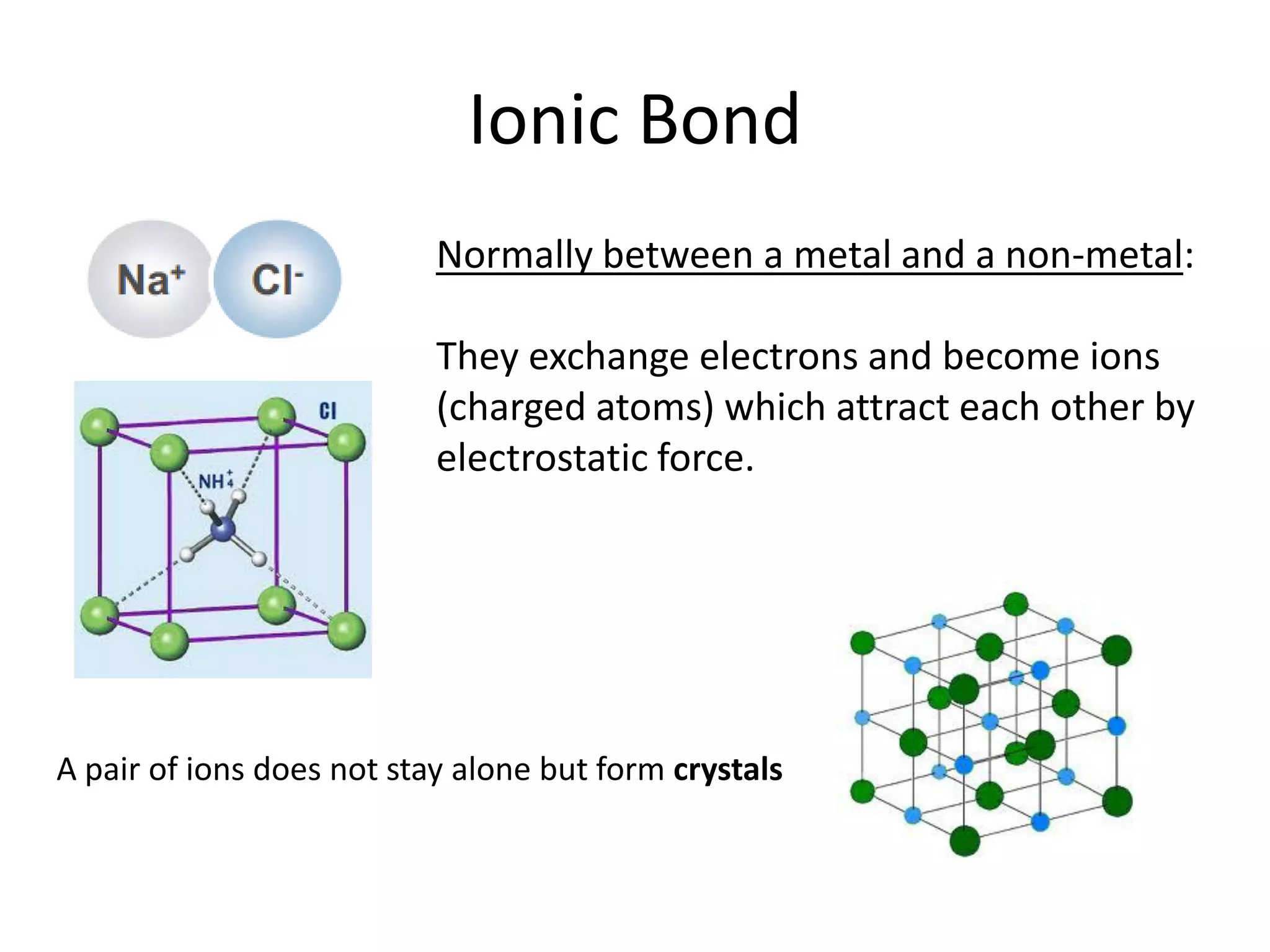
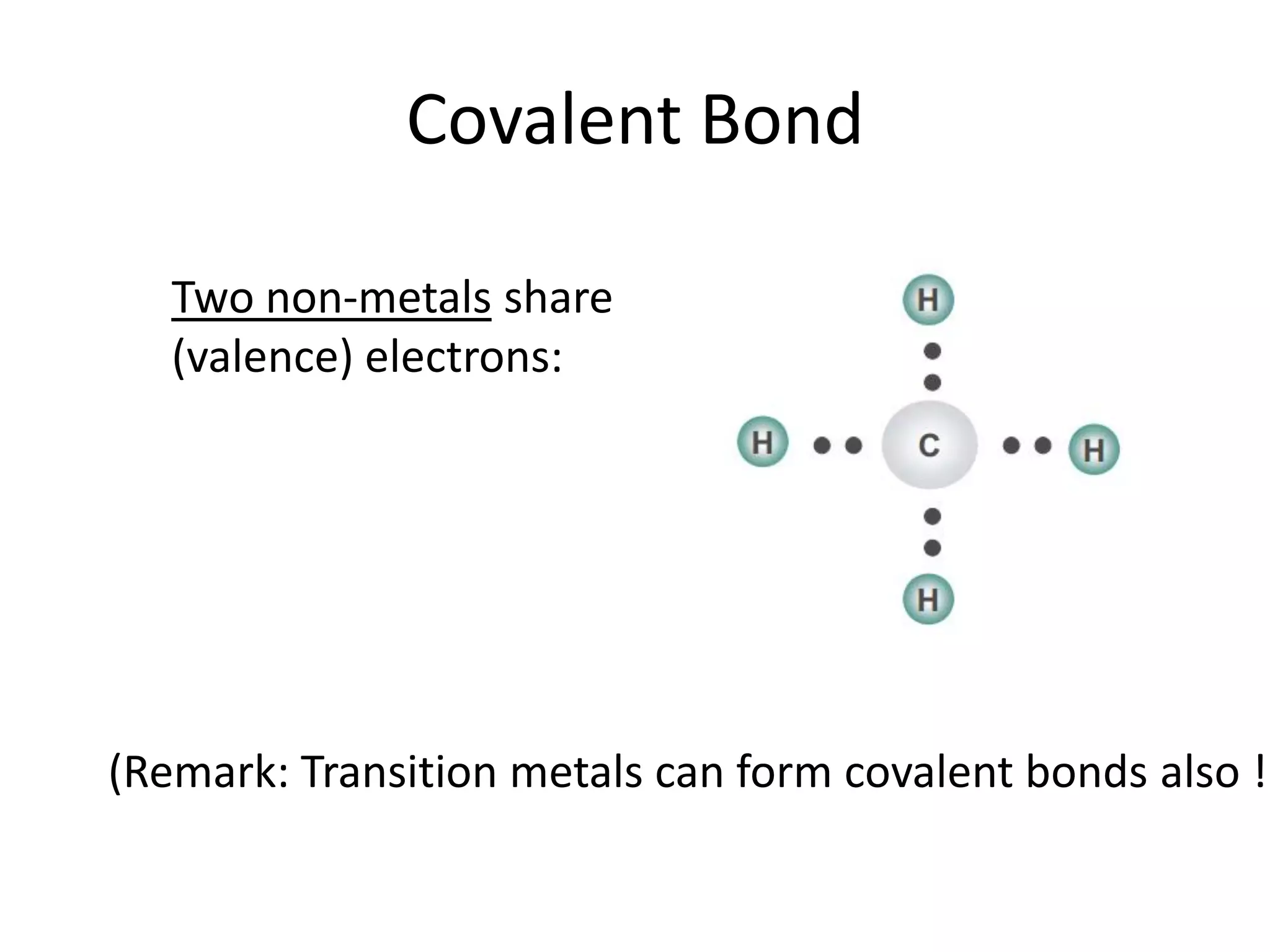
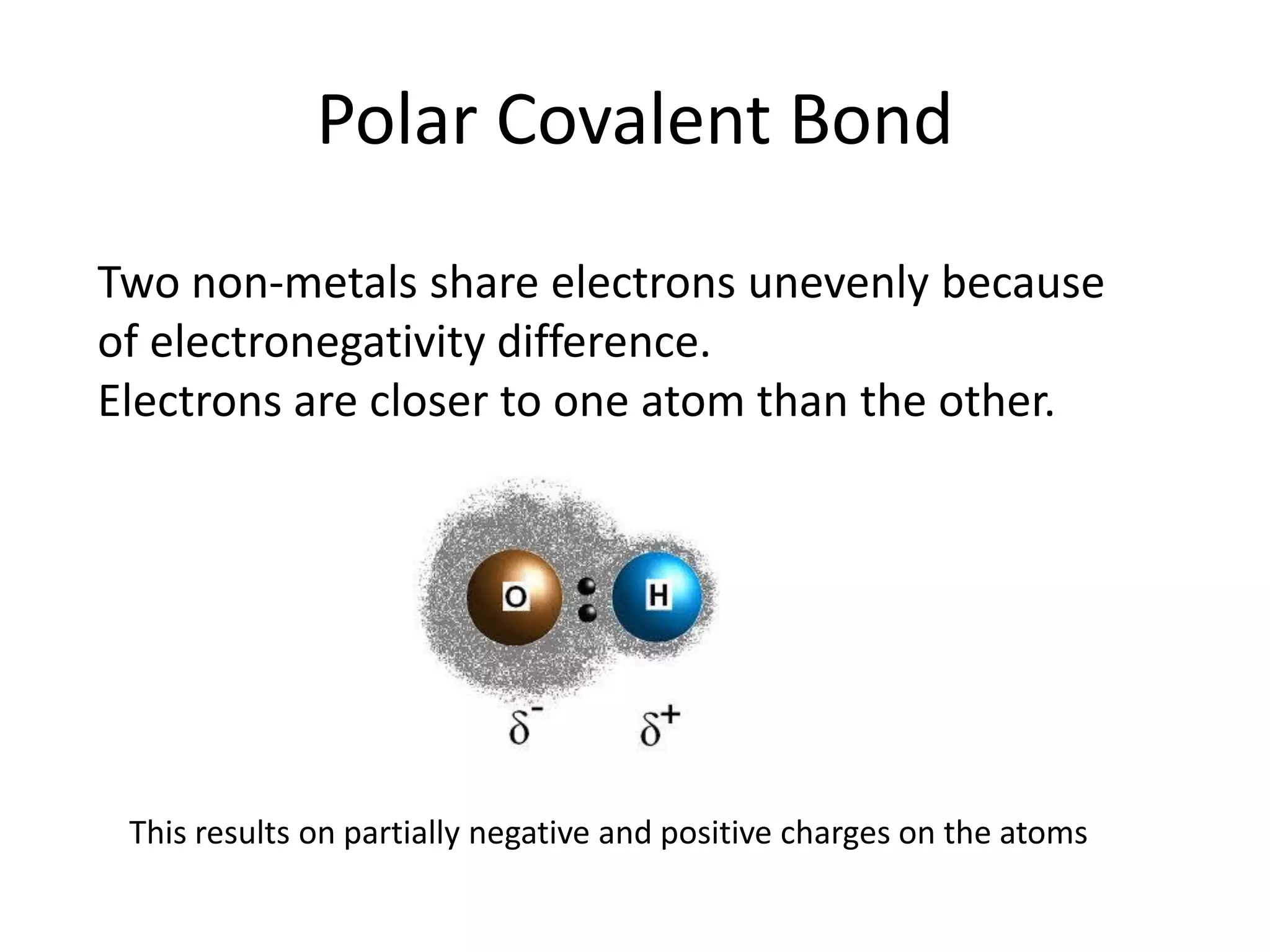
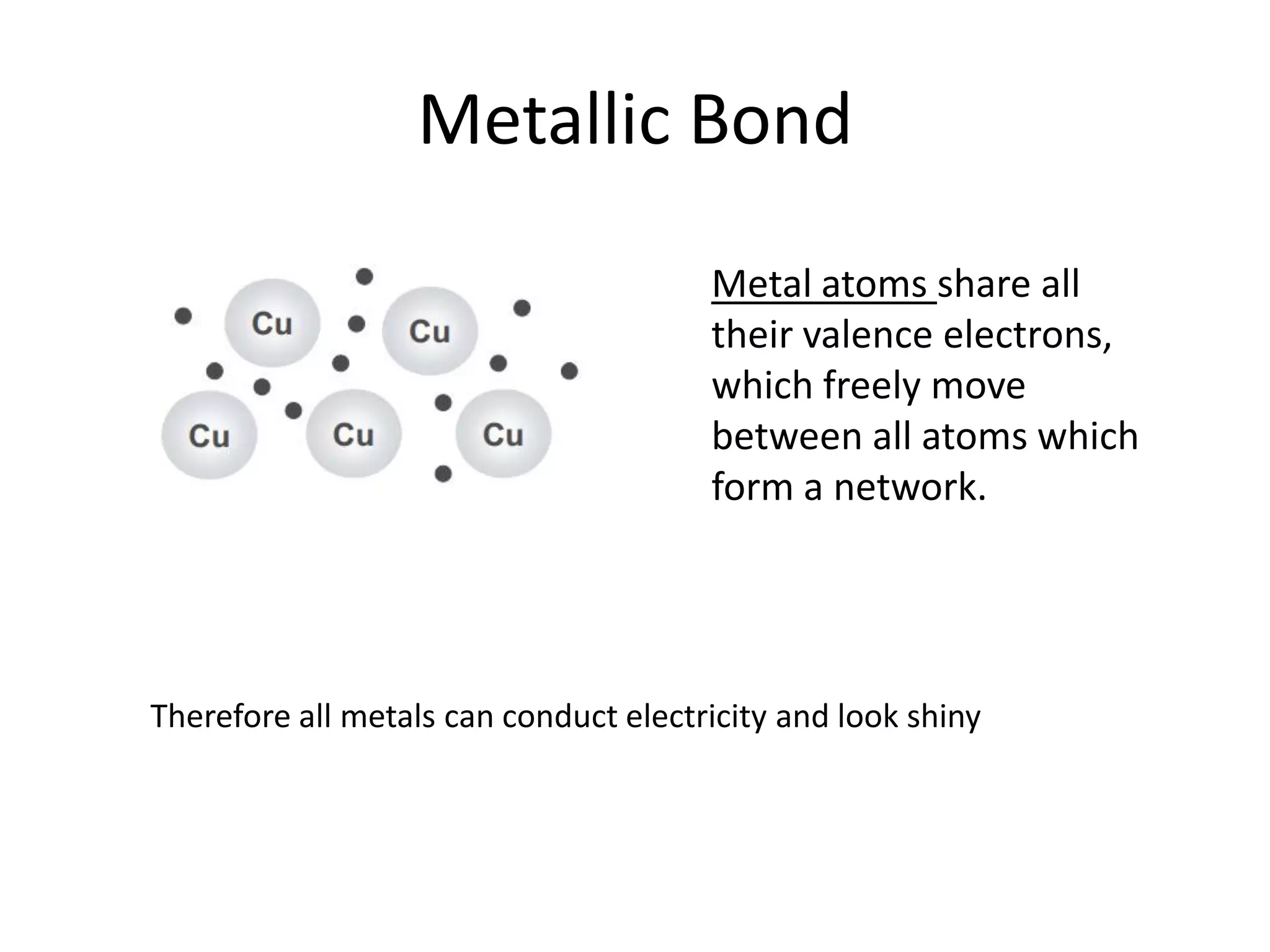
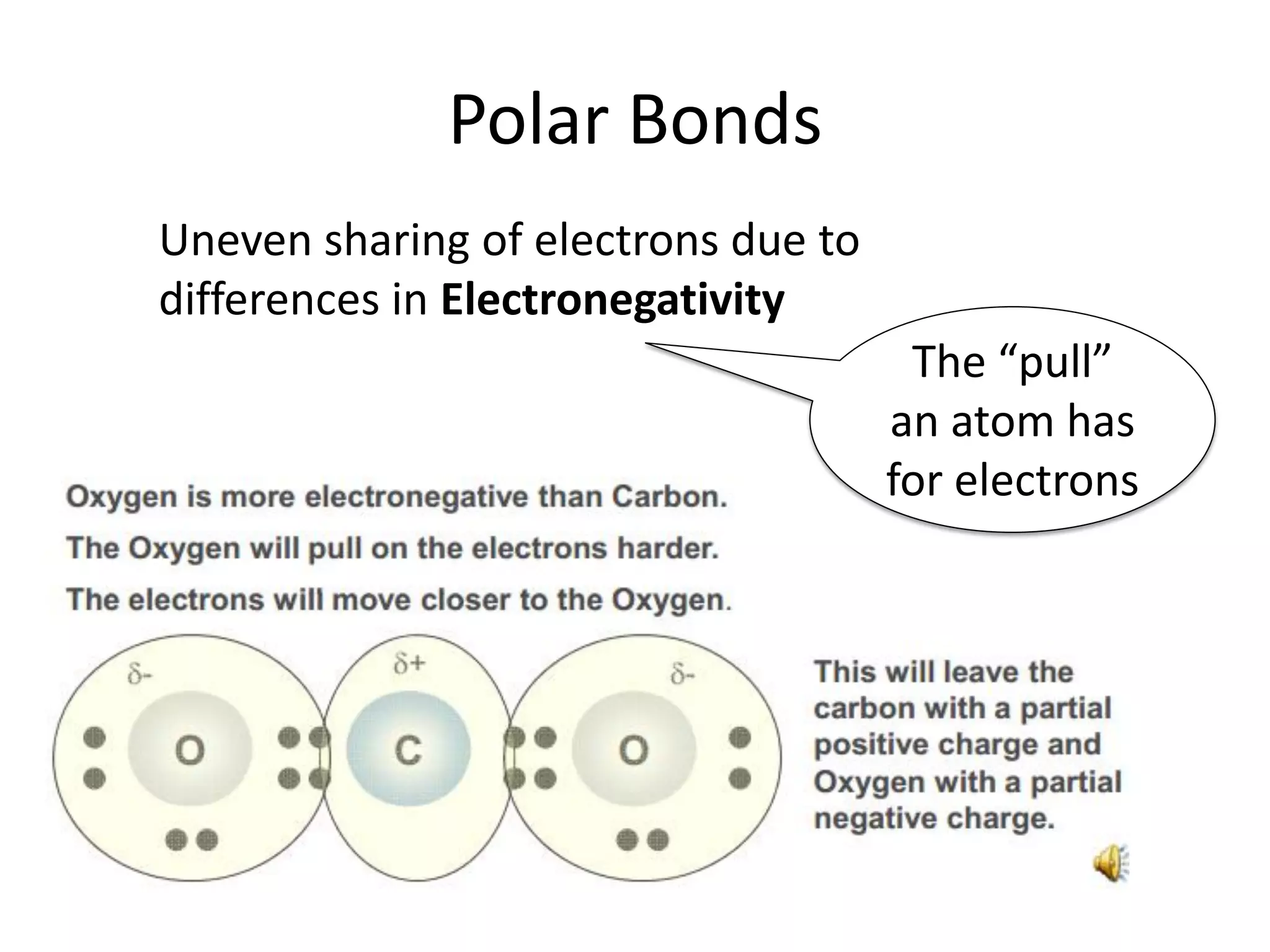
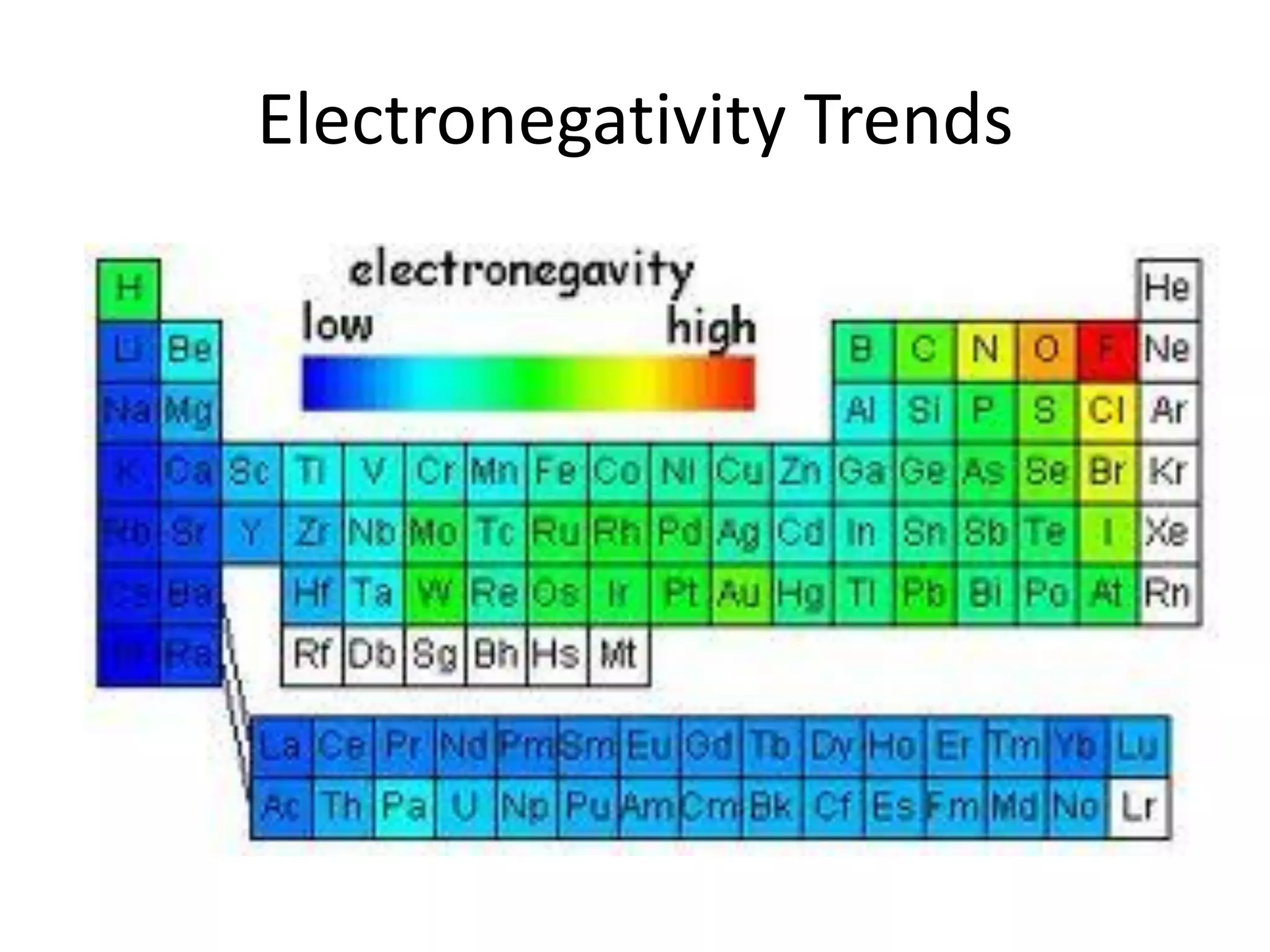
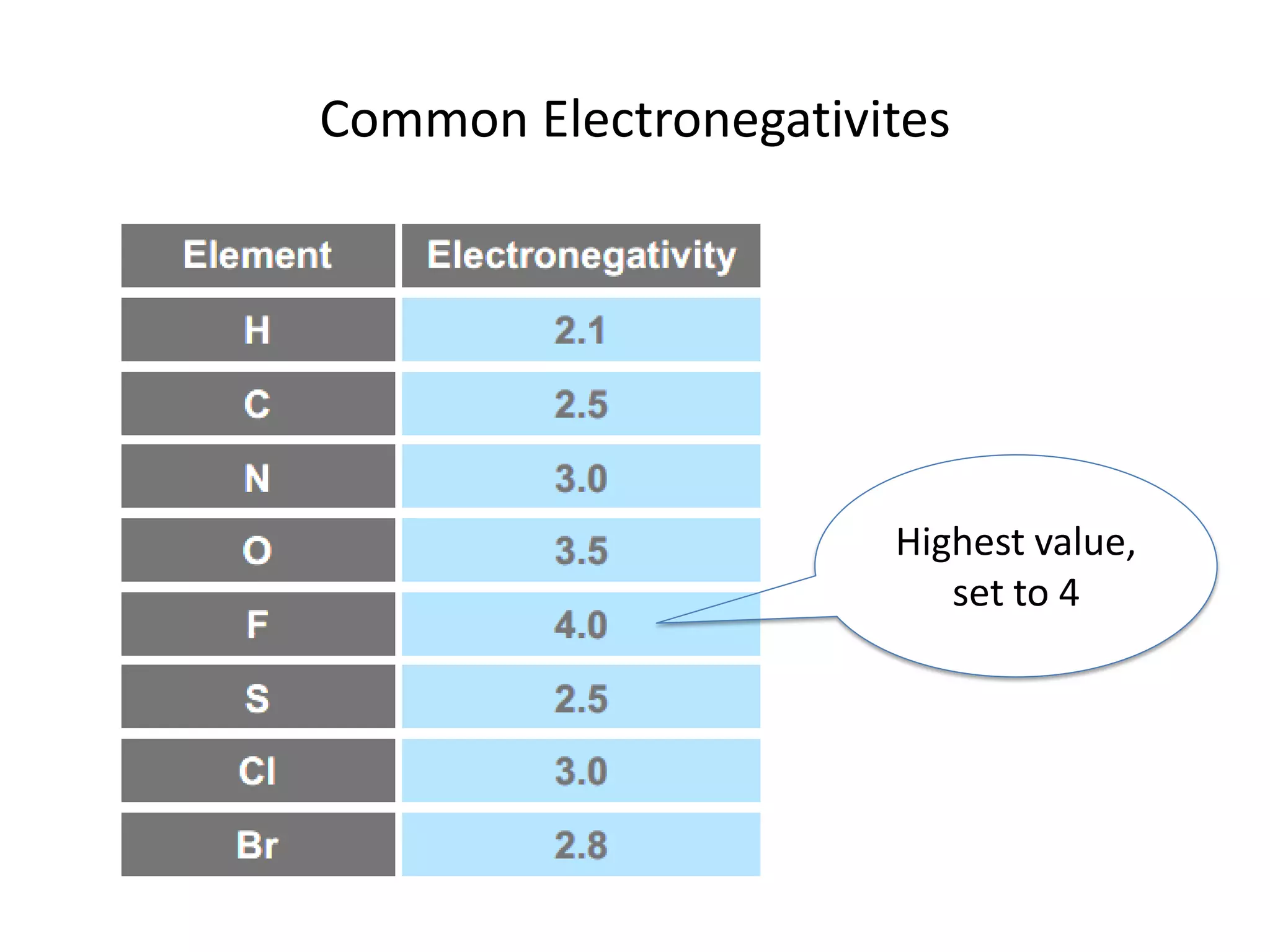
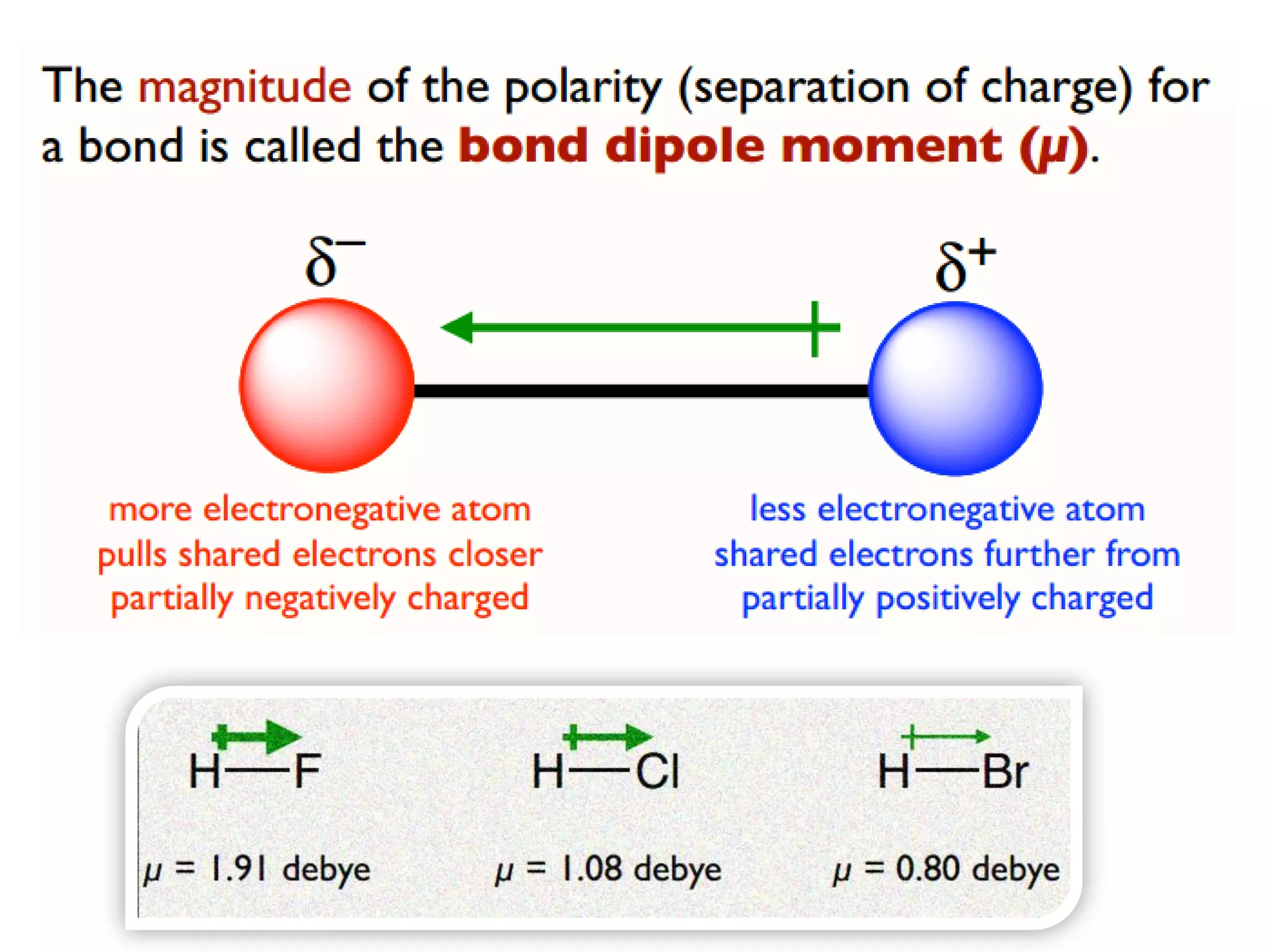
