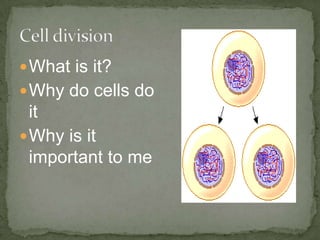
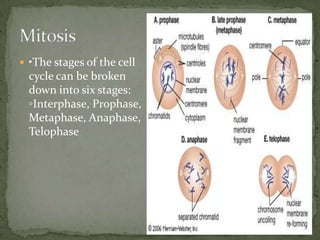
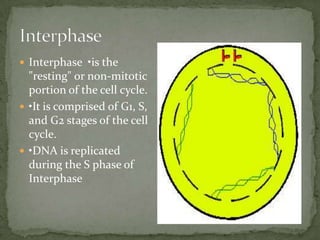
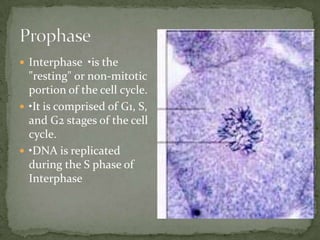
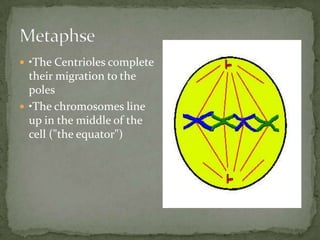
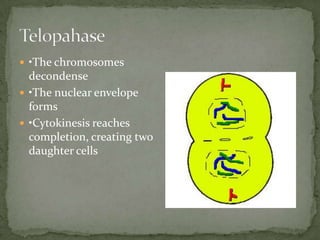
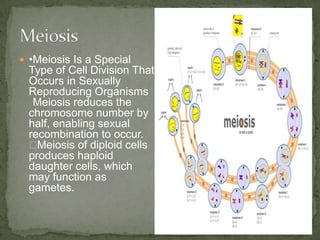
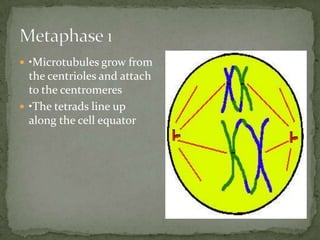
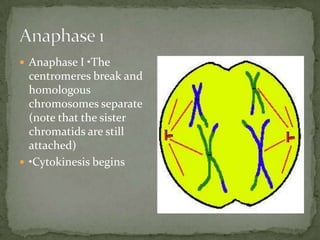
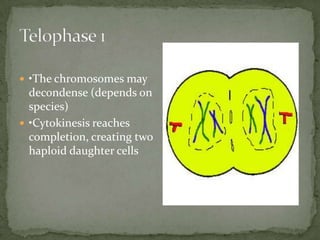
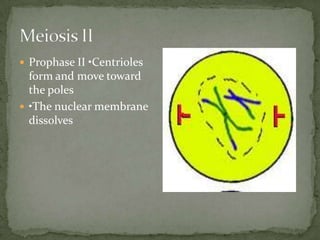
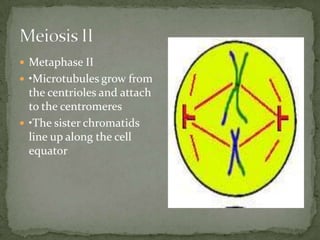
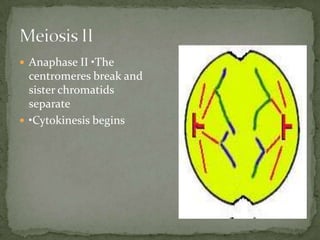
Mitosis and meiosis are two types of cell division. Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell during growth and tissue repair. Meiosis produces gametes like sperm and egg cells, reducing the chromosome number by half so fertilization restores the number. The cell cycle includes interphase where DNA replicates and cell growth occurs, as well as mitosis where chromosomes separate into two daughter cells. Unregulated cell division can lead to cancer.