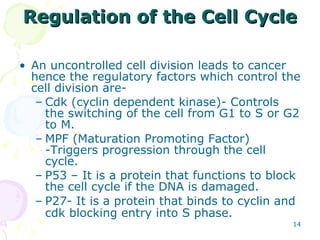
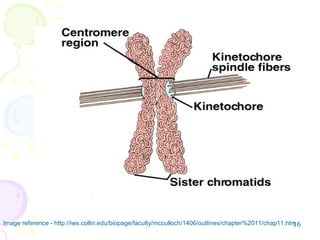
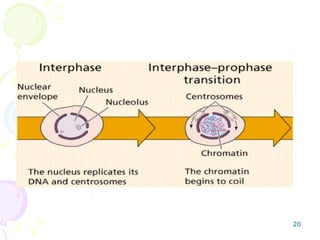
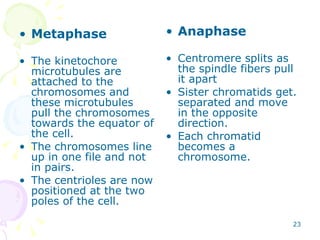
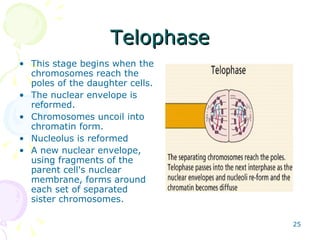
Cell division in eukaryotes occurs mainly through mitosis, where a parent cell divides into two genetically identical daughter cells, and meiosis, which produces gametes for reproduction. The cell cycle consists of interphase—where the cell grows and duplicates DNA—and mitosis, divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, followed by cytokinesis. Uncontrolled cell division can lead to cancer, highlighting the importance of regulatory factors in maintaining normal cellular processes.