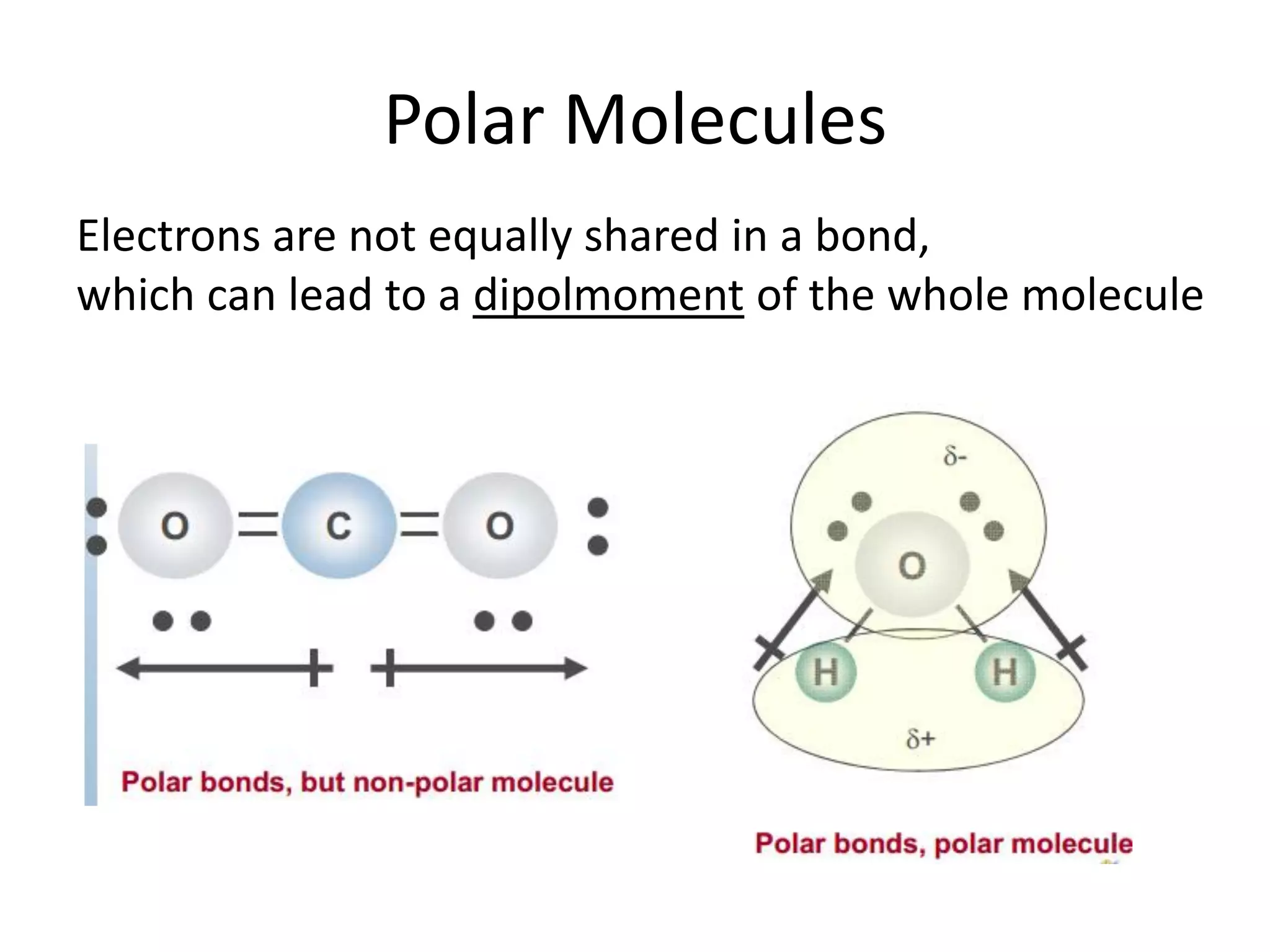
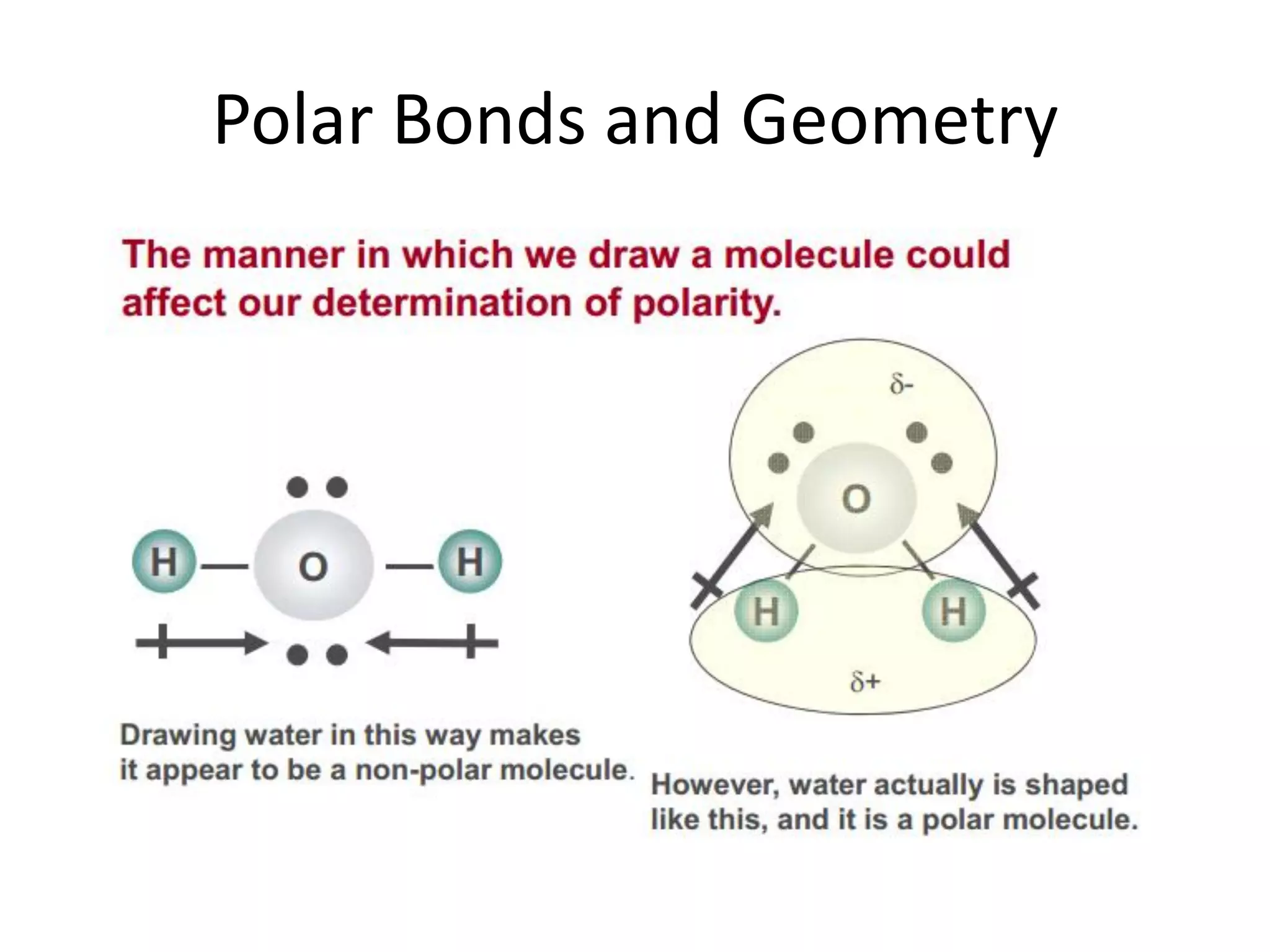
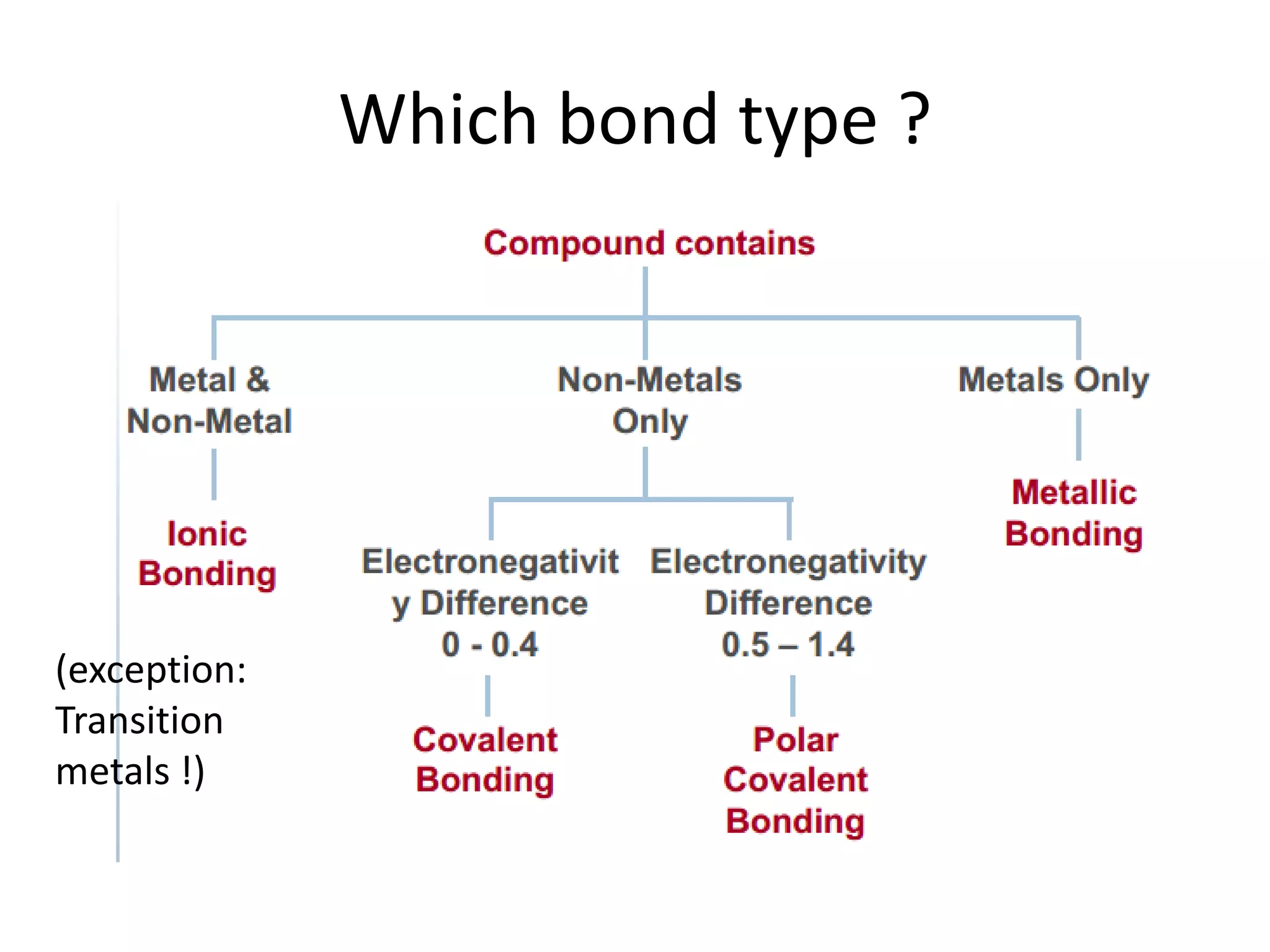
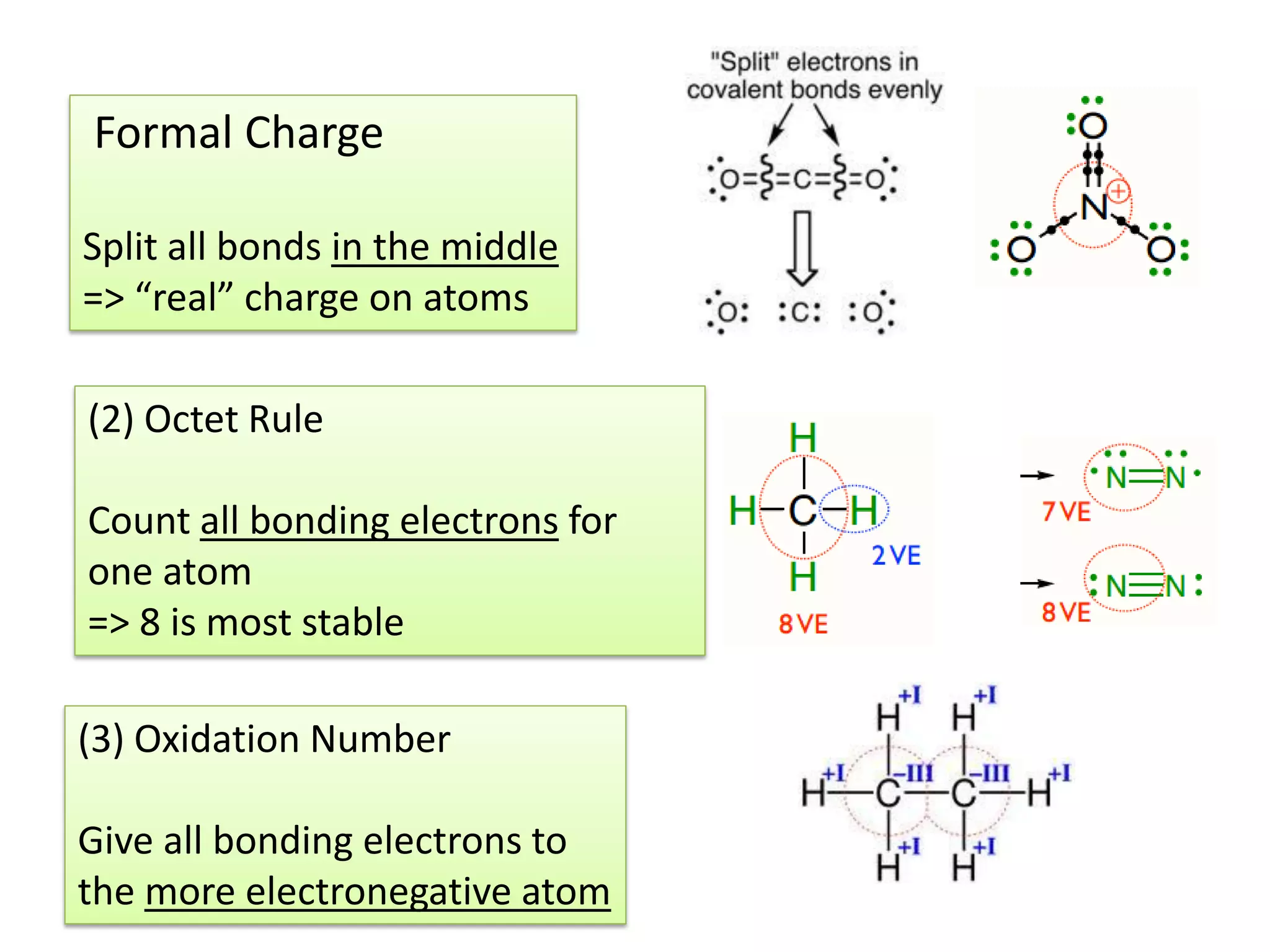
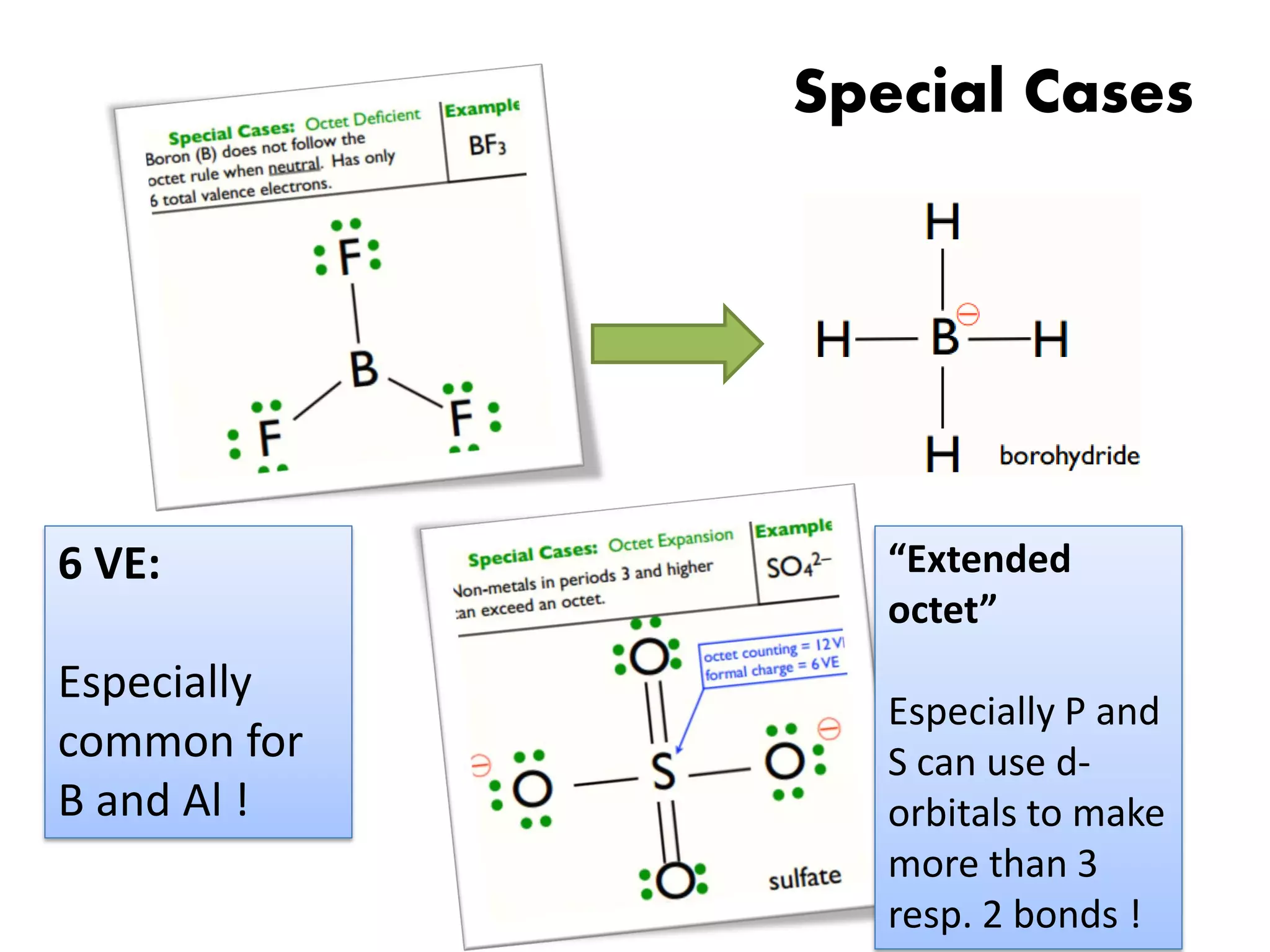
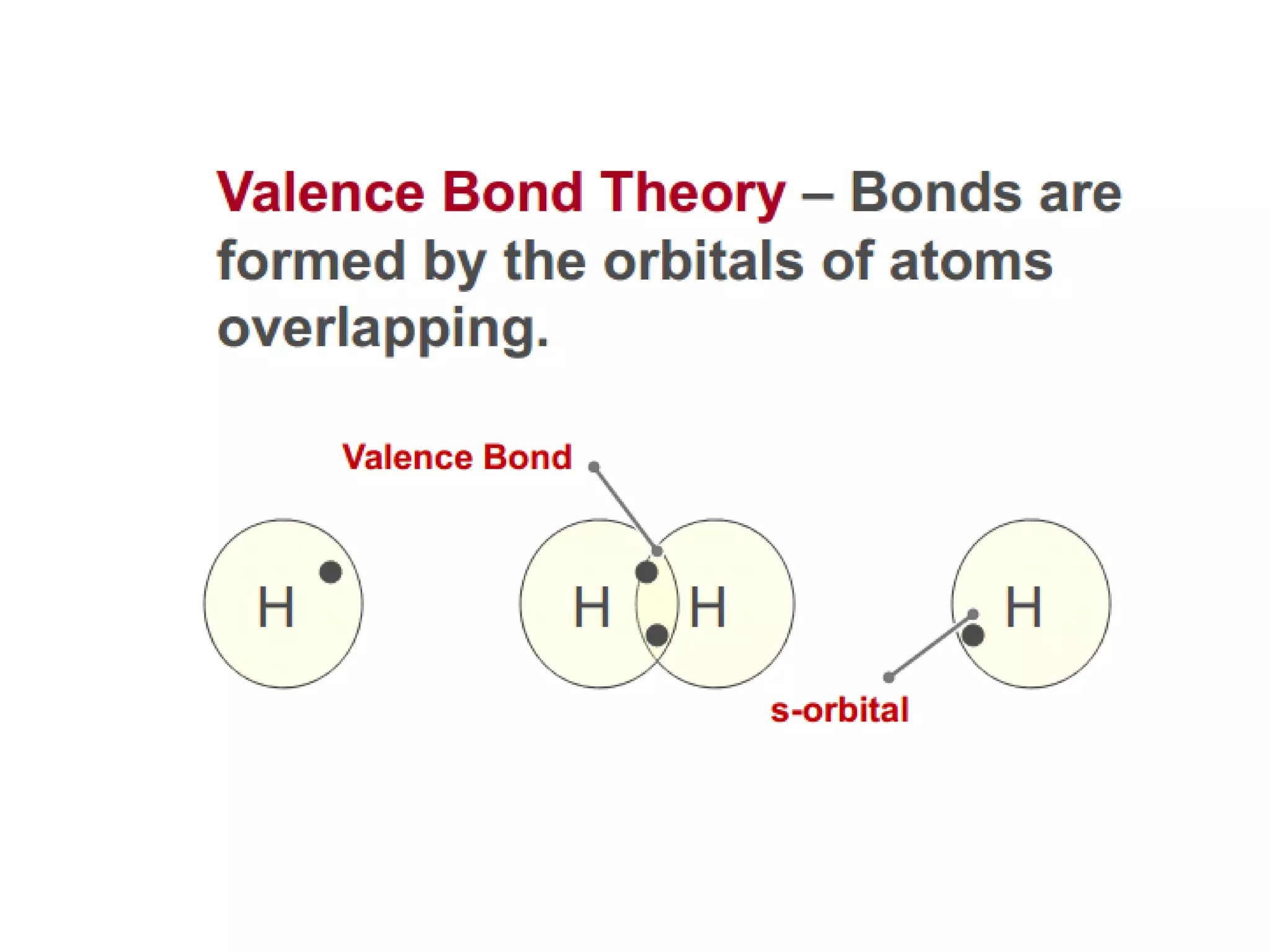
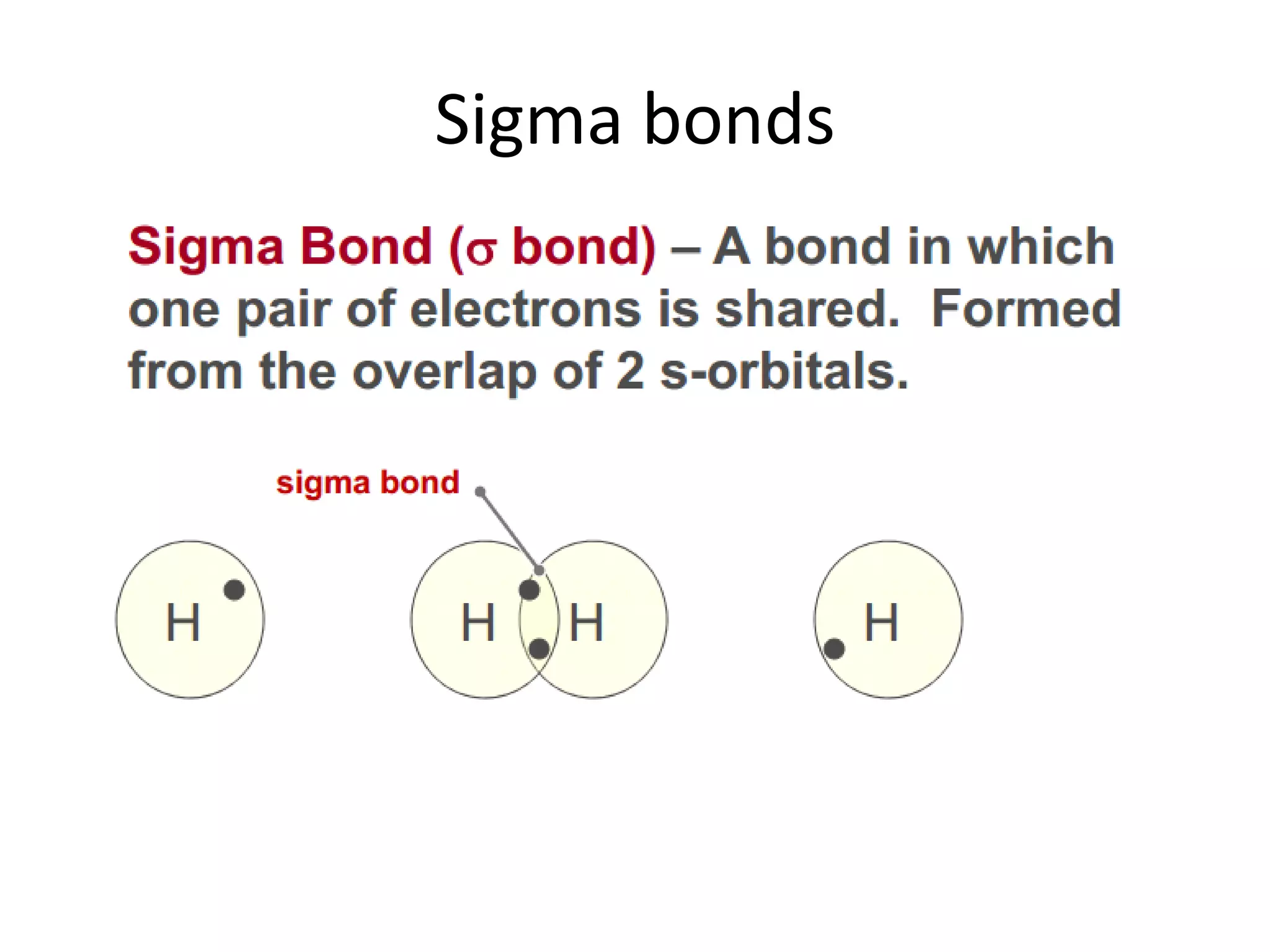
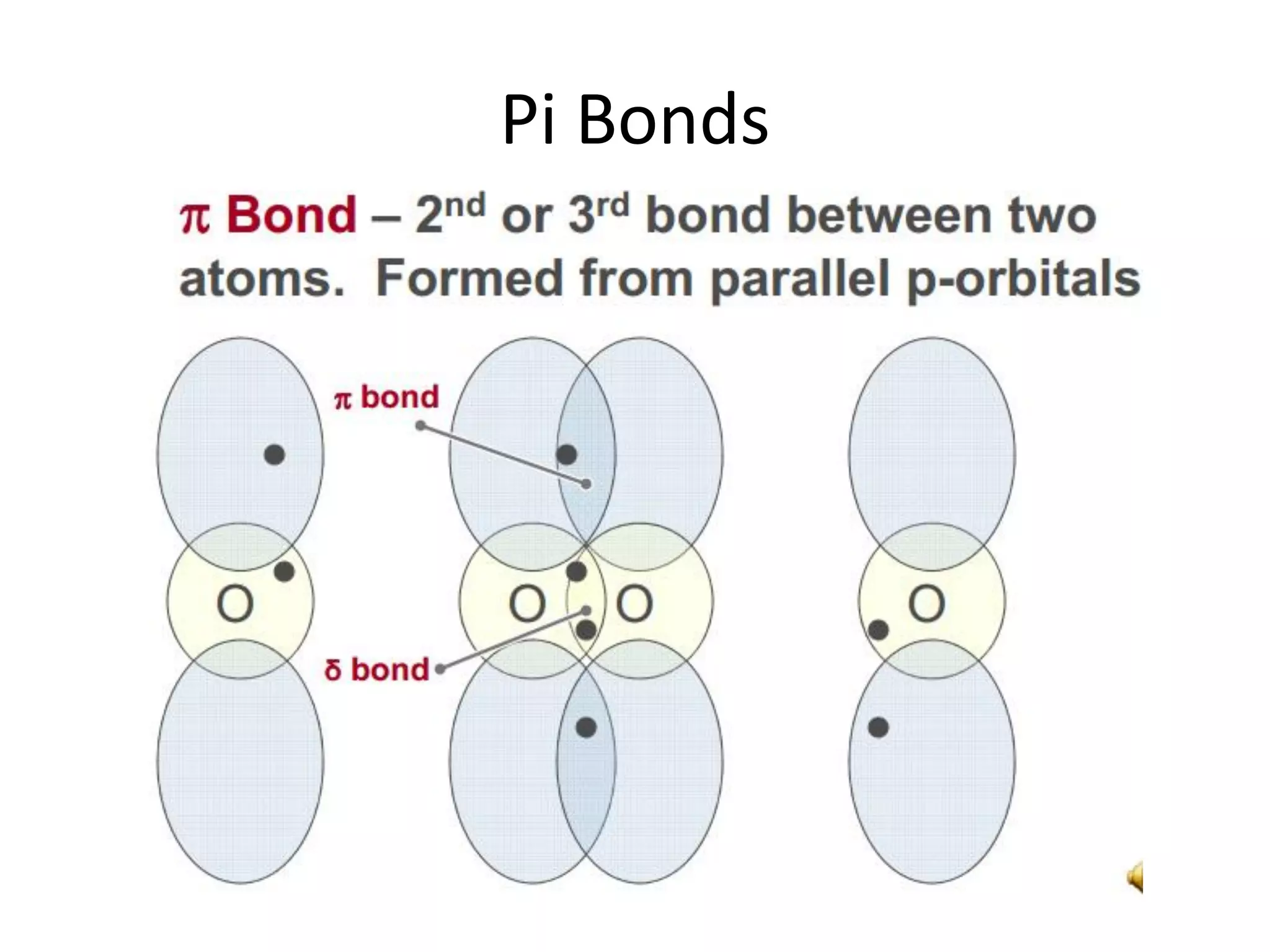
