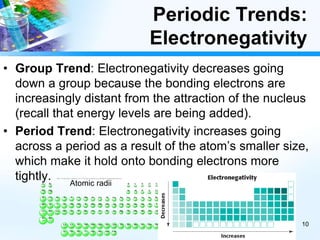
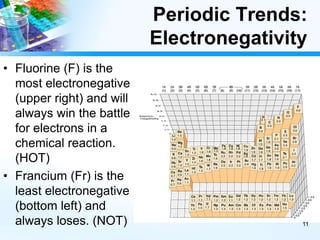
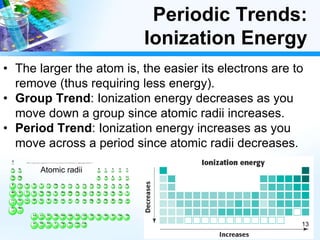
The document discusses periodic trends in chemical and physical properties revealed by the periodic table. It examines six key trends: atomic number, atomic mass, atomic radius, electronegativity, ionization energy, and reactivity. For each trend, it describes how the property changes as you move down groups or across periods on the periodic table, enabling predictions about an element's chemical behavior.