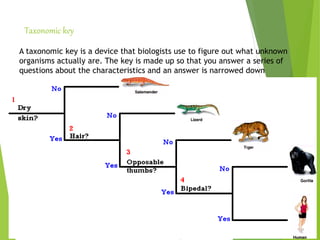
This document discusses the key characteristics of living organisms and principles of taxonomy and classification. It outlines the five defining characteristics of living organisms as growth, reproduction, metabolism, cellular organization, and response to stimuli. It then discusses the principles of taxonomy, including the need for classification and binomial nomenclature. The major taxonomic categories from species to kingdom are defined. Various taxonomic aids that help in identification and classification of organisms, such as herbaria, botanical gardens, museums, and zoological parks are also outlined.