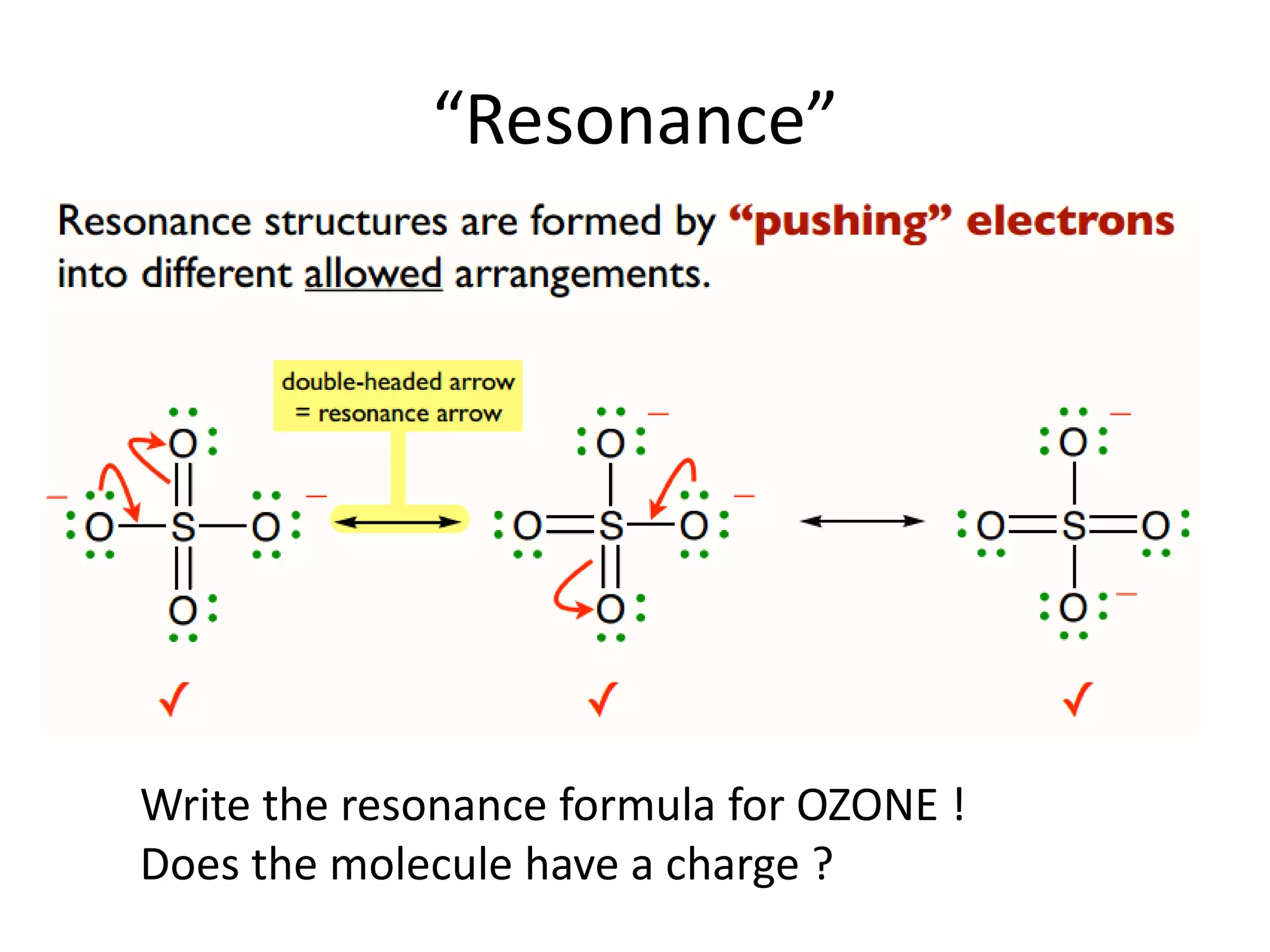
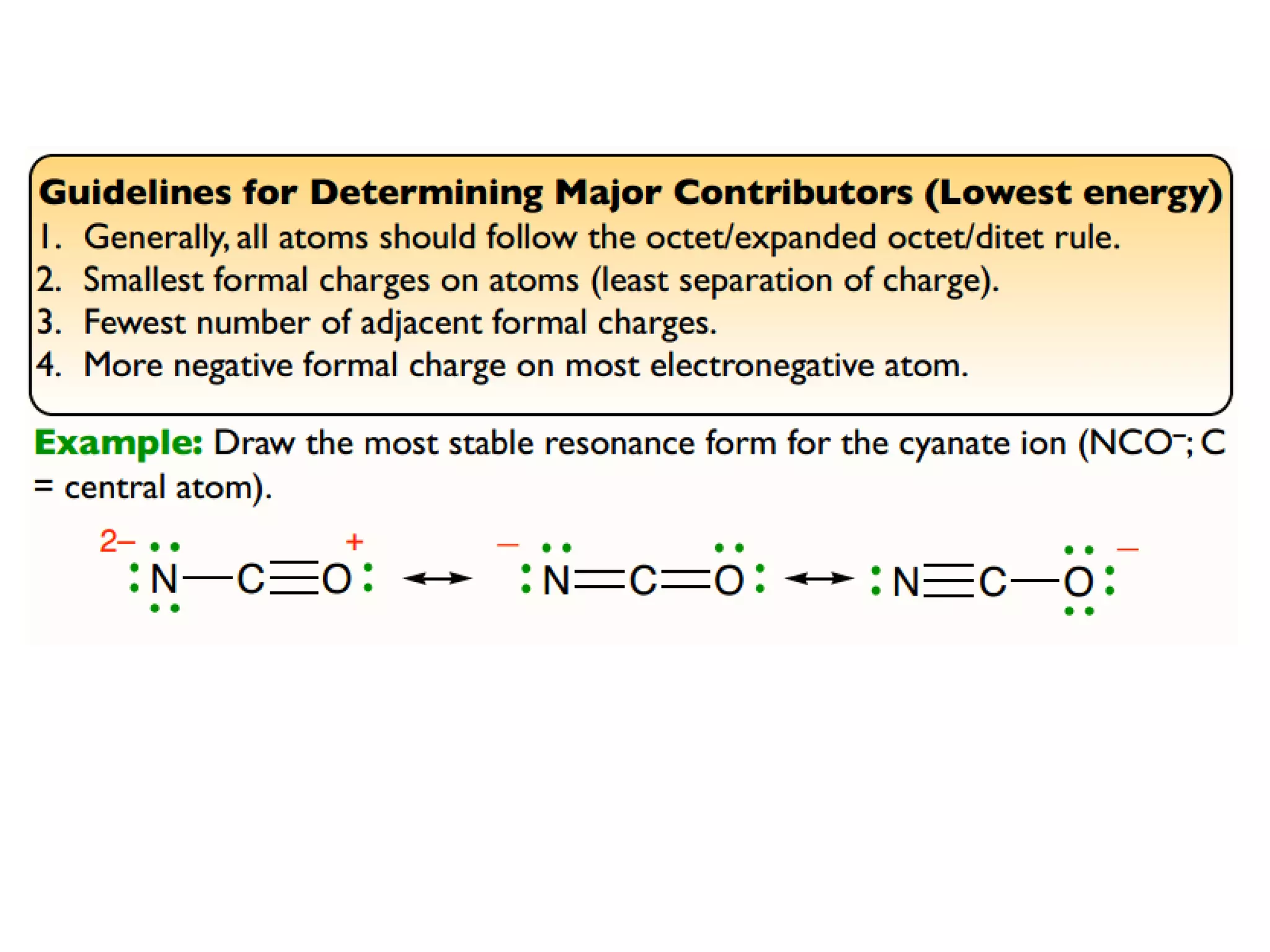
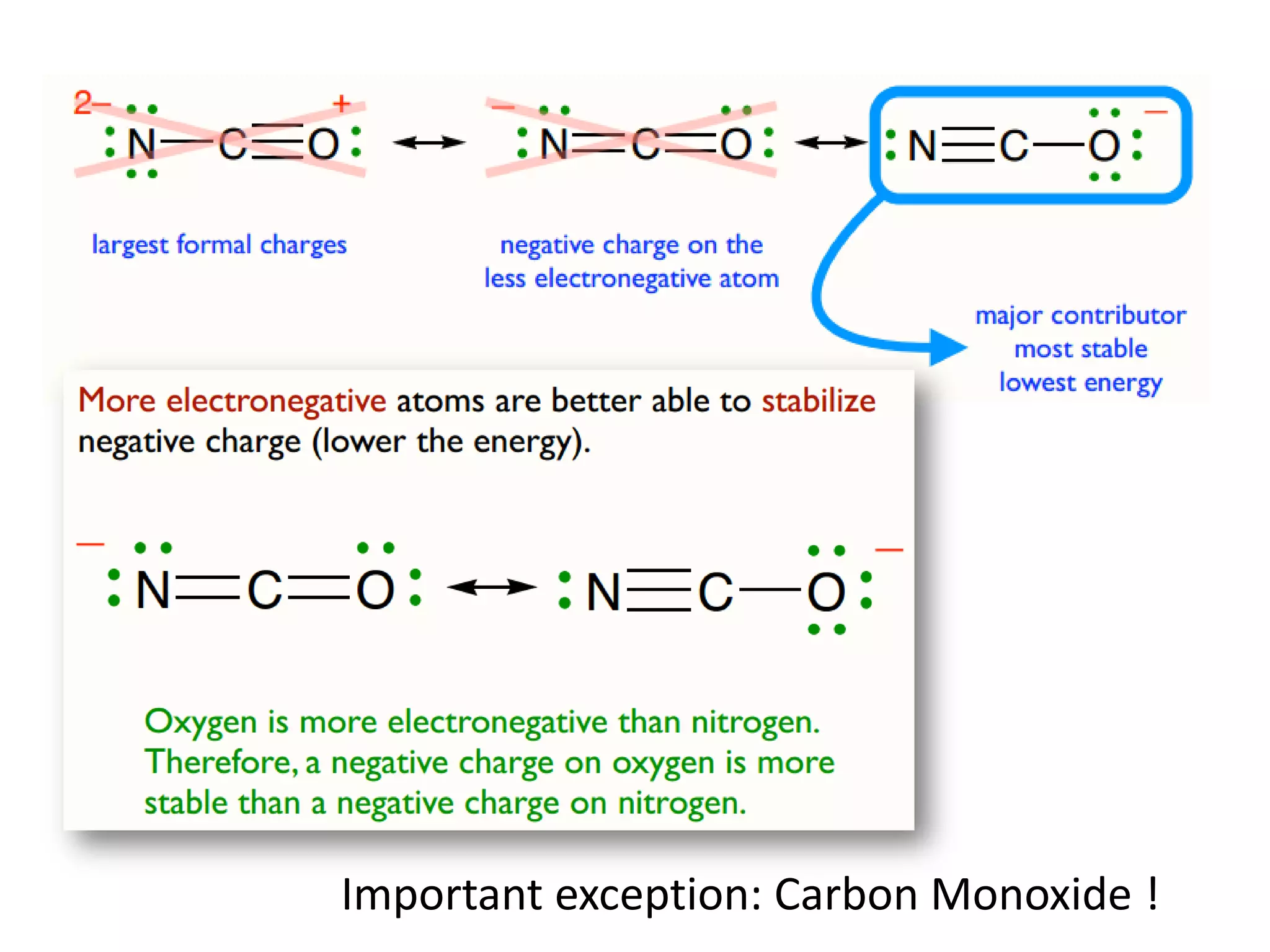
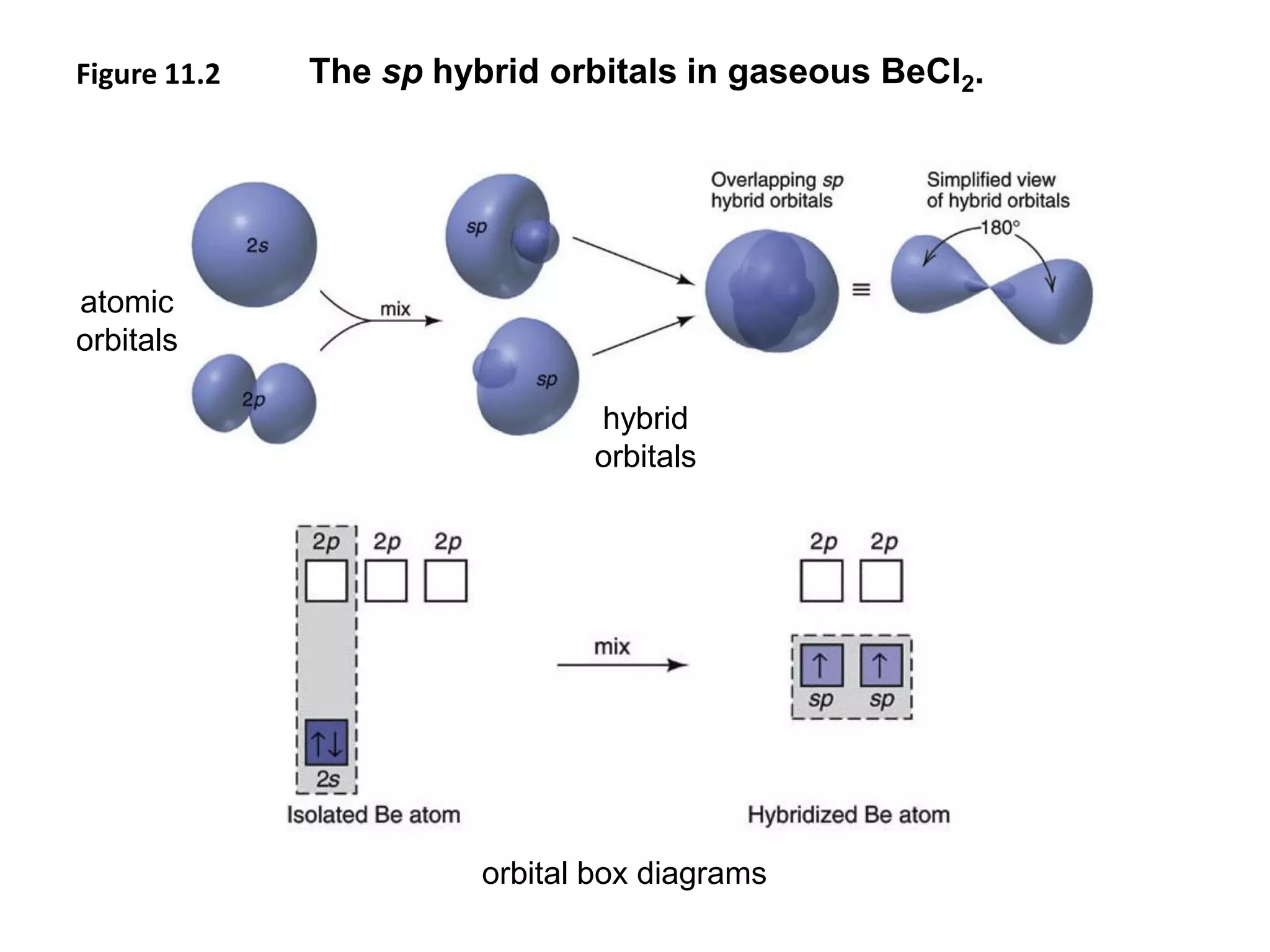
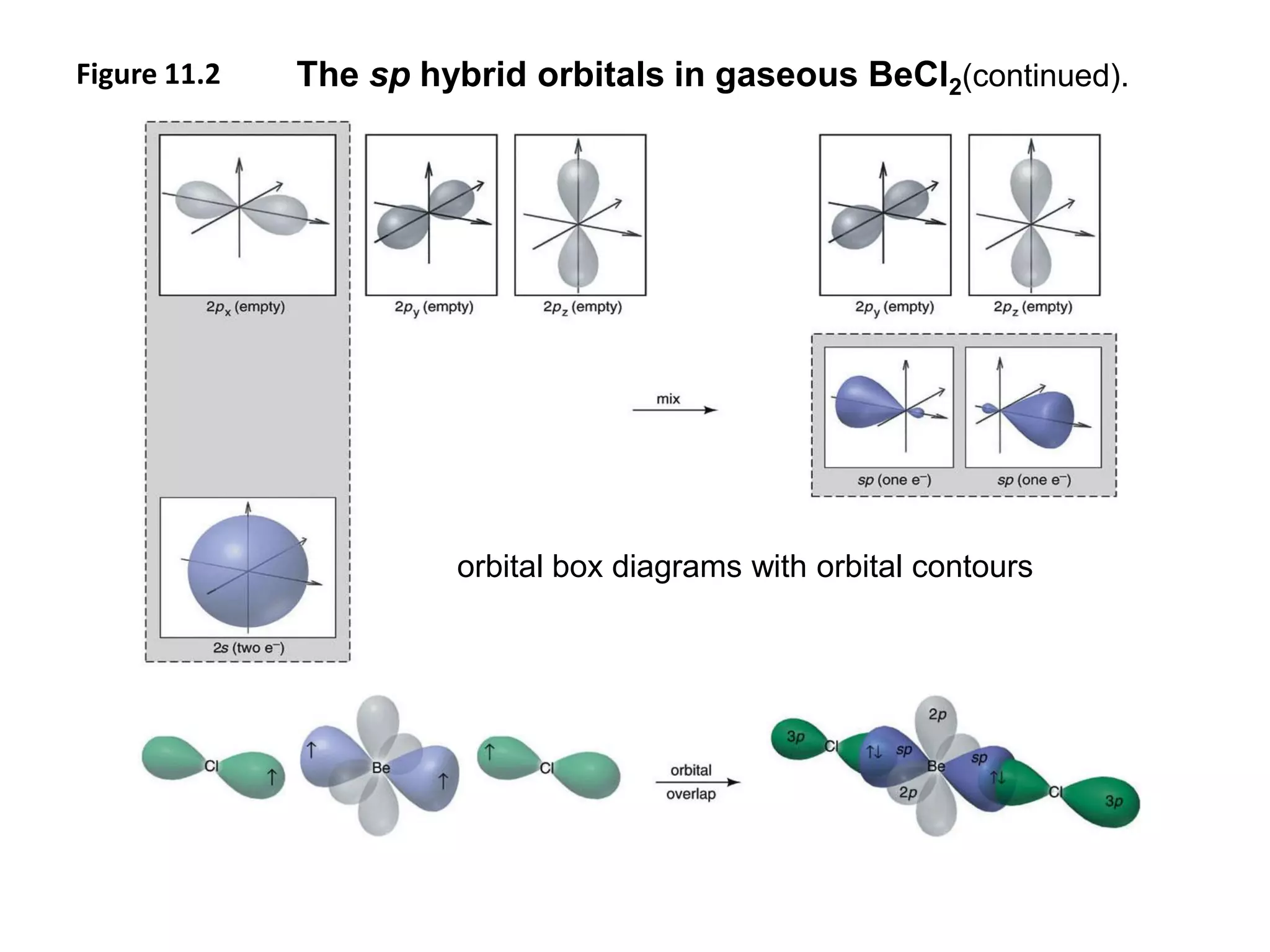
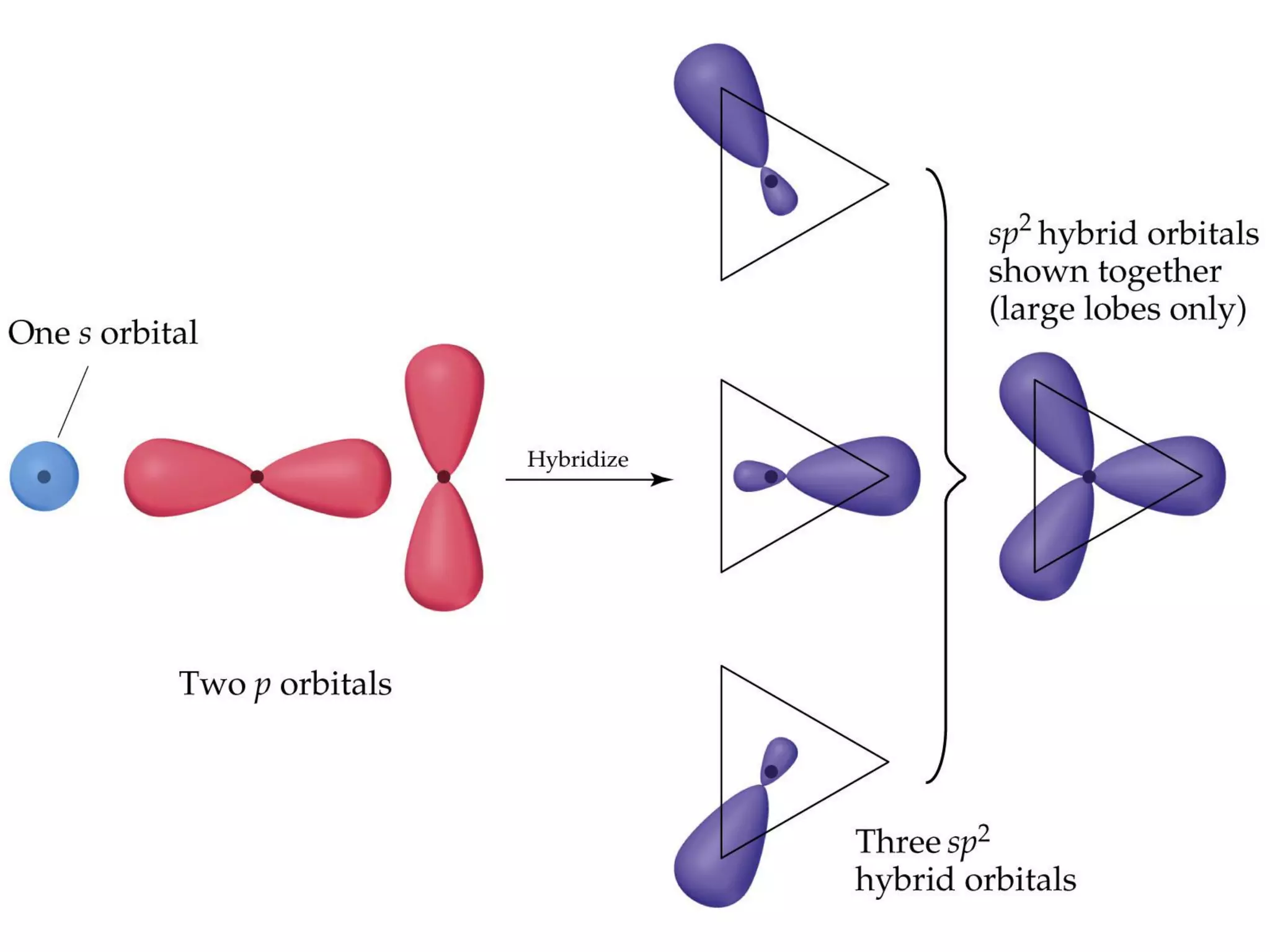
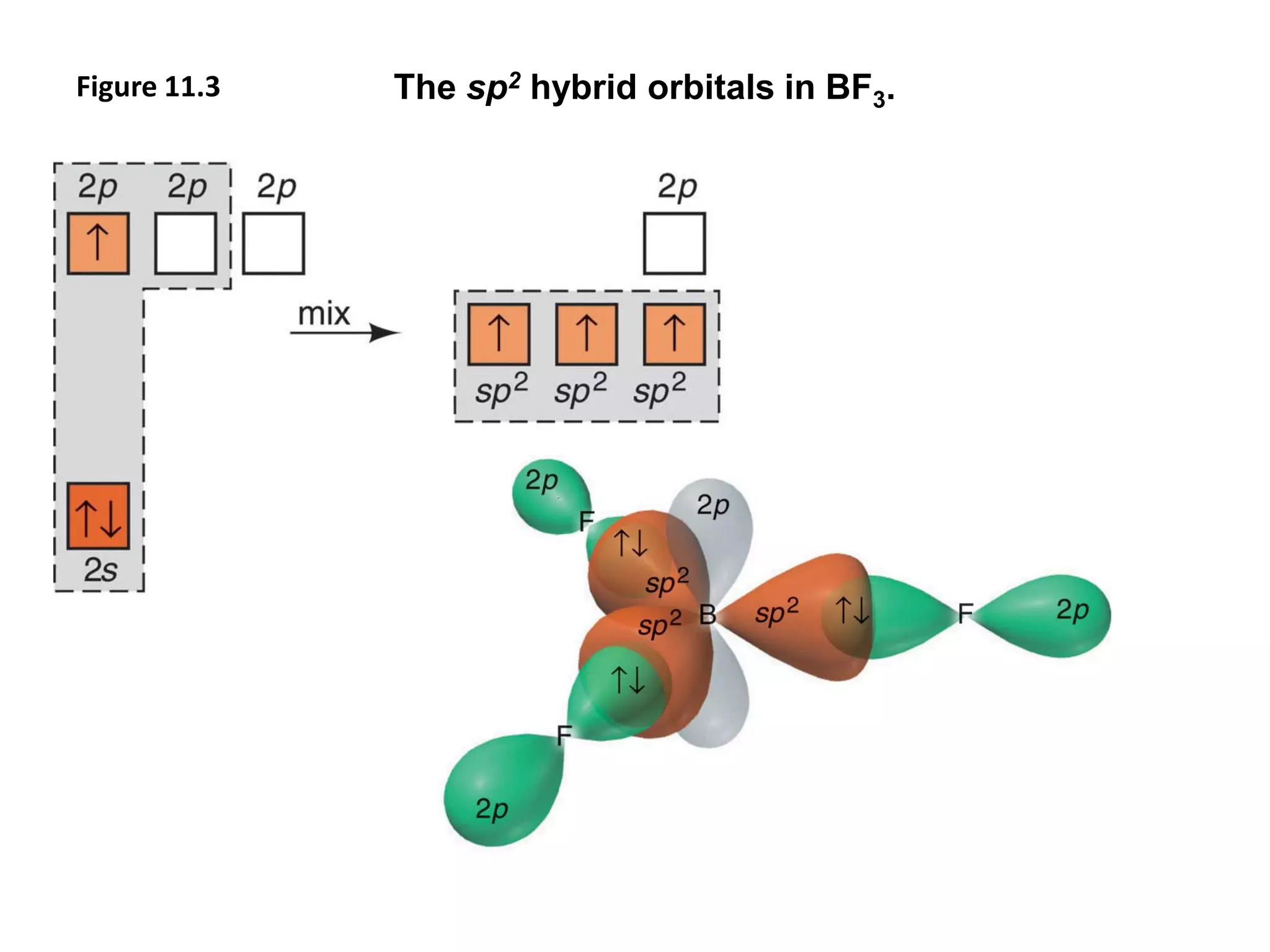
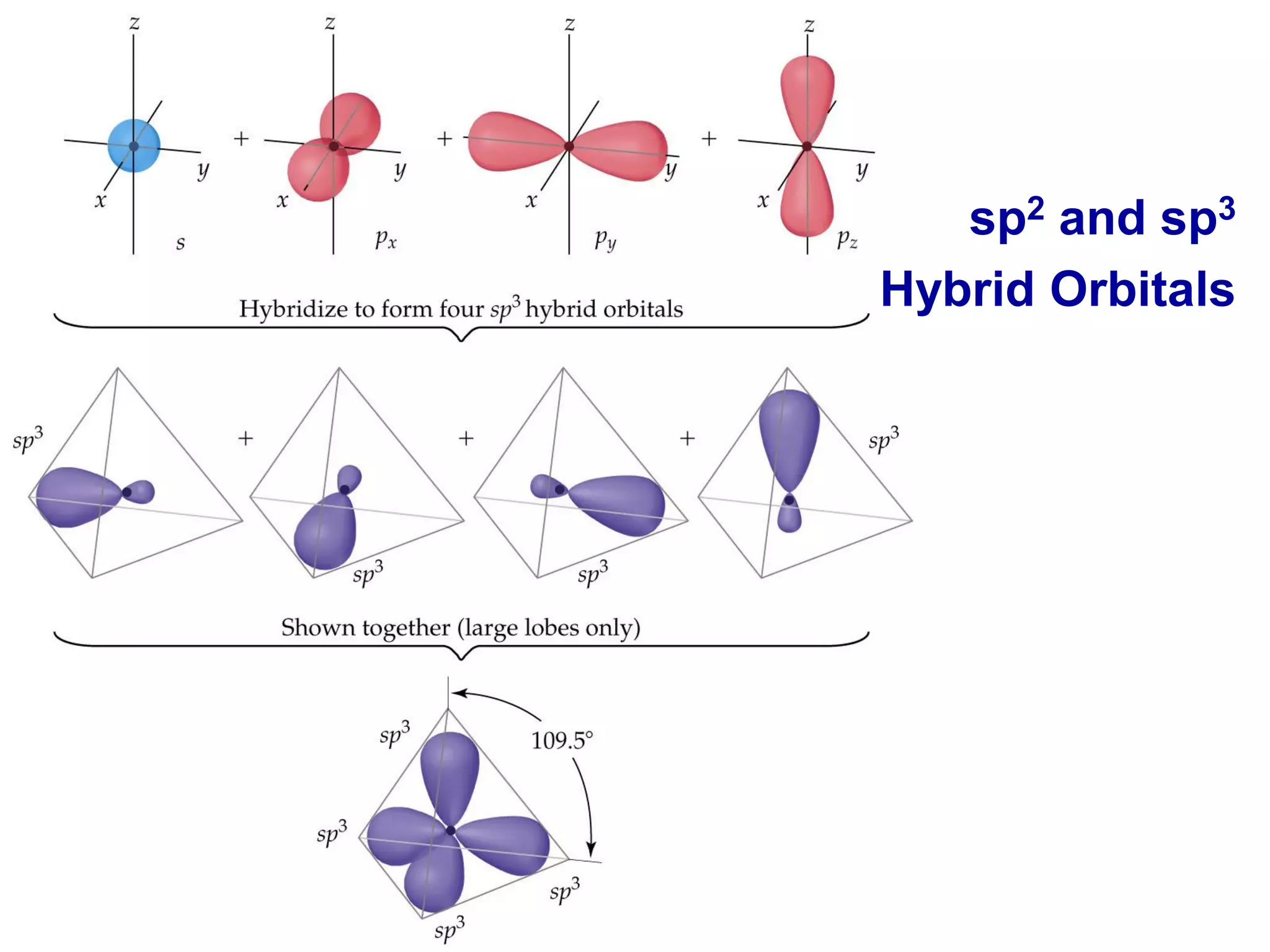
