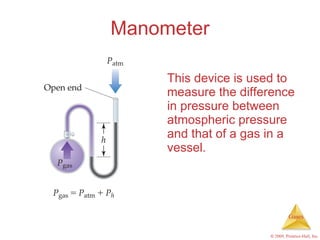
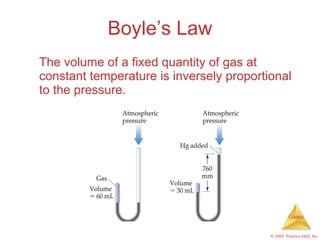
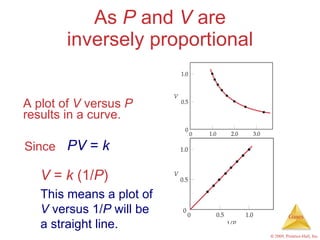
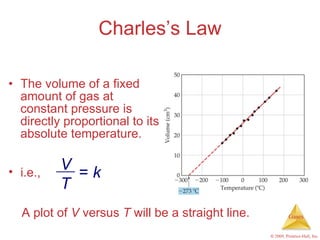
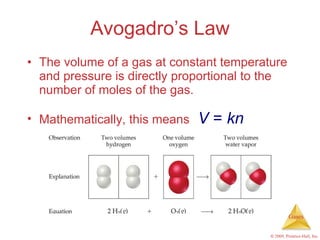
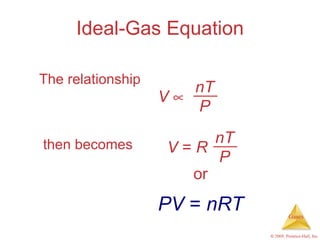
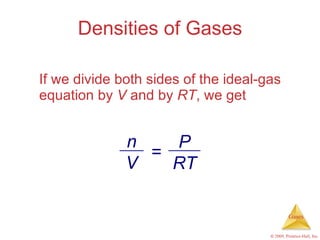
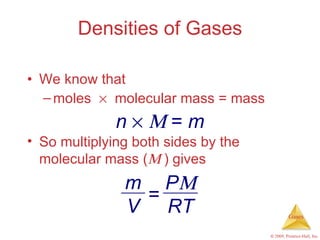
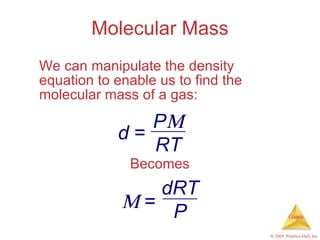
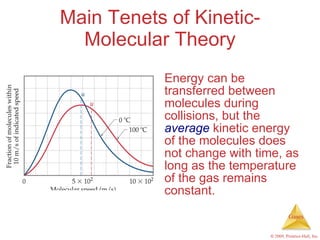
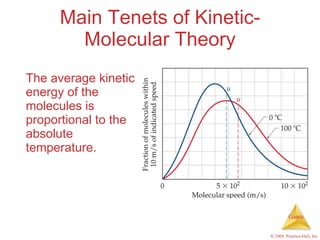
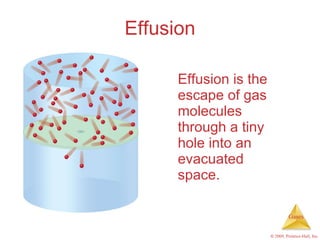
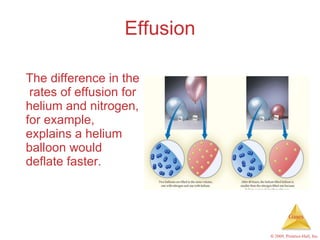
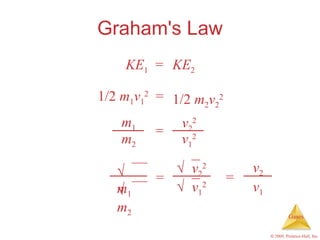
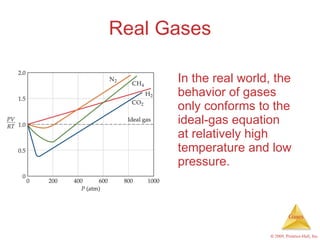
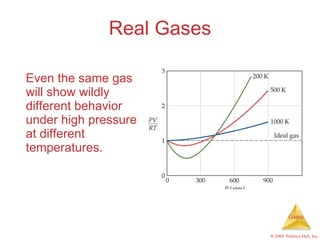
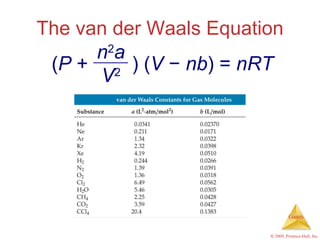
Gases are highly compressible and expand to fill their containers, with pressure inversely proportional to volume according to Boyle's Law. The properties and behavior of gases can be explained by the kinetic molecular theory, which models gases as large numbers of molecules in random motion. Real gases deviate from ideal gas behavior at high pressures and low temperatures due to intermolecular forces and molecular volumes.