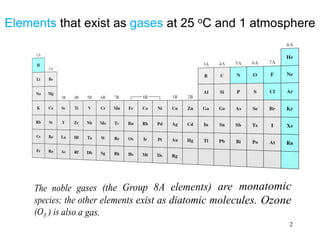
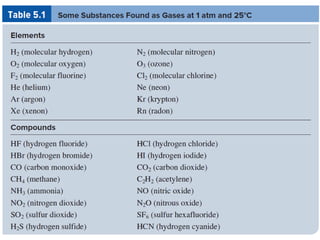
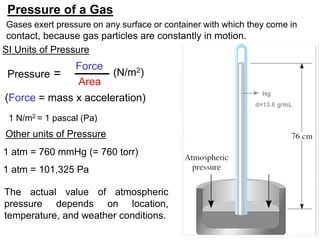
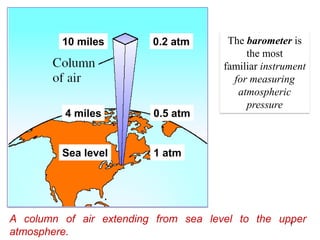
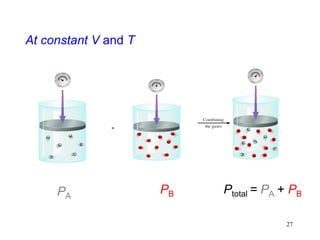
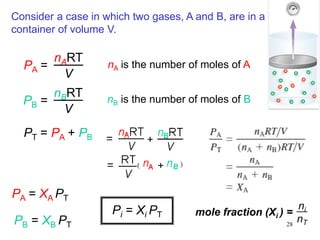
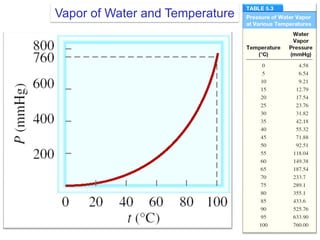
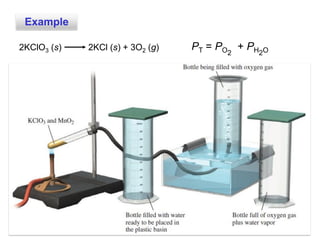
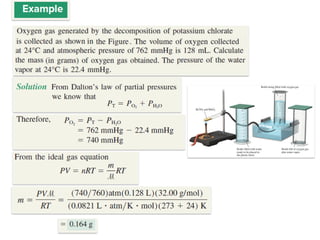
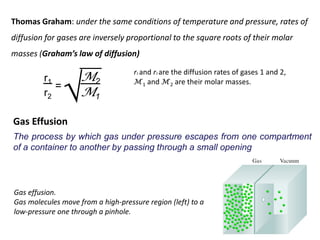
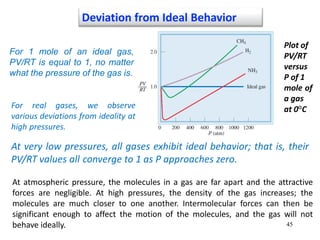
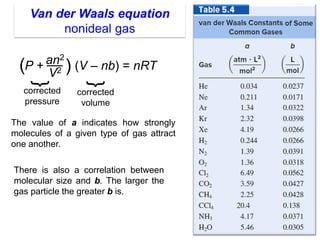
1. Gases have no definite shape or volume but take the shape of their container. Gas particles are in constant random motion and collide with each other and the container walls.
2. The kinetic molecular theory provides an explanation for gas behavior at the molecular level. It states that gas particles are in constant random motion and exert pressure due to collisions with container walls.
3. The gas laws describe the macroscopic behavior of gases through relationships between pressure, volume, temperature, and amount of gas. The kinetic molecular theory qualitatively explains the gas laws based on gas particle motion and interactions.