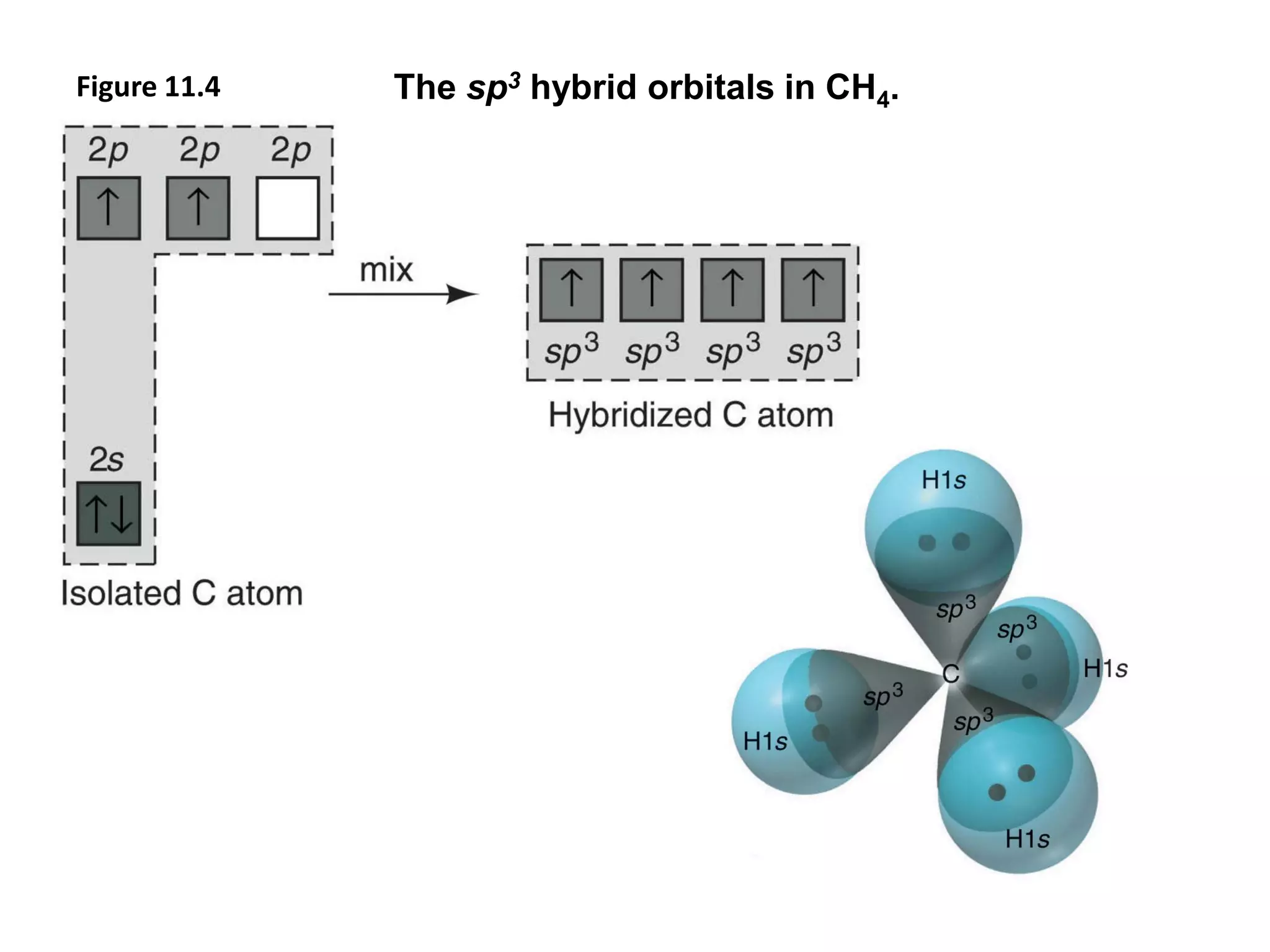
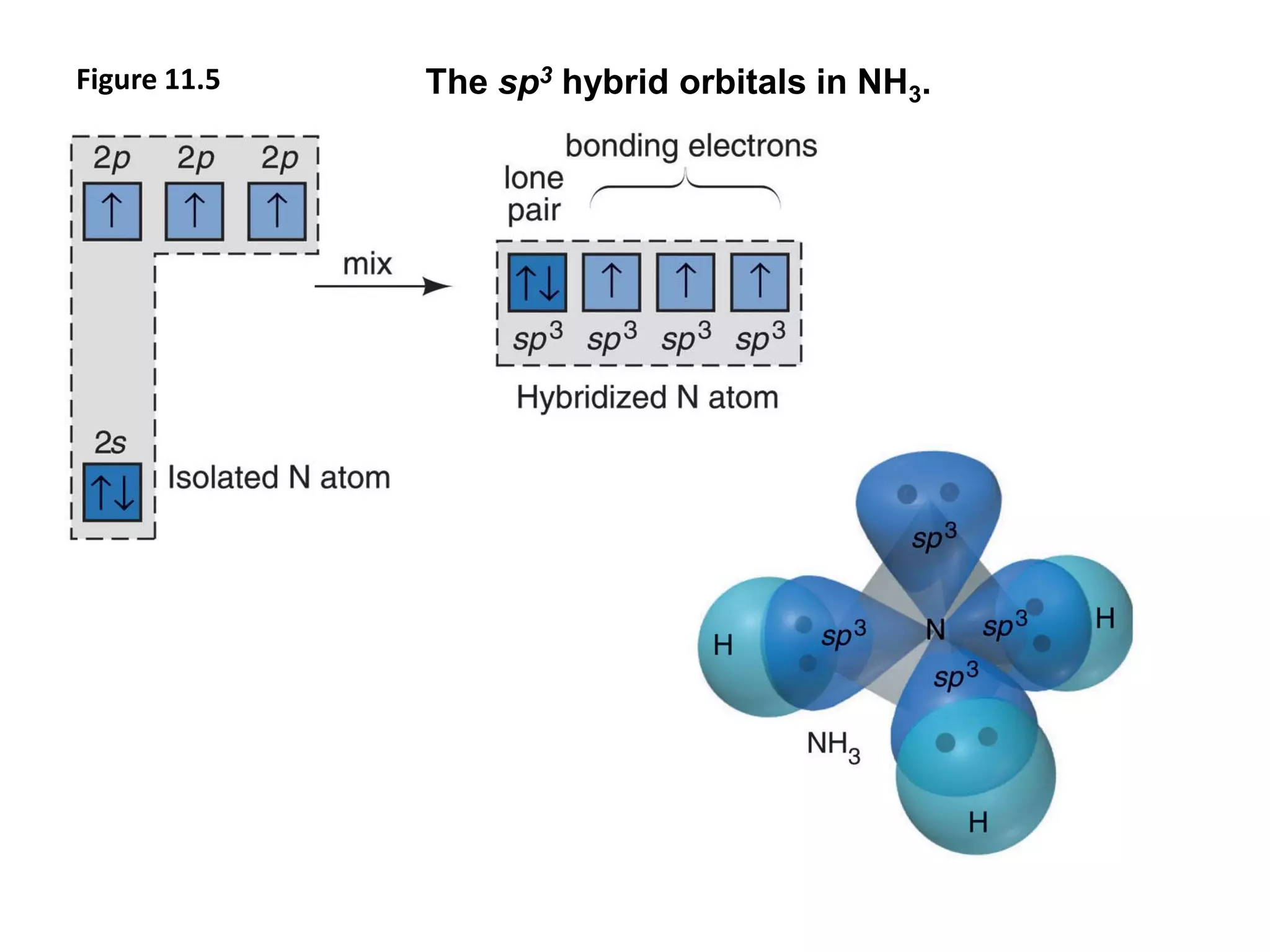
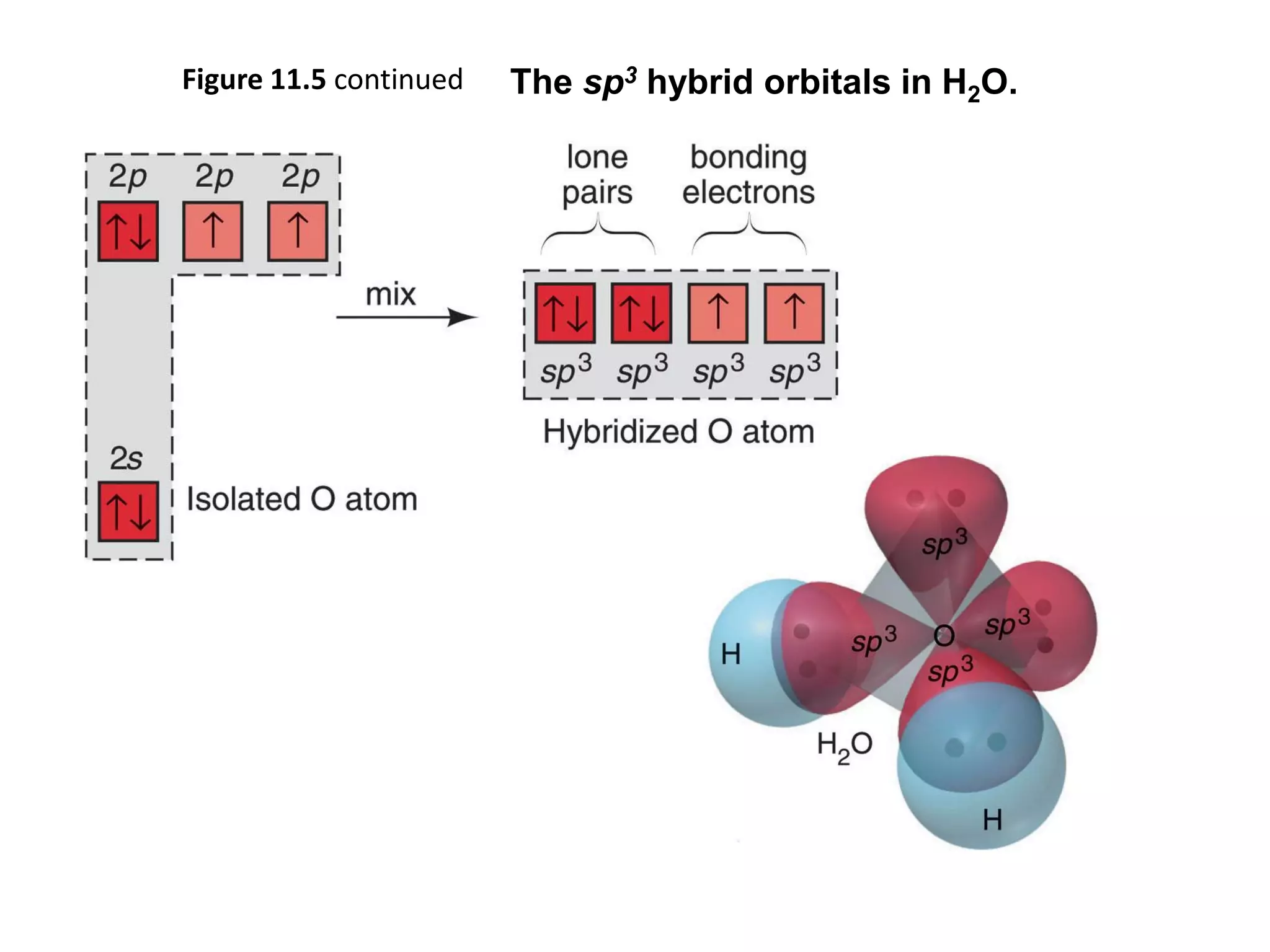
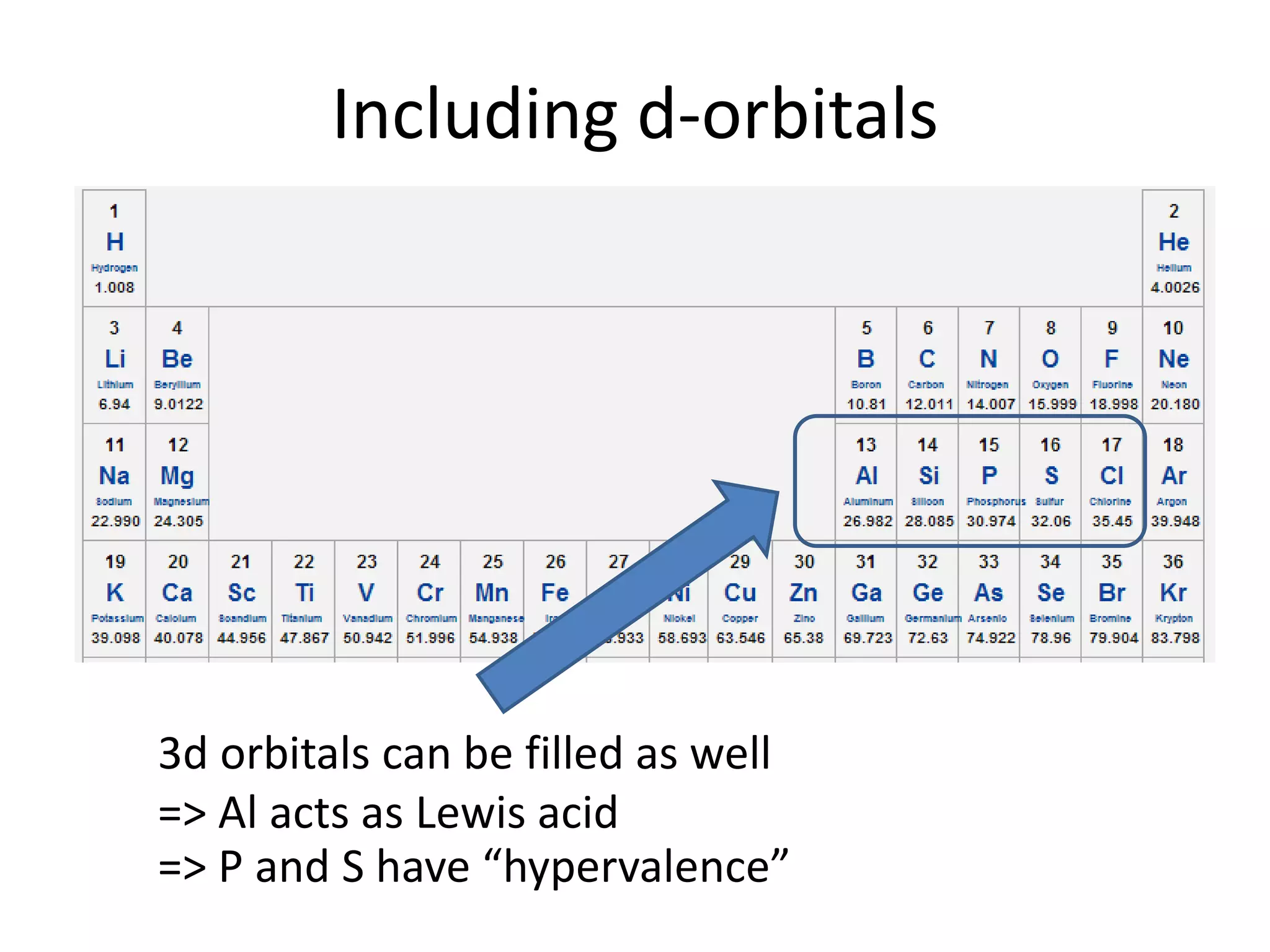
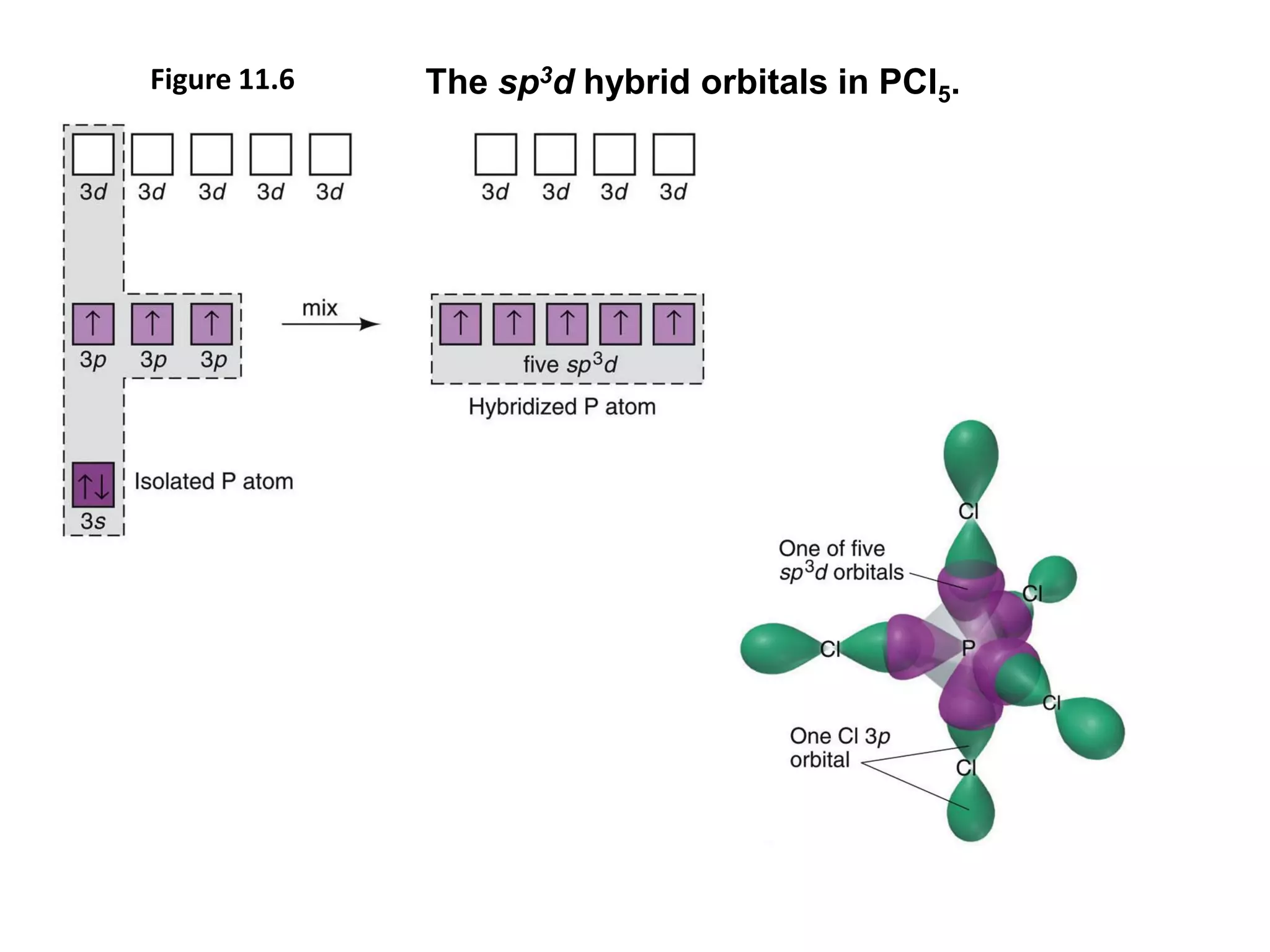
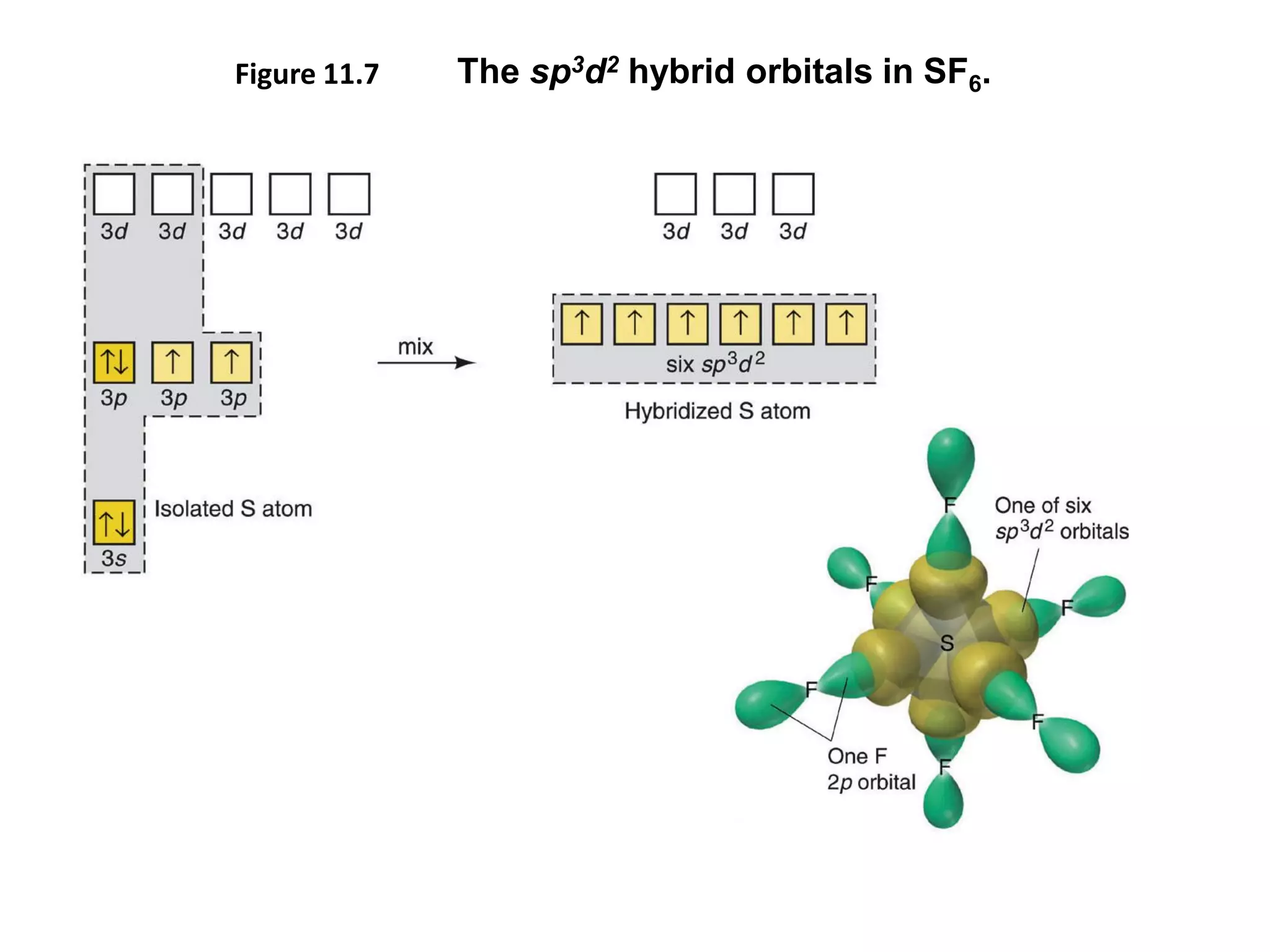
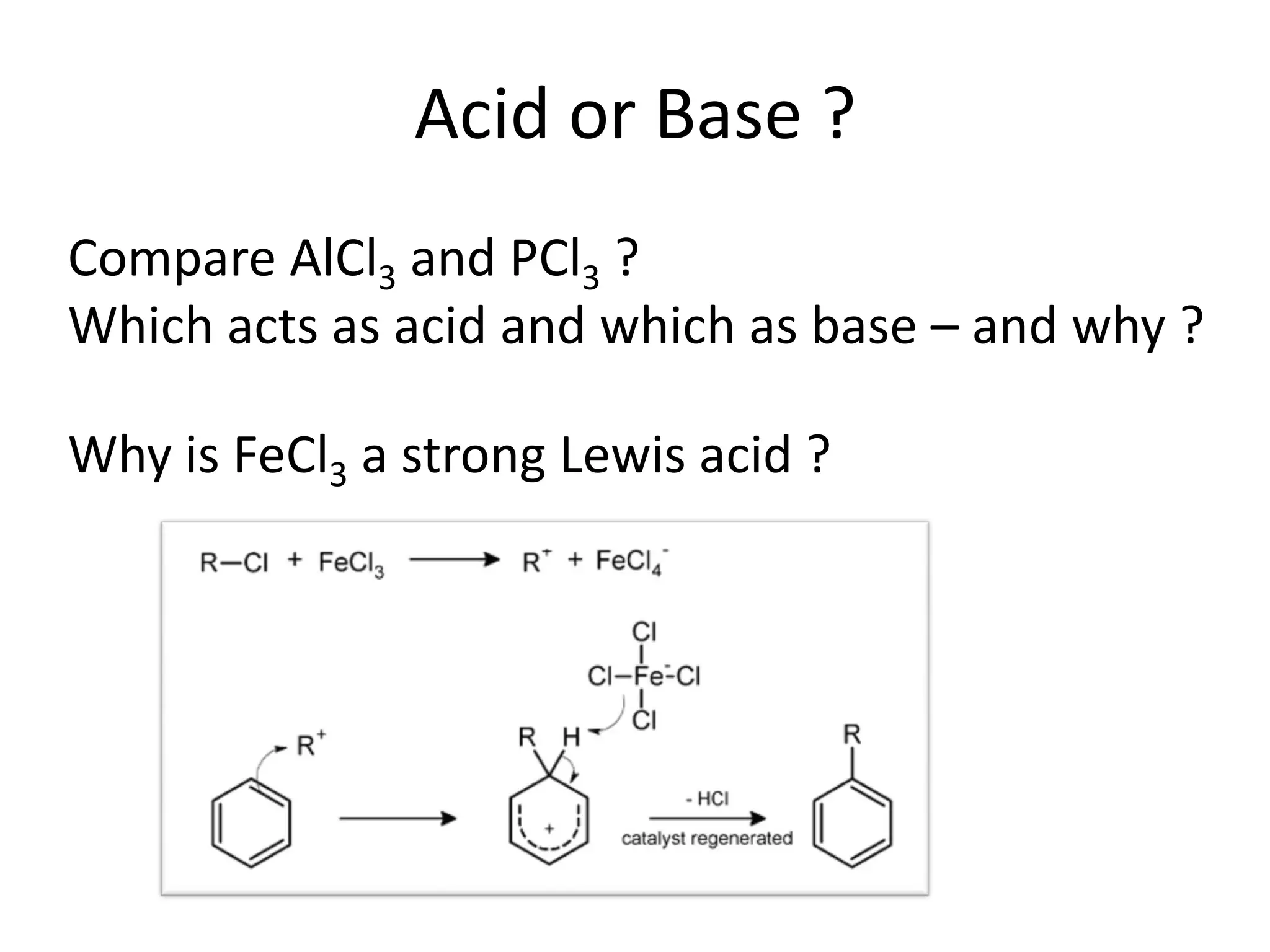
