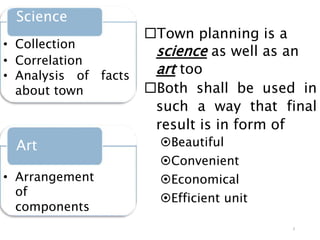
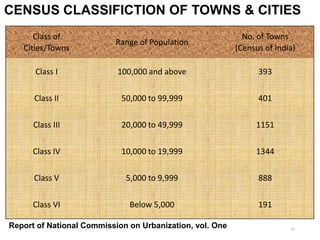
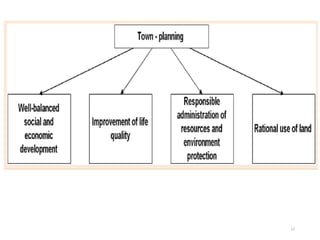
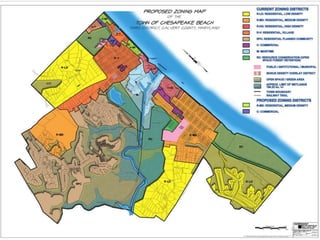
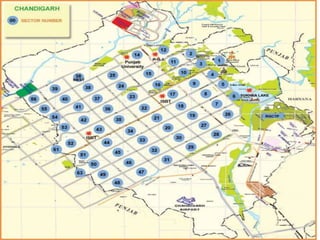
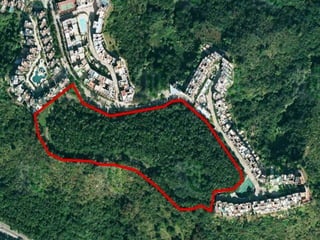
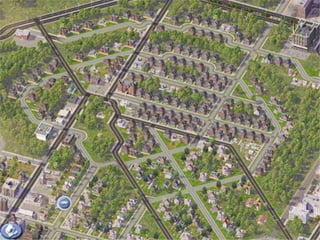
Town planning is both an art and a science that aims to organize land use and infrastructure in a way that maximizes economy, convenience, and beauty. It involves collecting and analyzing data to arrange components of a town or city, including transportation networks, public buildings, housing, recreation areas, and zoning. Proper town planning is necessary to avoid uneven and chaotic development, congestion, and unhealthy living conditions without adequate amenities. Key principles of town planning include zoning land uses, establishing green belts, providing different housing types, well-placed public buildings, recreation centers, efficient road and transportation systems.