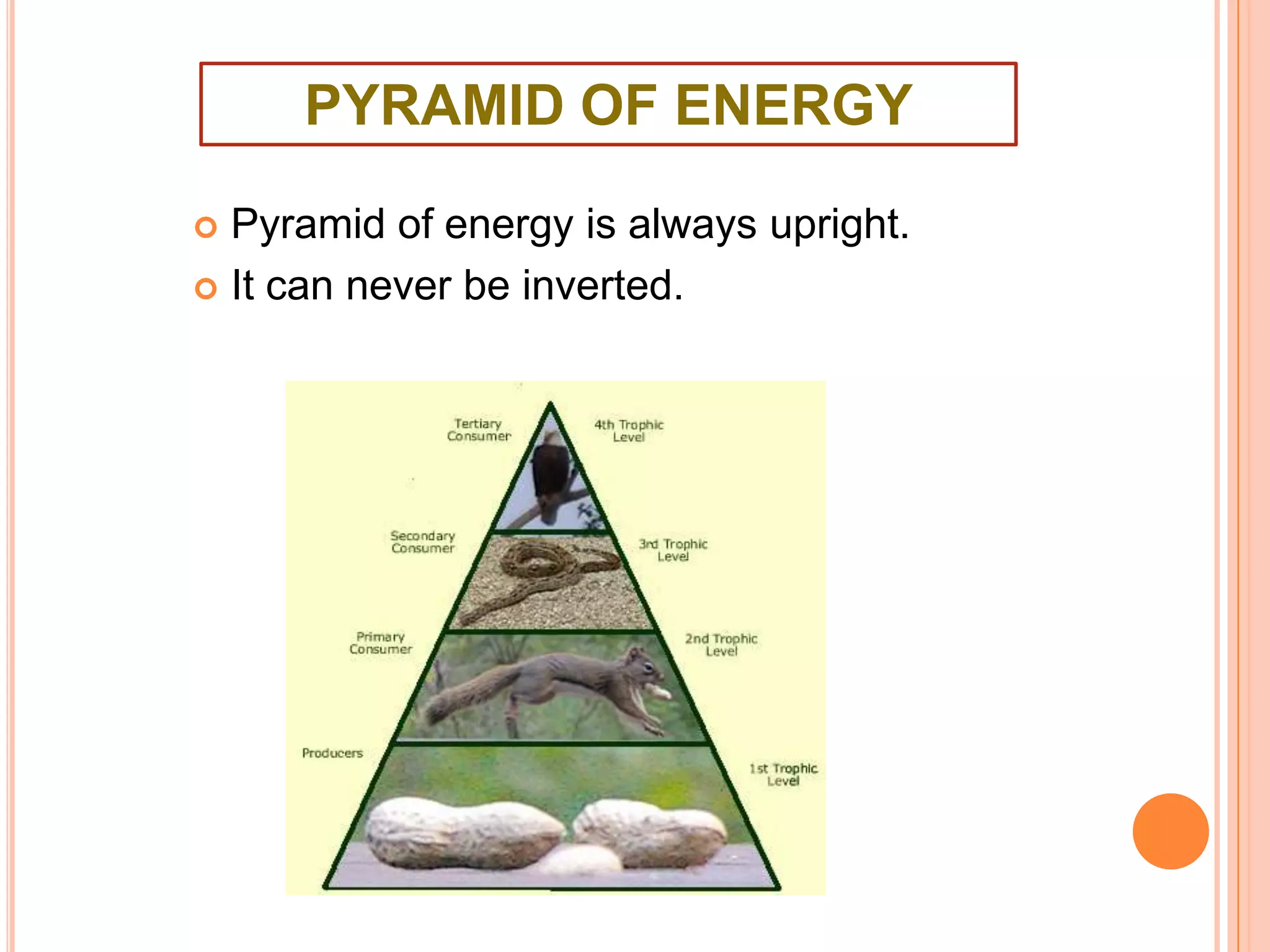
The document defines key terms related to ecosystems, including that an ecosystem was first defined by A.G. Tansley as the basic functional unit of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. It provides examples of different ecosystem types, such as grasslands, forests, and oceans. Within ecosystems, biotic components include producers, consumers, and decomposers. Energy flows through ecosystems from producers to higher trophic levels, and nutrients cycle through ecosystems via processes like decomposition. Ecological pyramids illustrate the structure of ecosystems by trophic level.