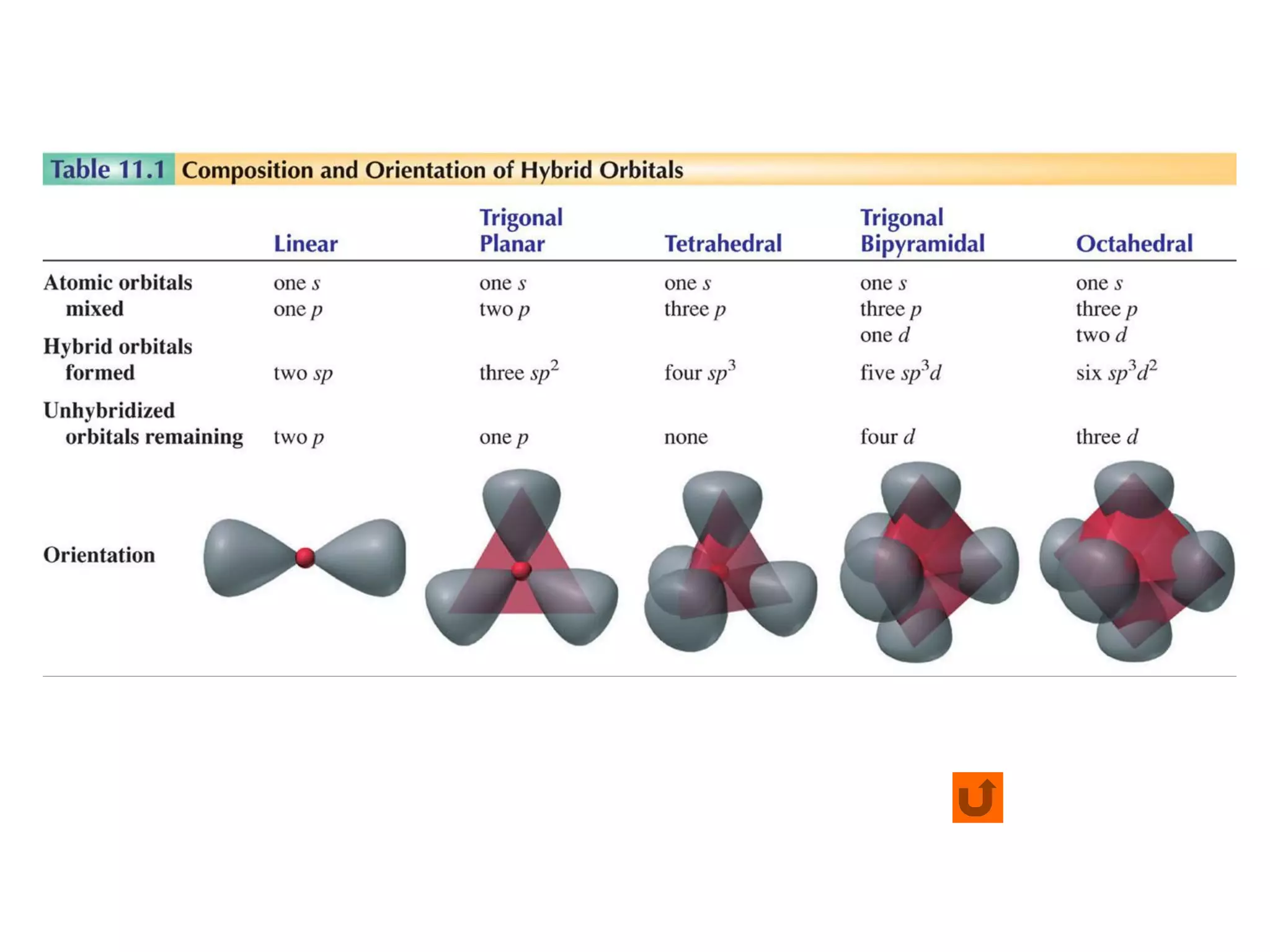
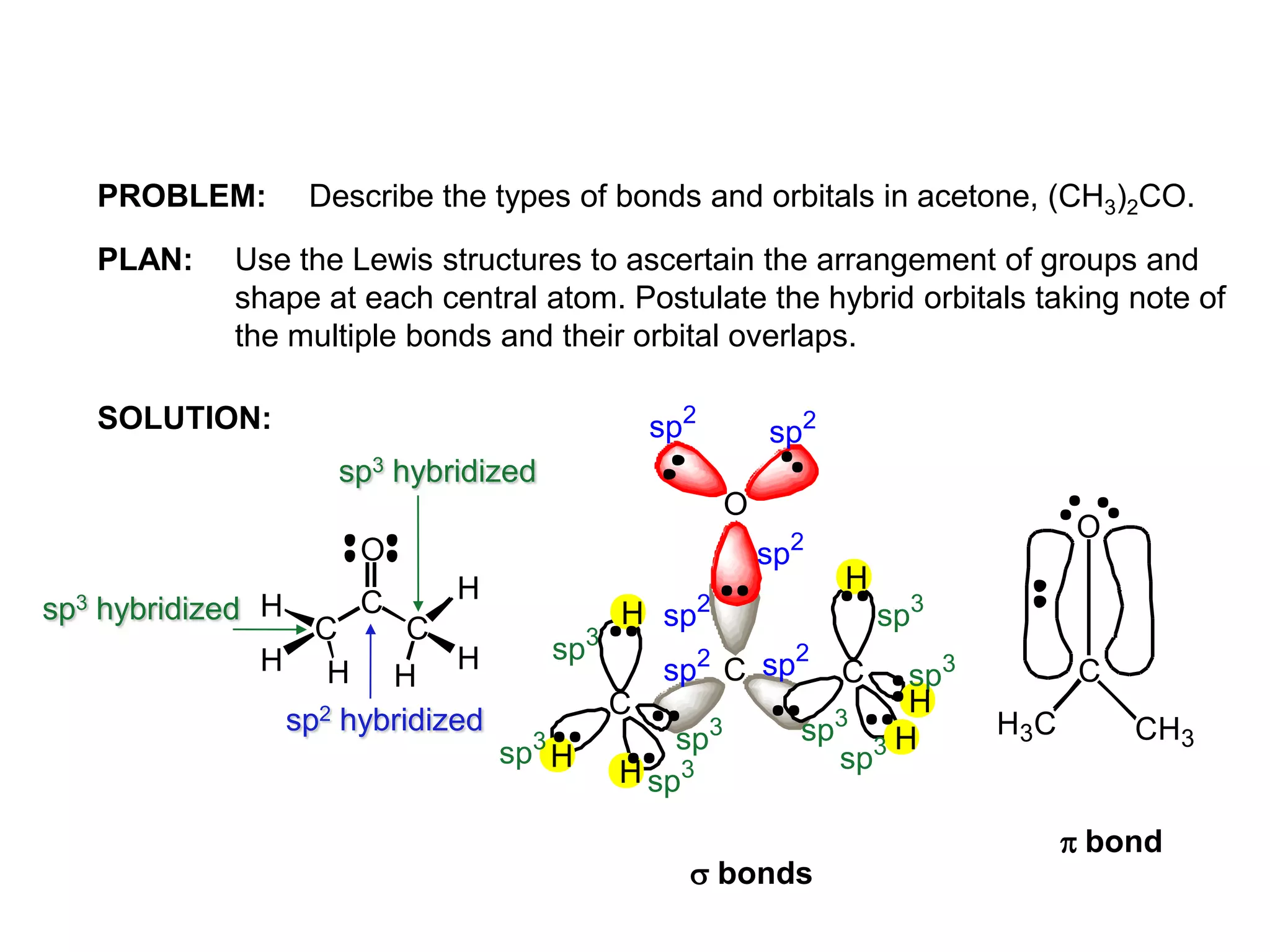
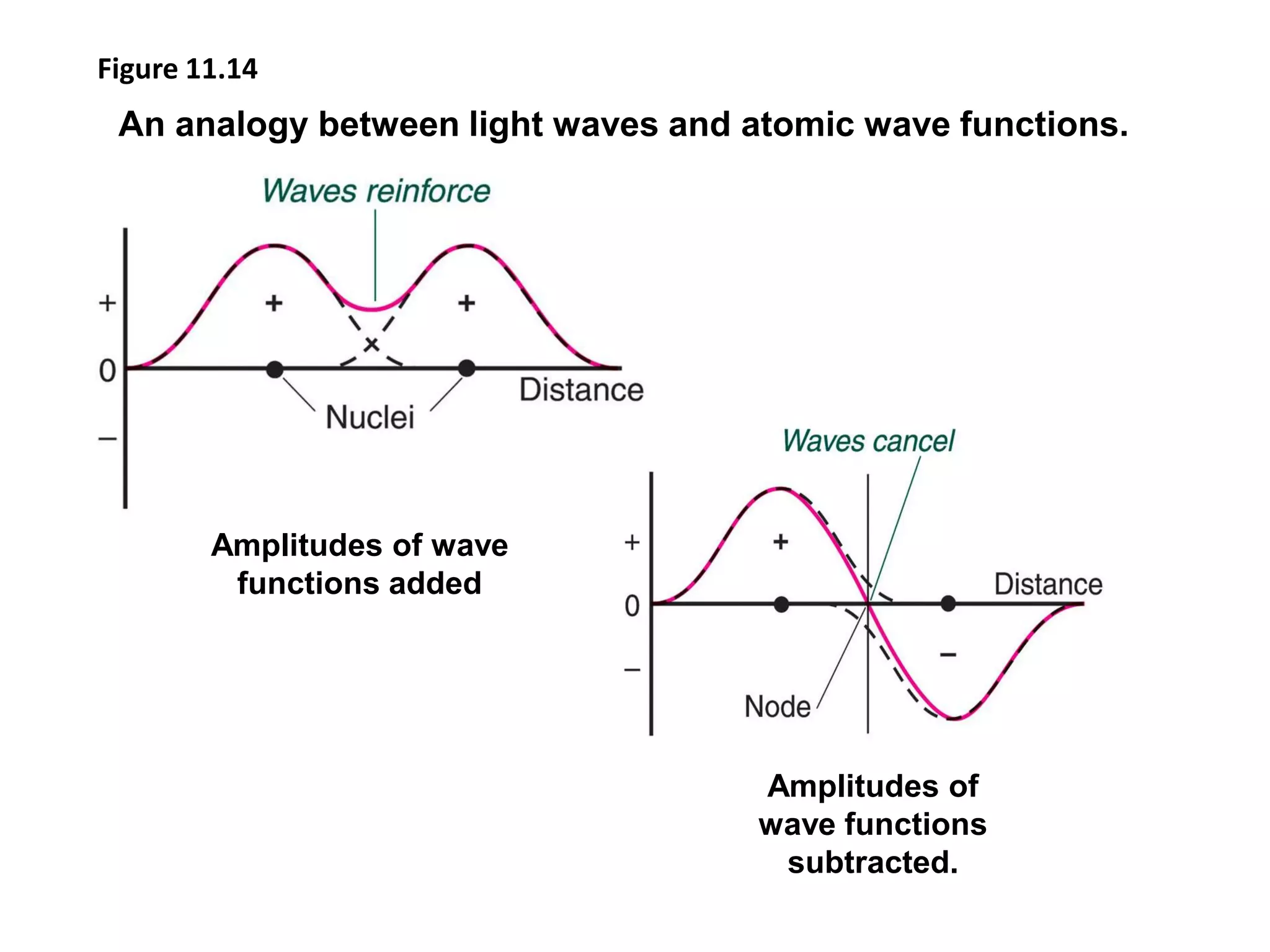
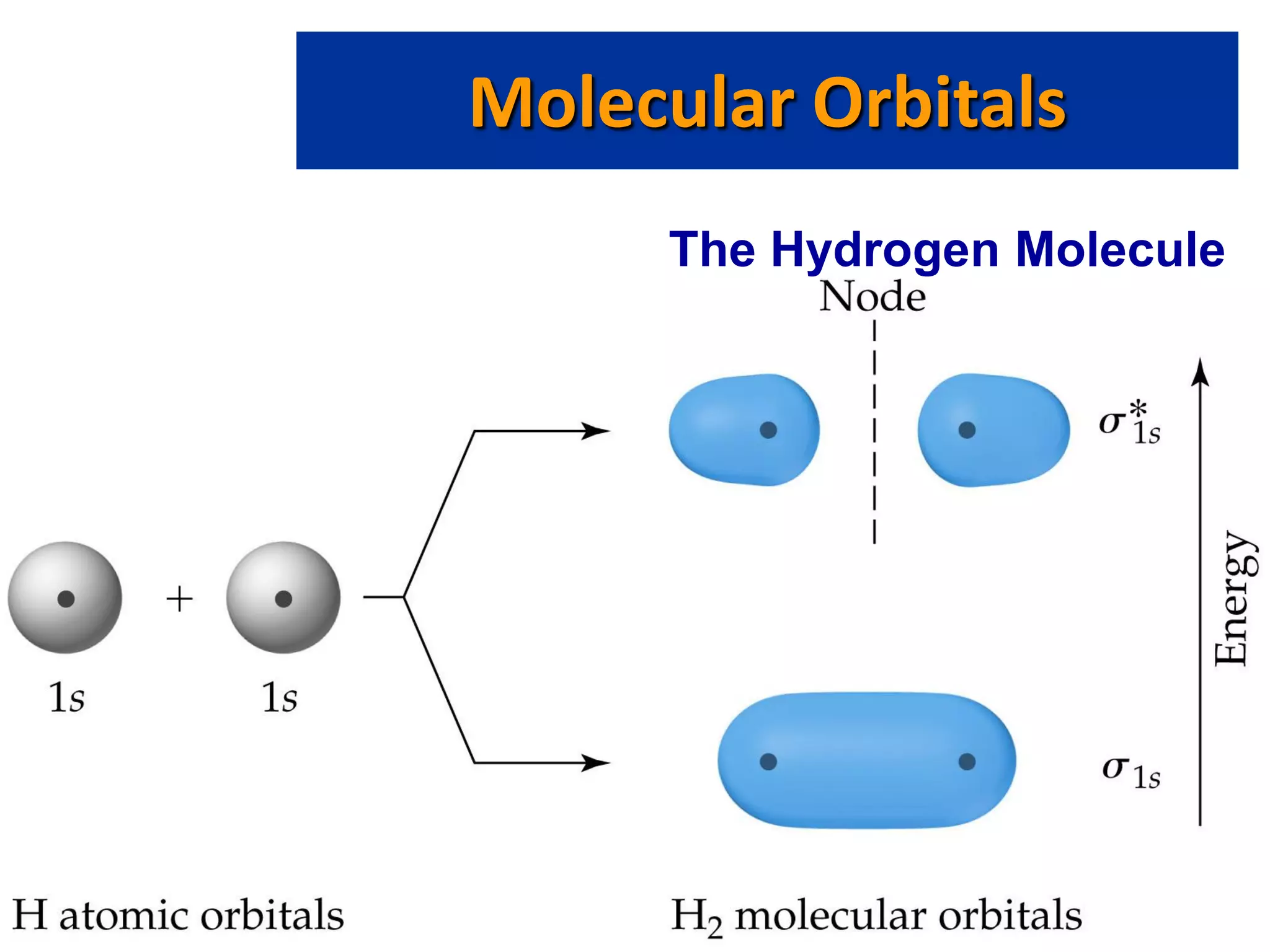
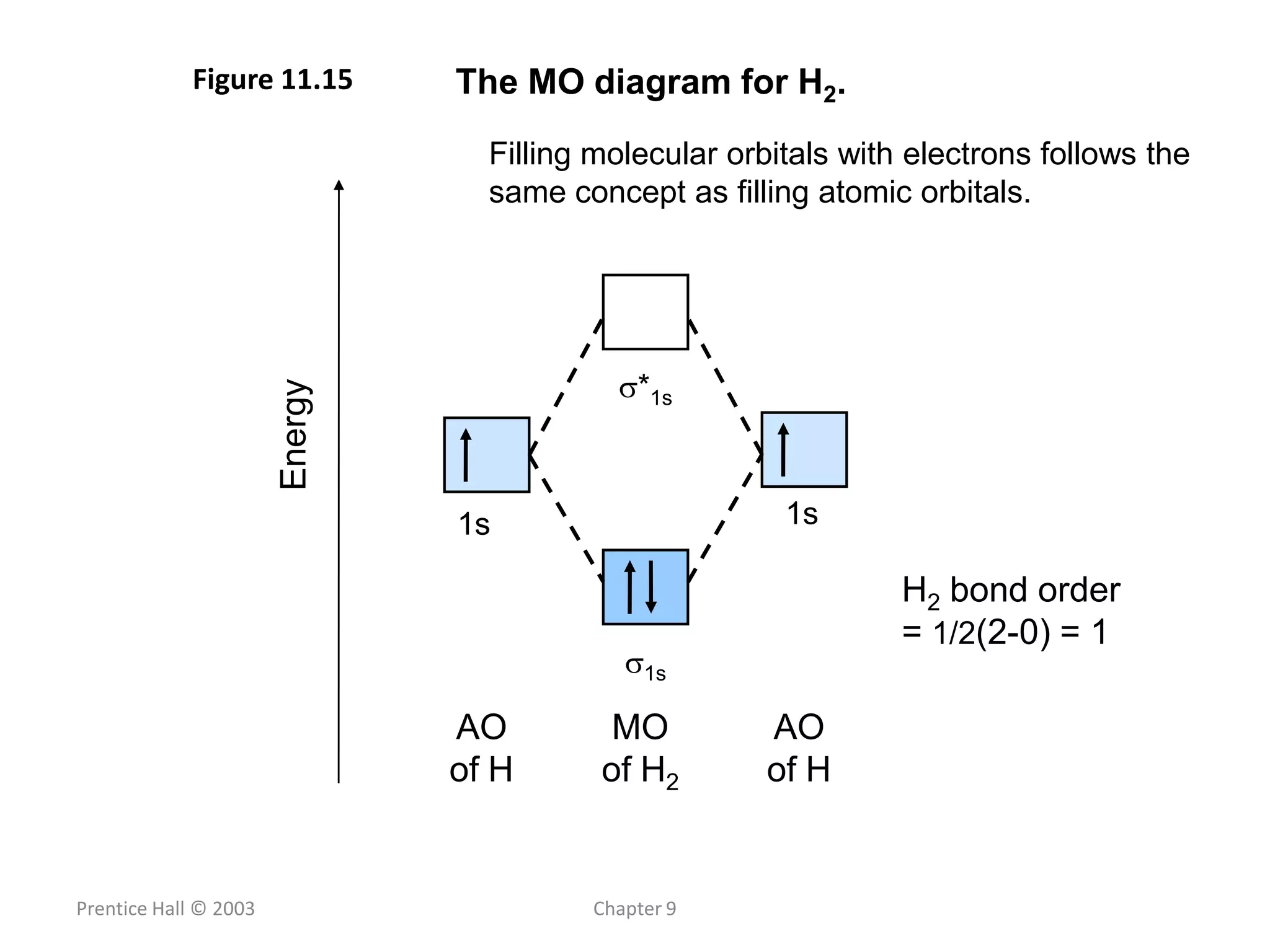
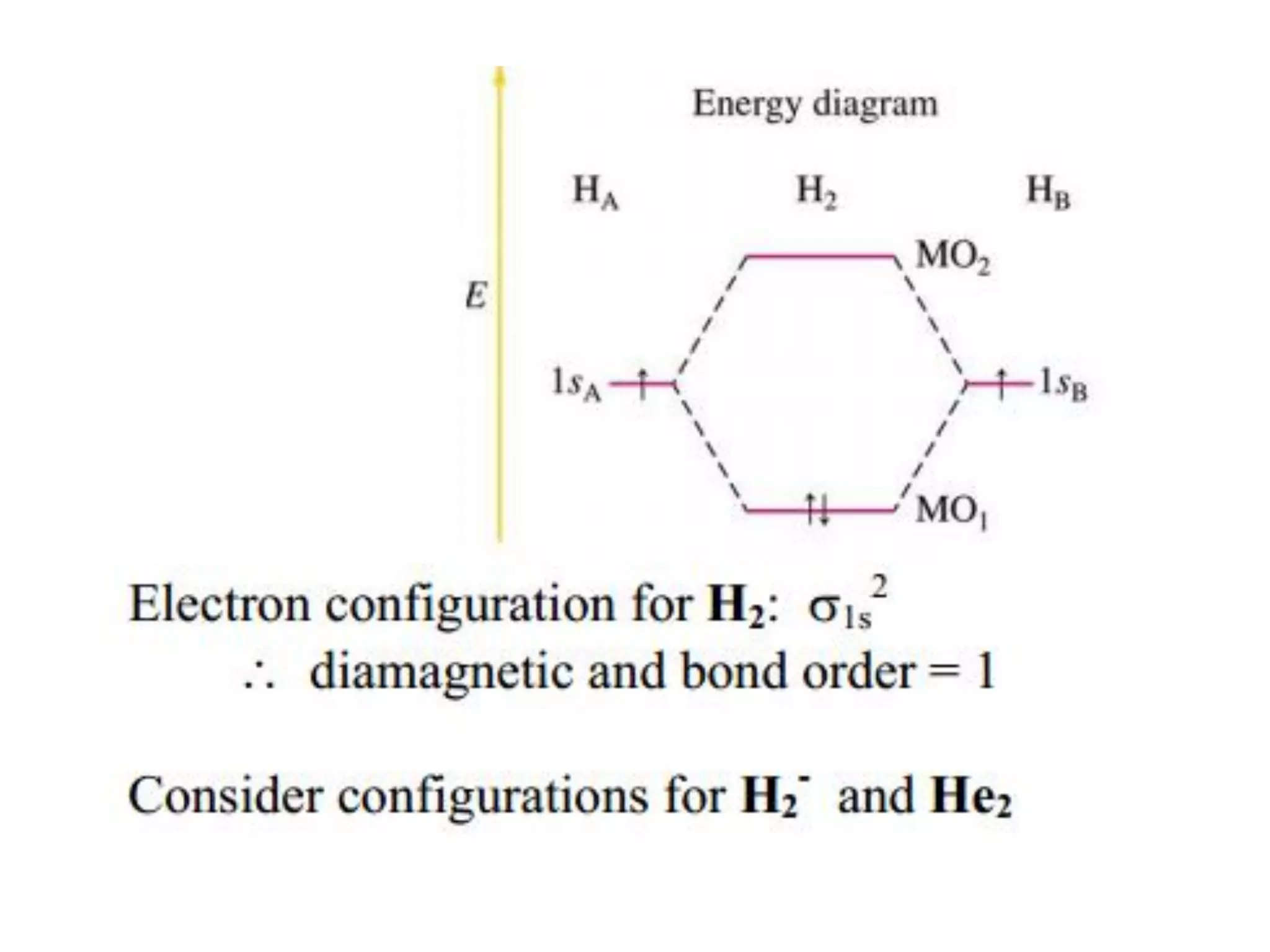
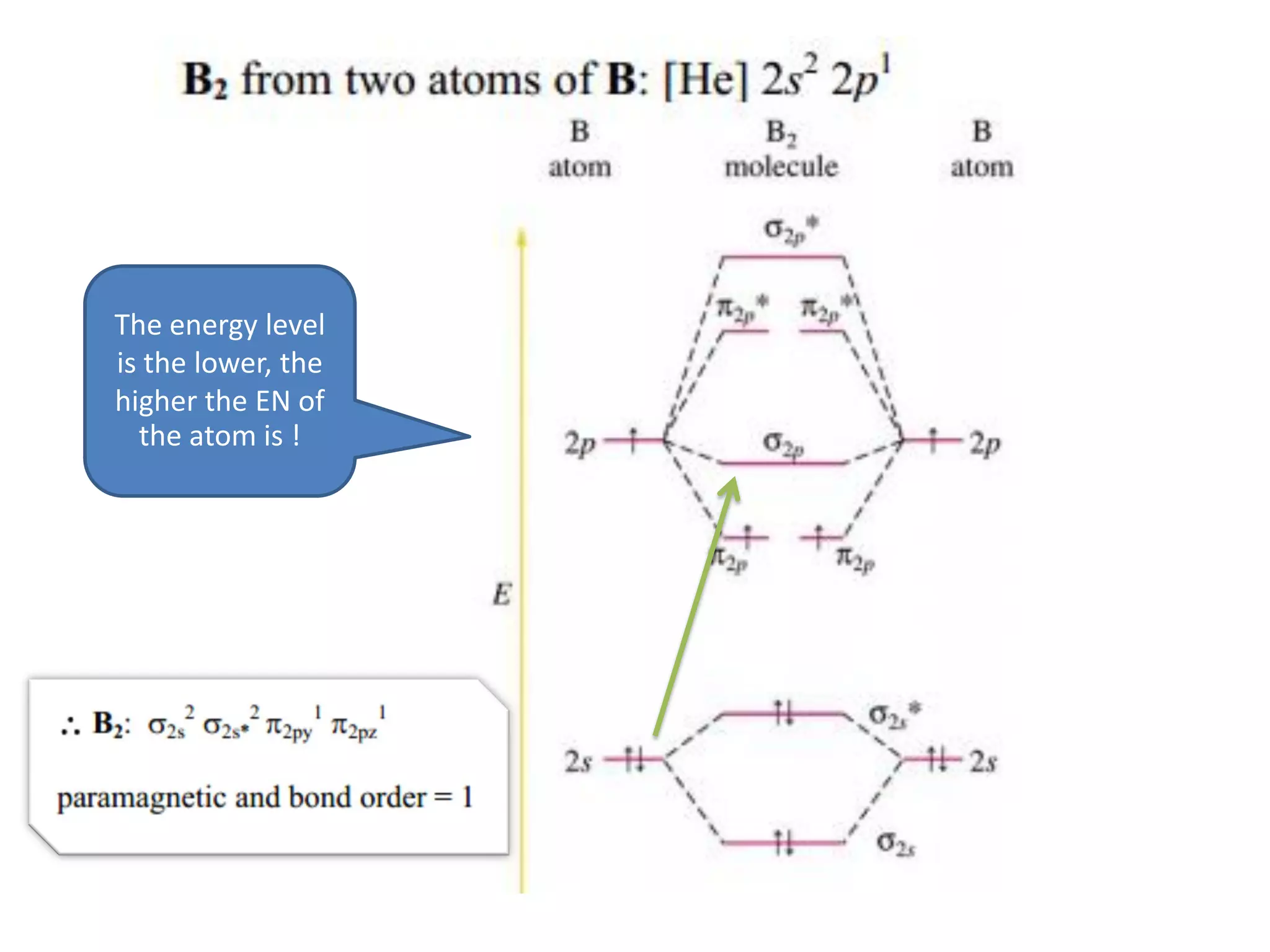
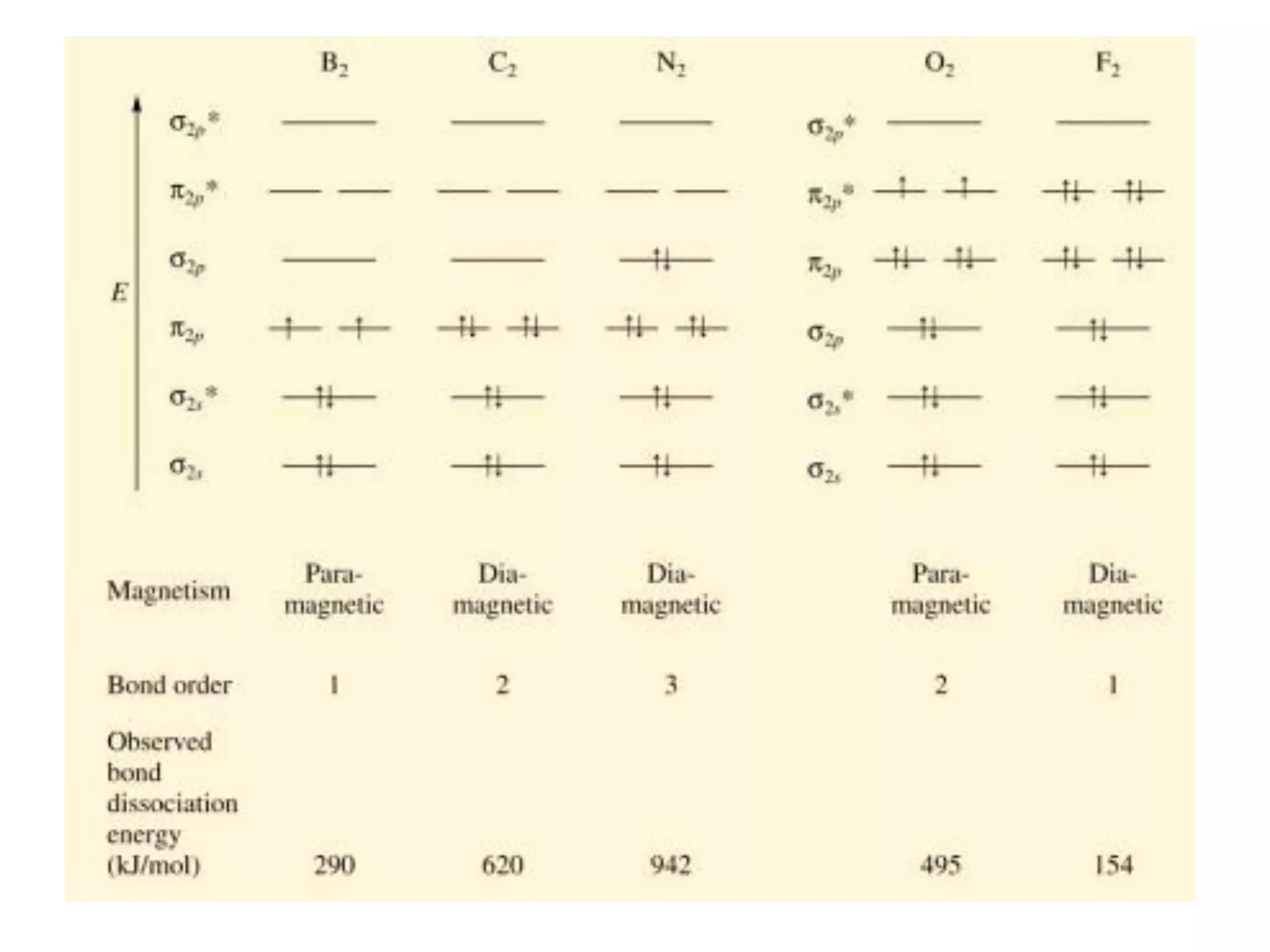
