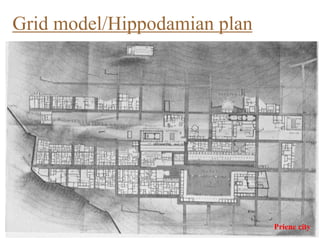
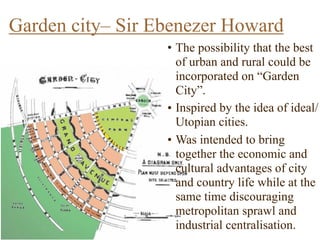
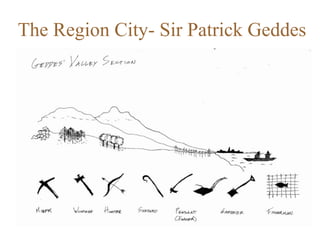
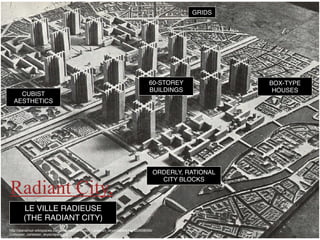
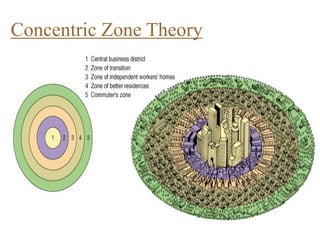
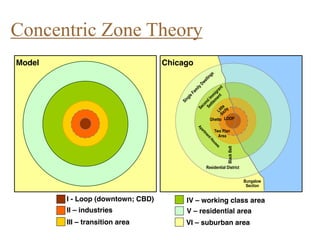
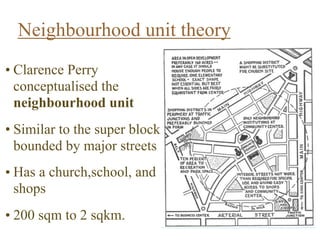
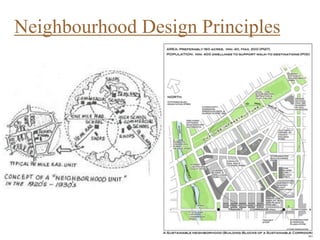
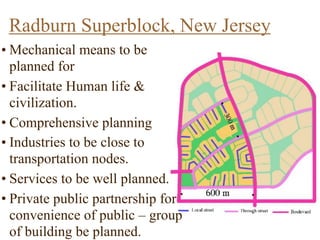
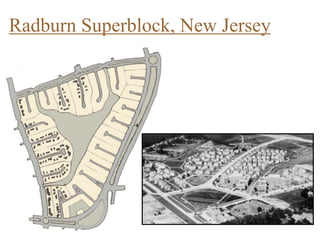
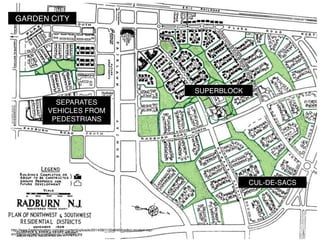
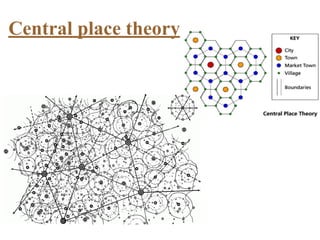
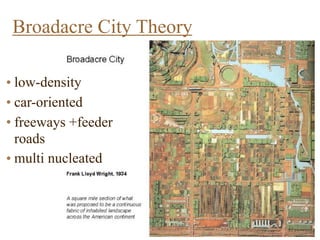
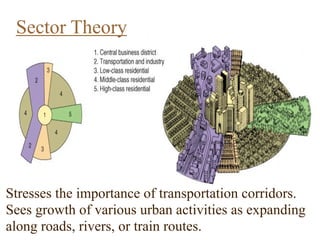
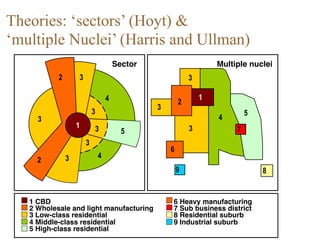
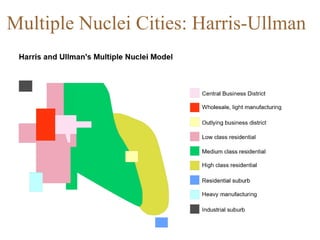
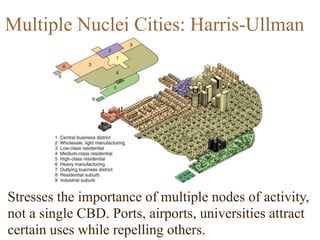
Urban planning theories have evolved over time in response to changes in populations, economies, and technologies. Early theories focused on orderly city layouts with separate zones. Hippodamus proposed dividing cities into public and private areas with grids. Howard's Garden Cities aimed to blend urban and rural advantages. Geddes emphasized relationships between people and environments. Later, modernist planners like Le Corbusier proposed high-density "Radiant Cities." Burgess' concentric zone model depicted socio-economic groups arranged in circles. Perry's neighborhood unit promoted walkable communities. Today, multiple nuclei and sector theories recognize dispersed growth around transportation networks.