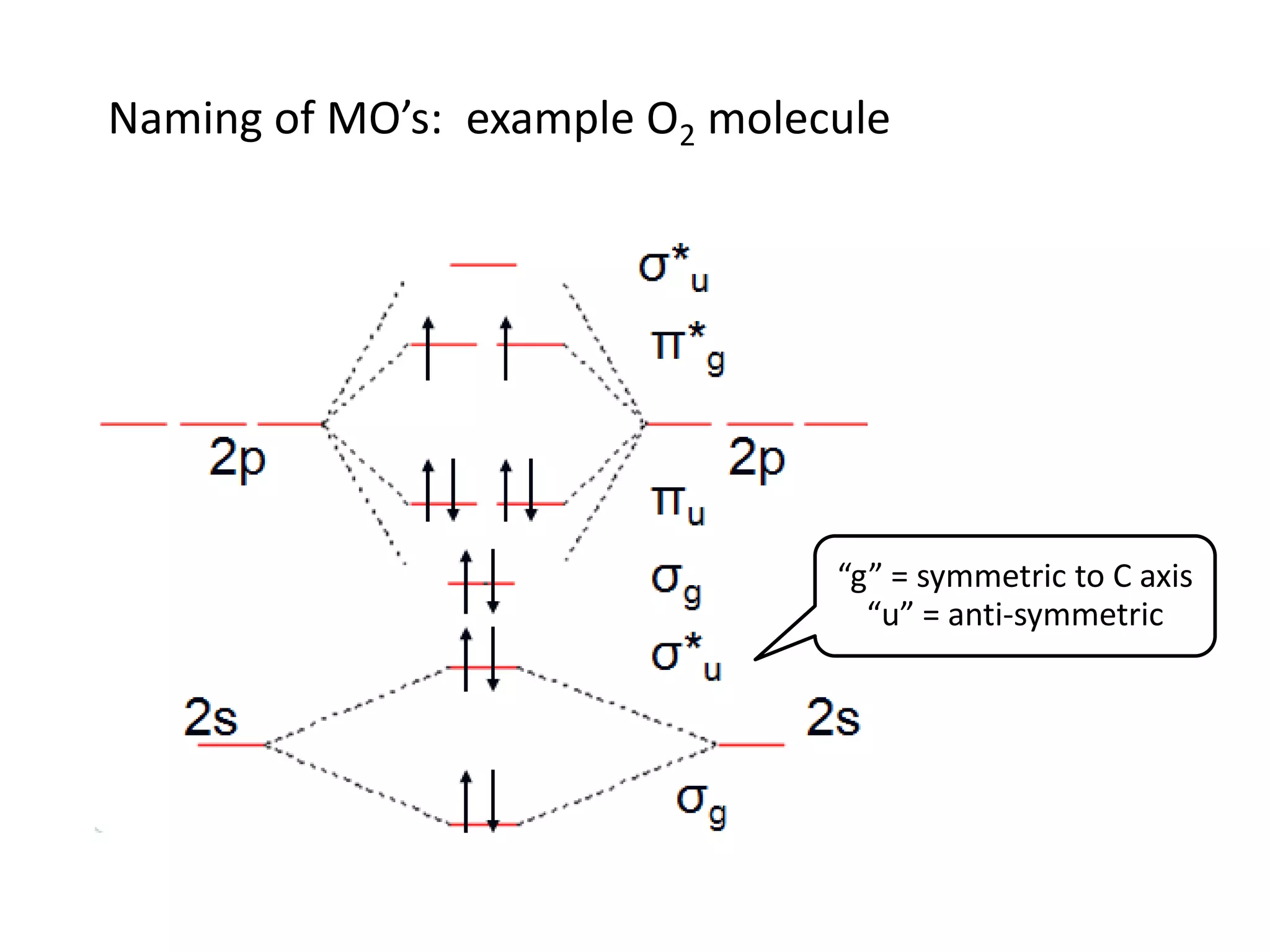
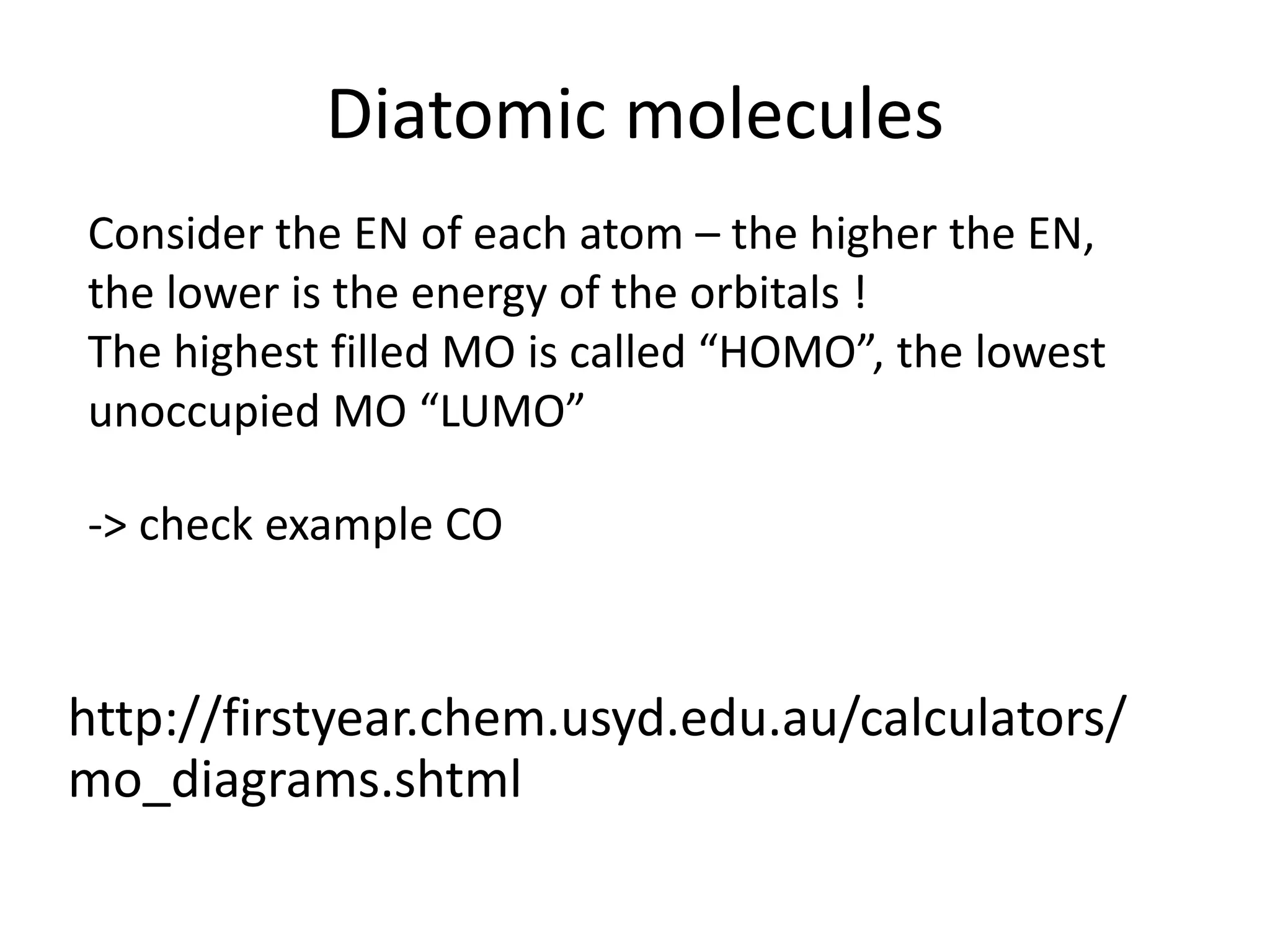
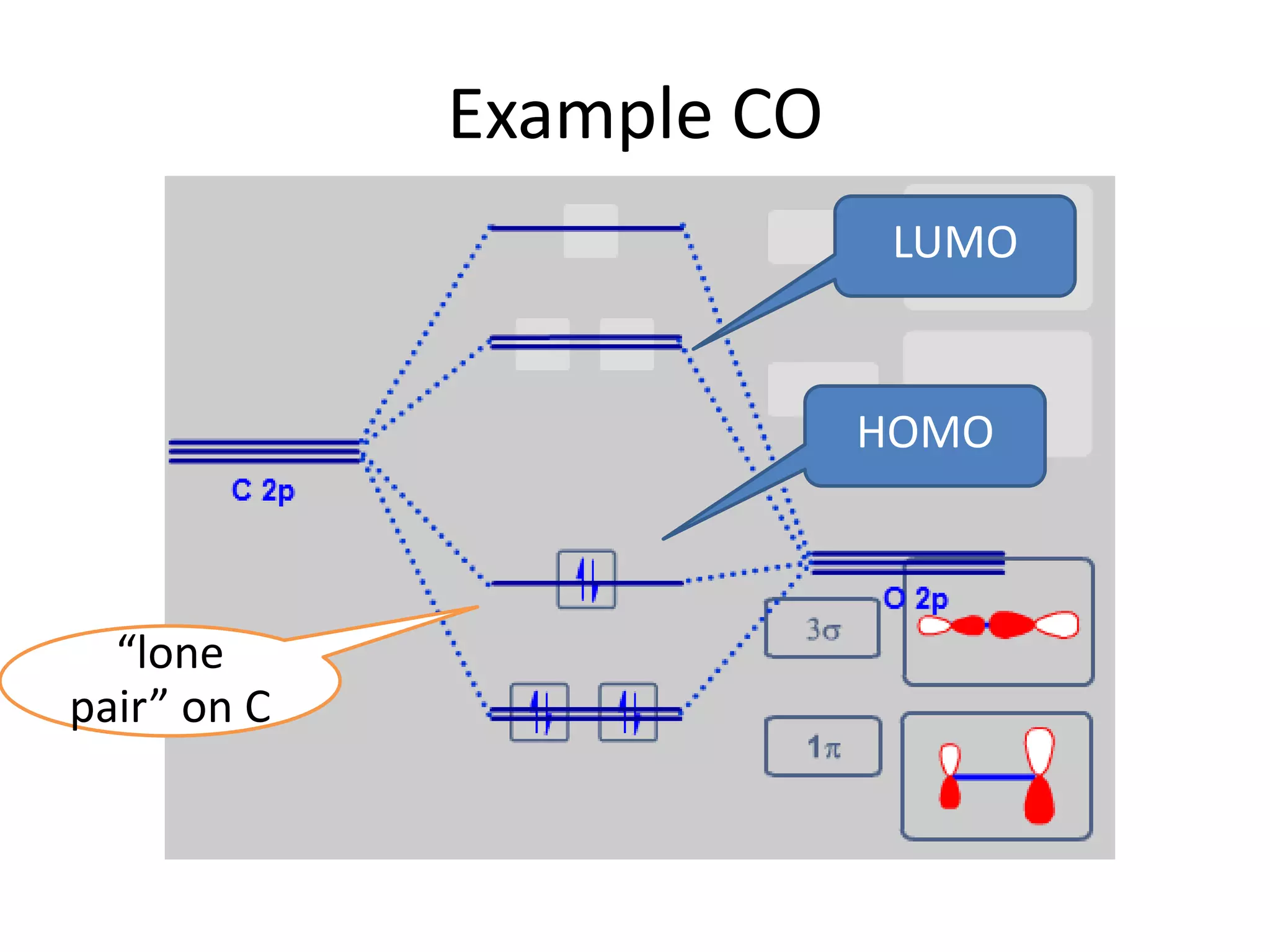
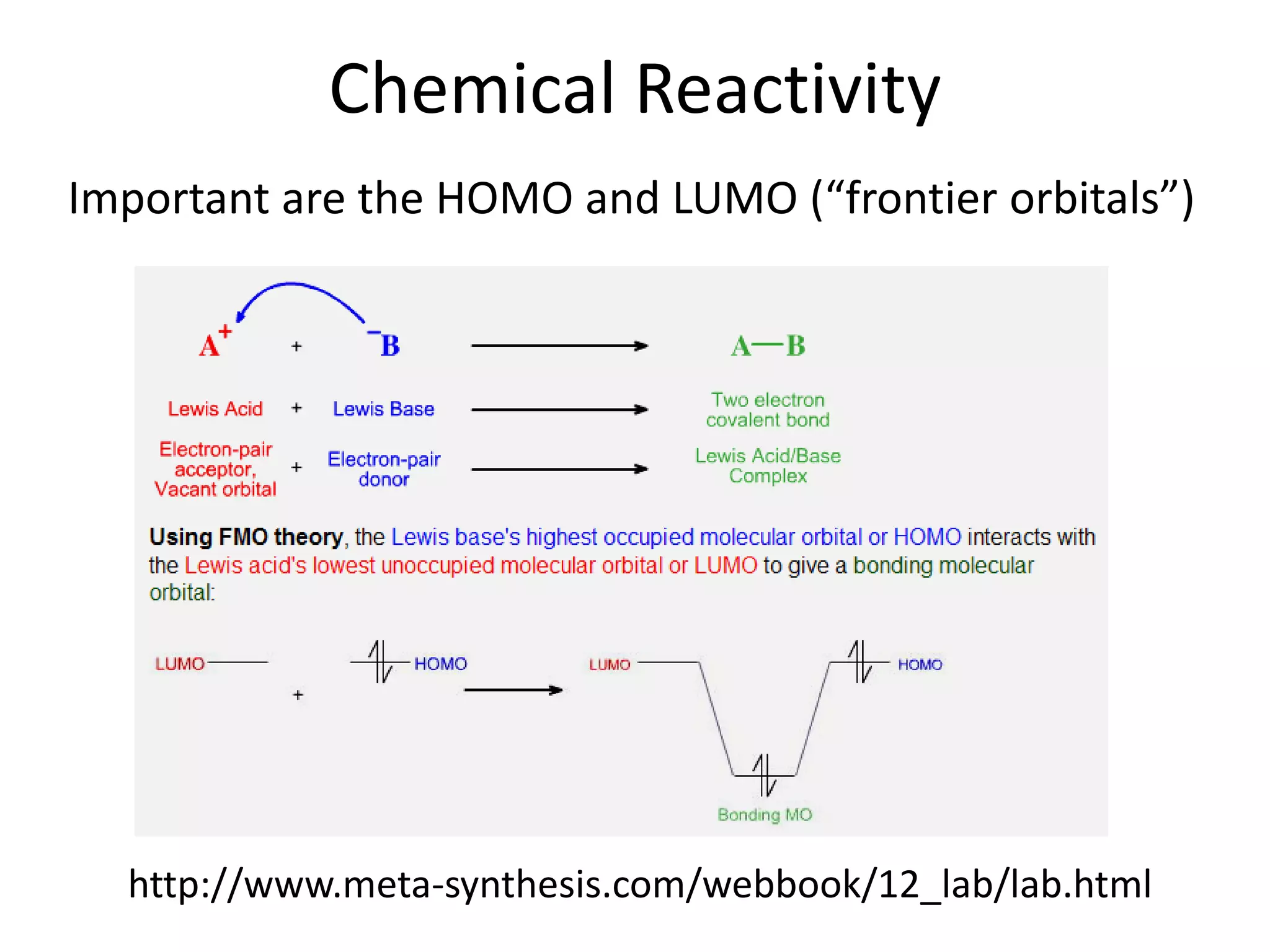
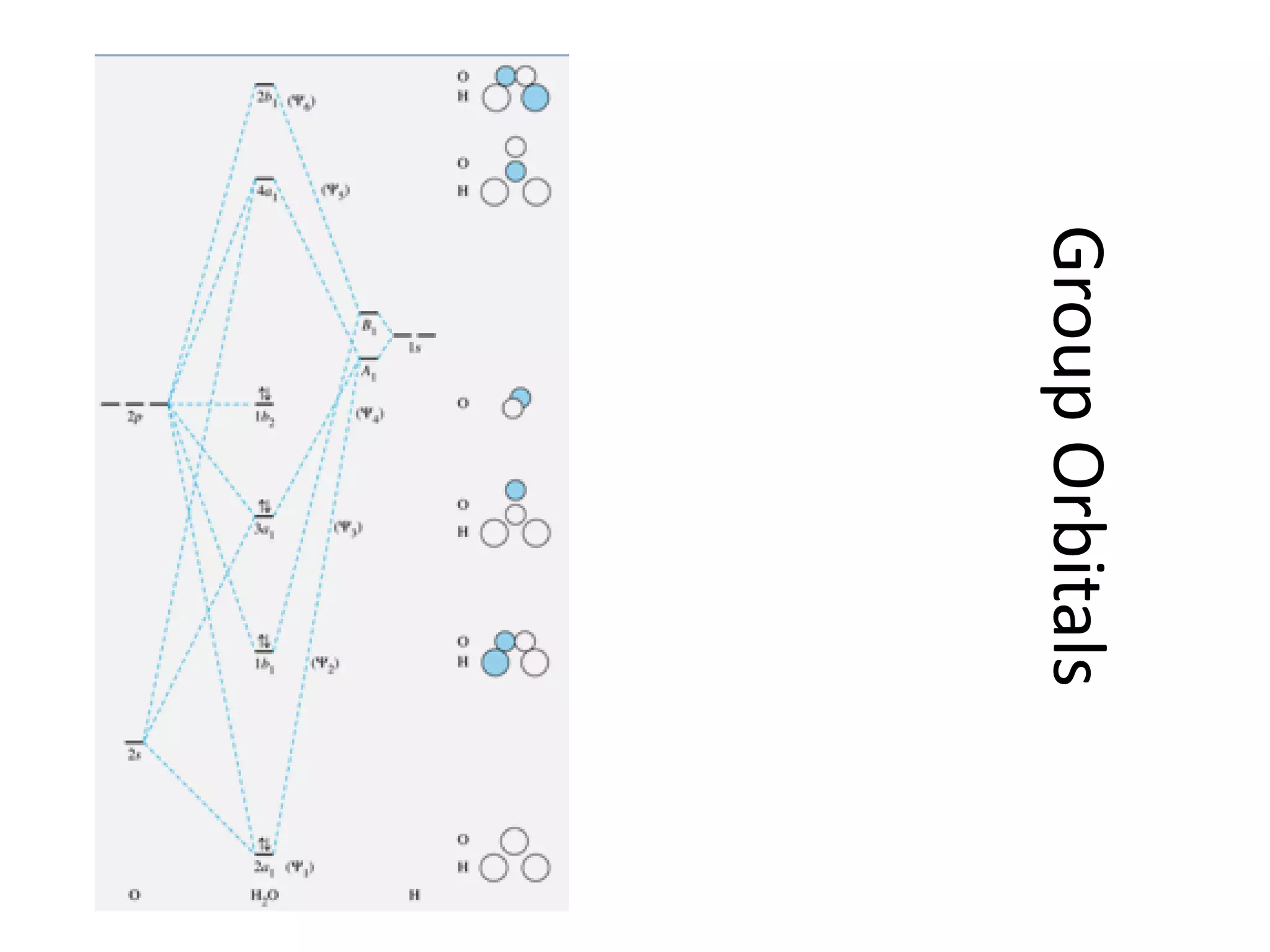
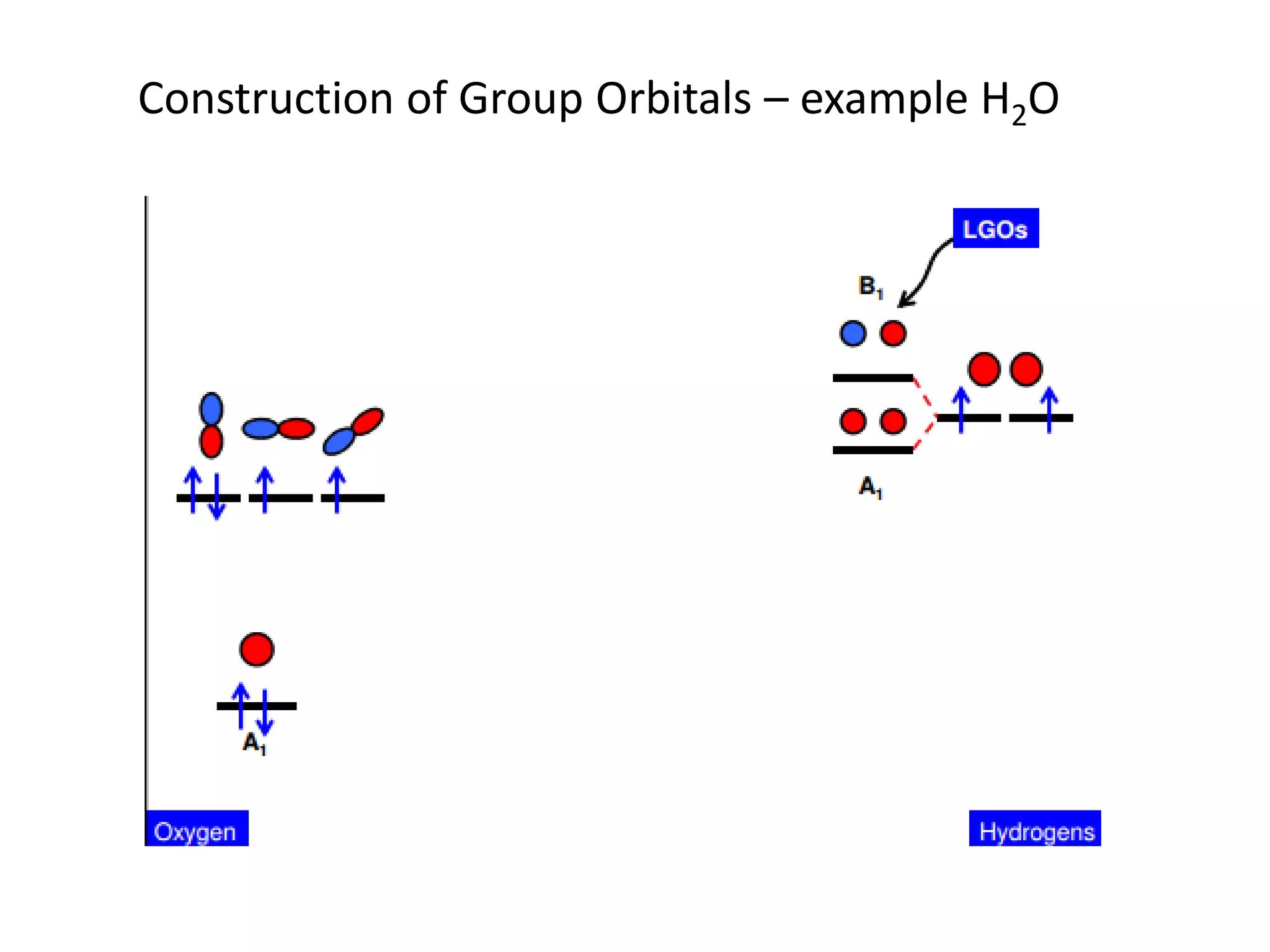
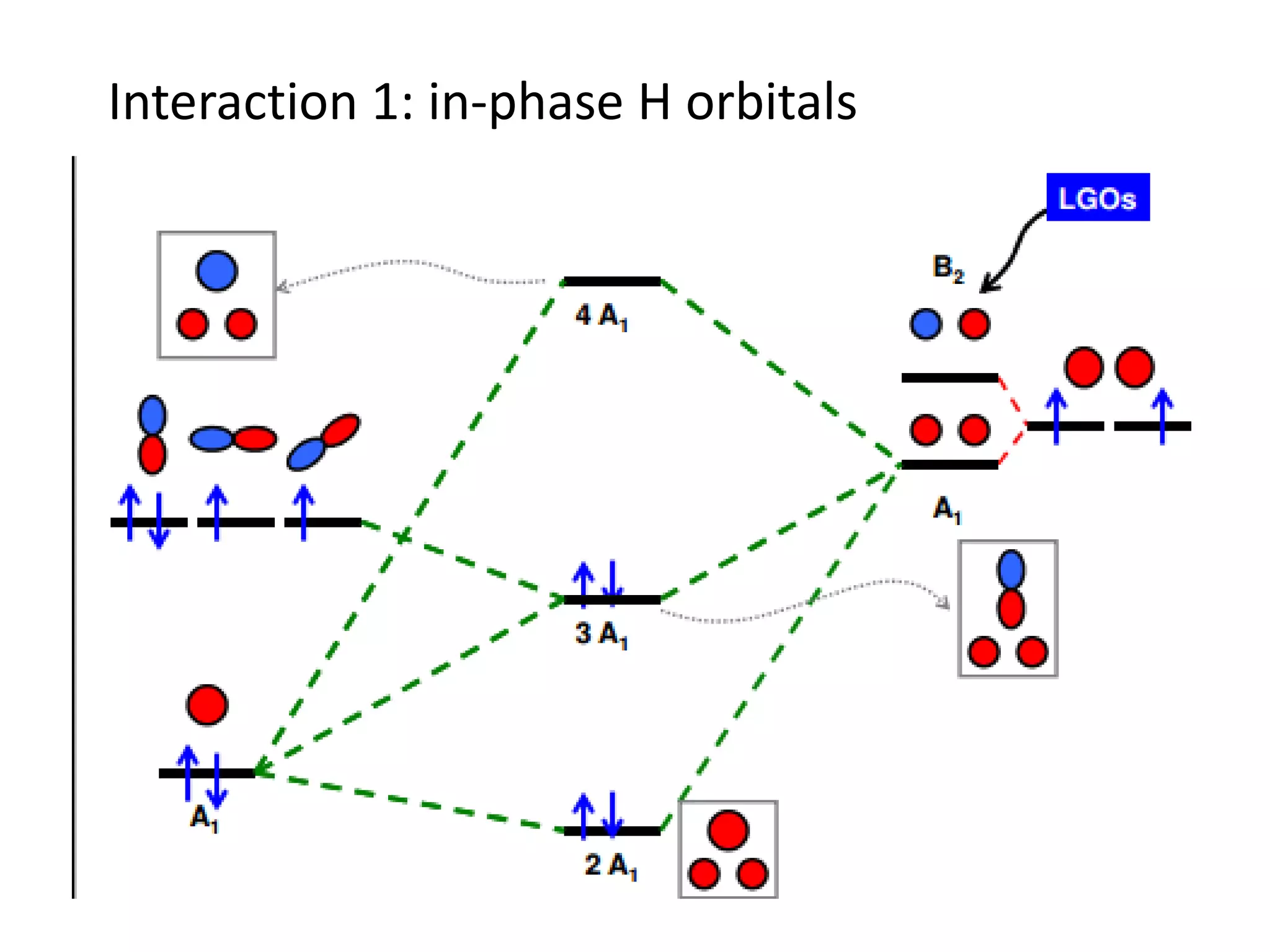
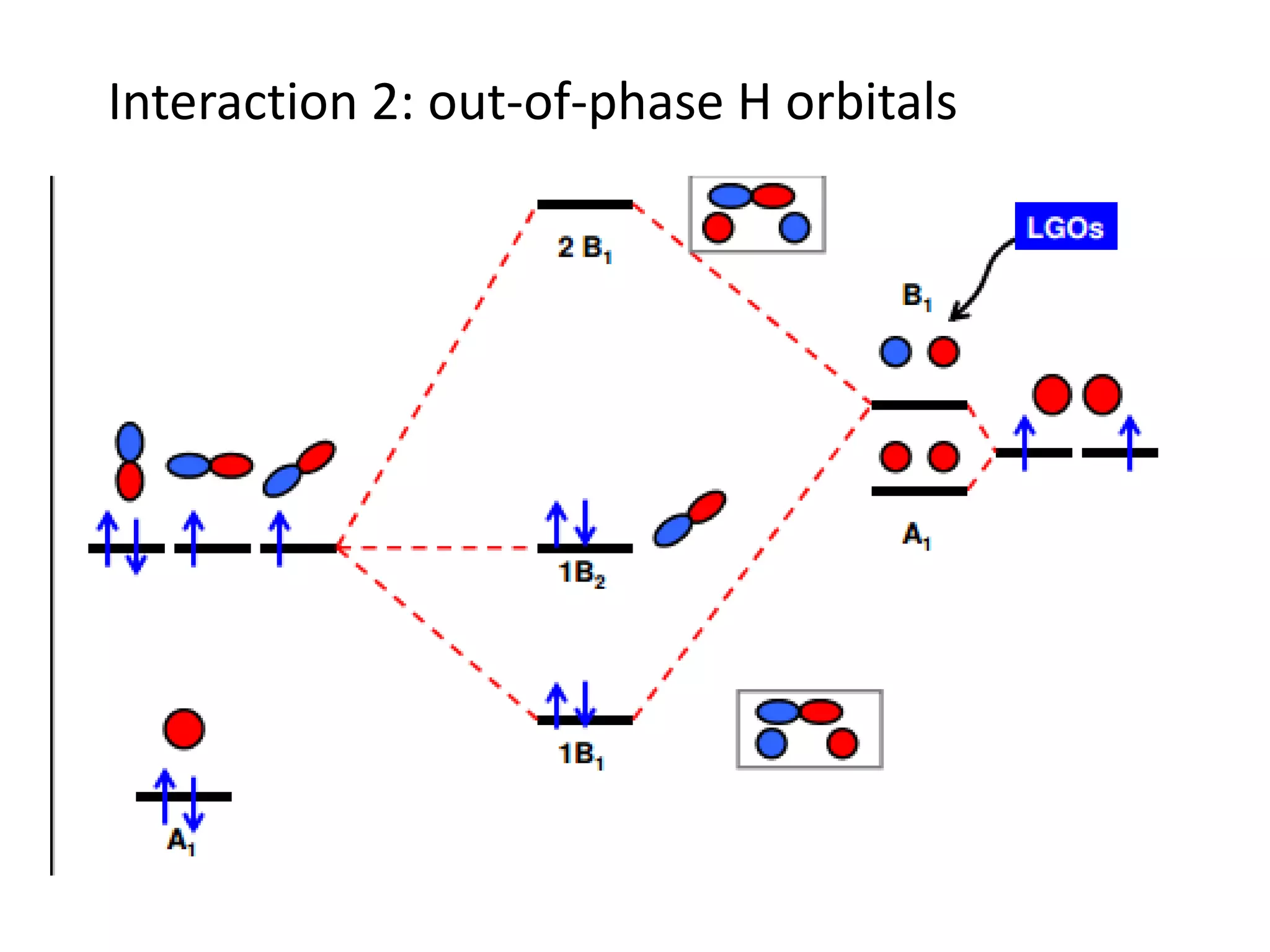
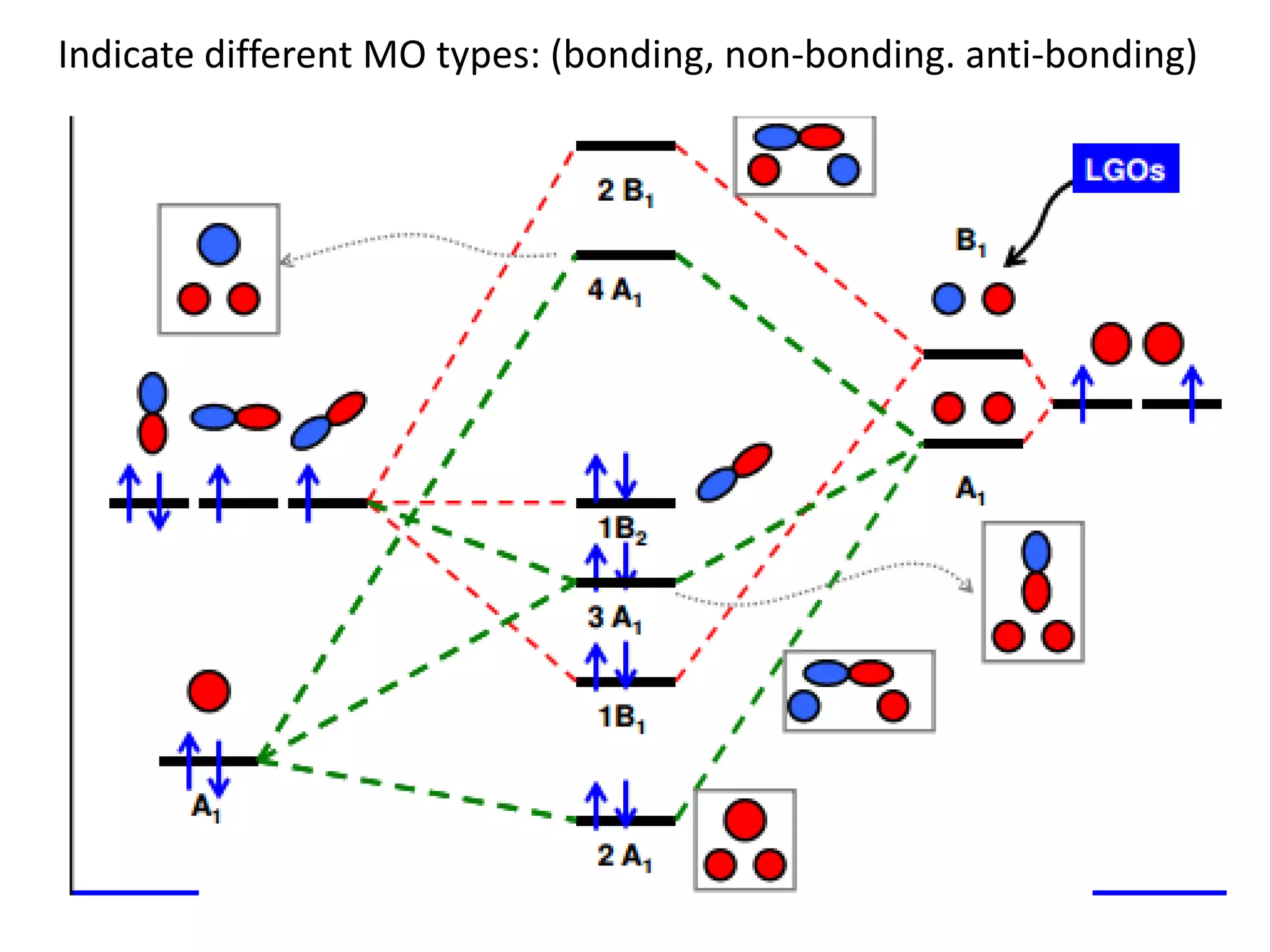
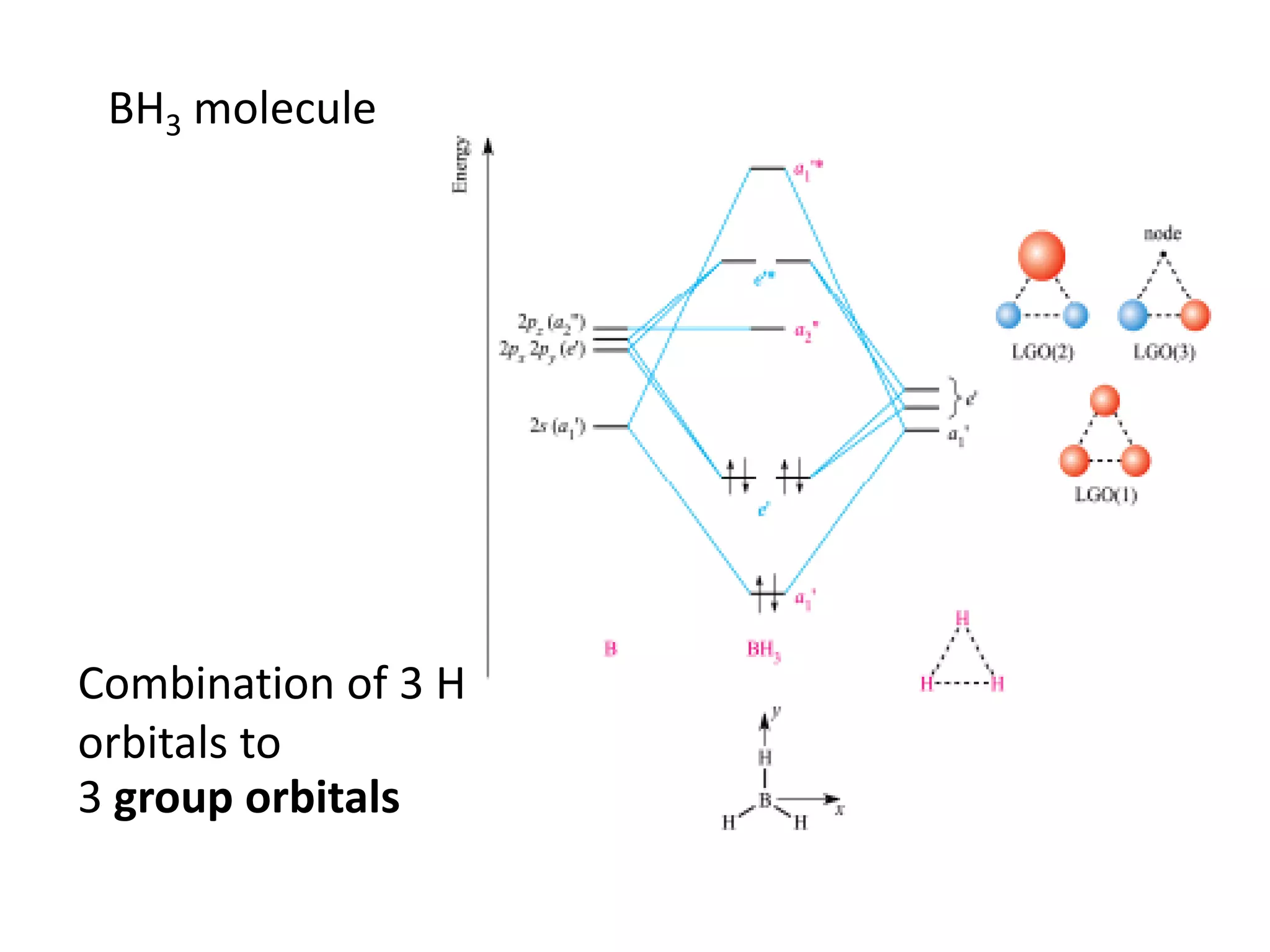
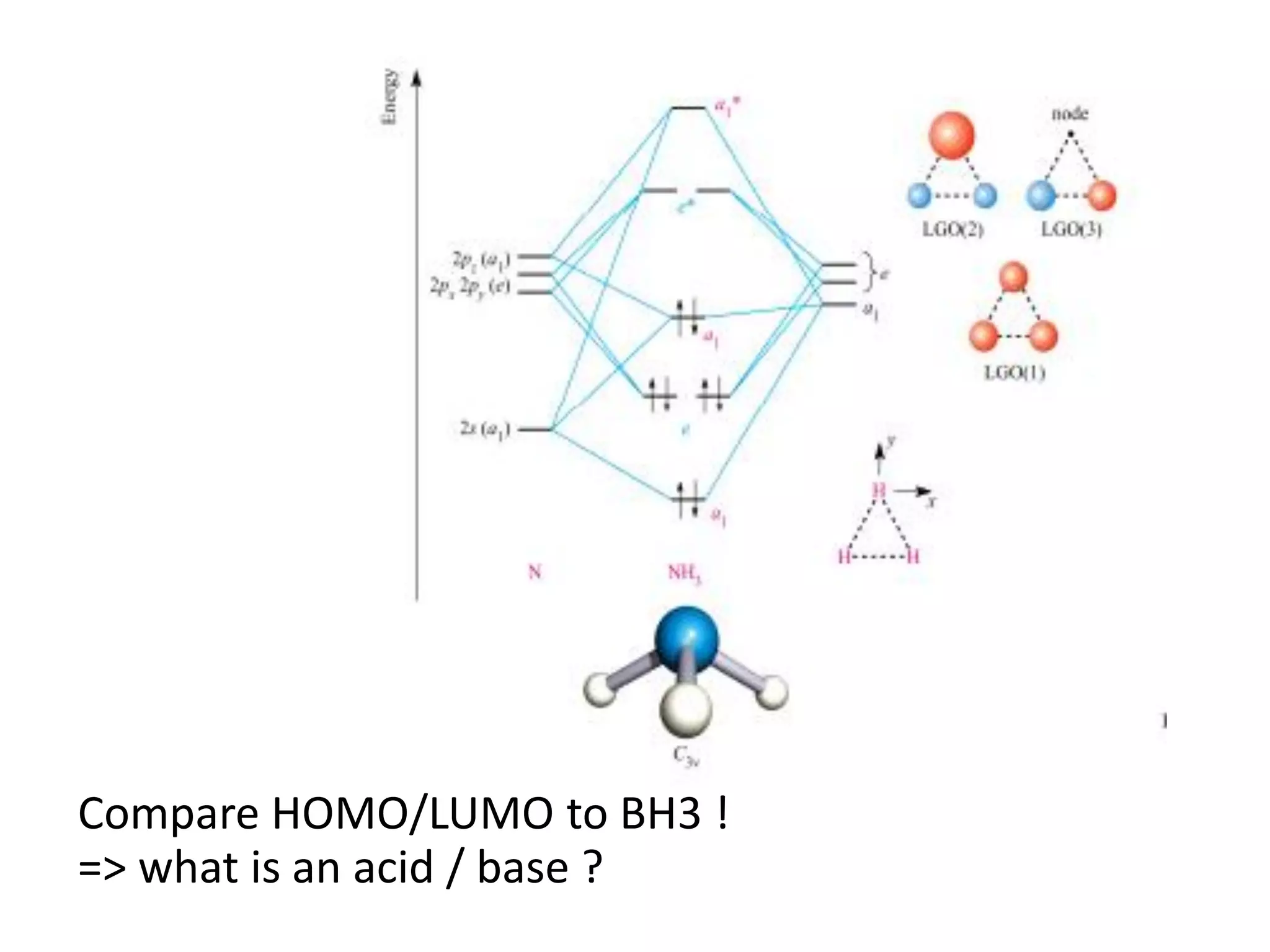
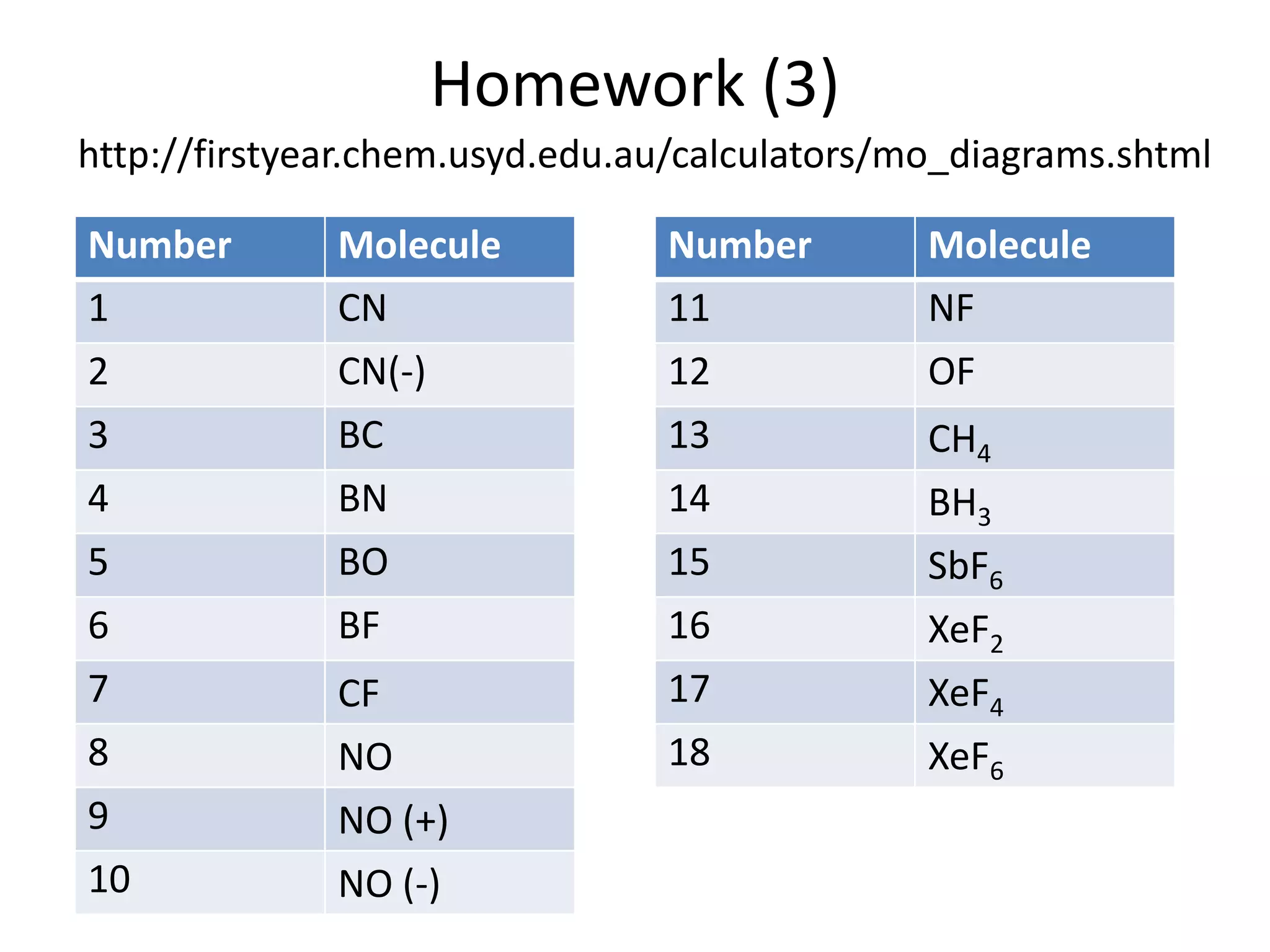
This document discusses chemical bonding and molecular structure, detailing various types of bonds such as ionic, covalent, polar covalent, and metallic bonds. It introduces valence bond theory and hybridization concepts while highlighting resonance and molecular orbital theory, showcasing how atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The document also addresses the properties and behaviors of molecules and the role of electronegativity and charge distribution in bonding.