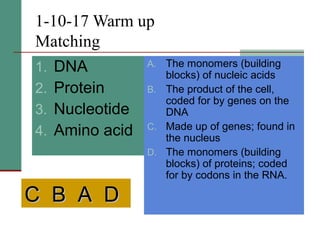
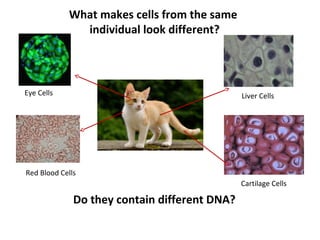
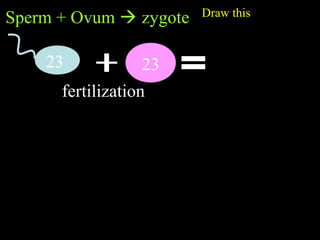
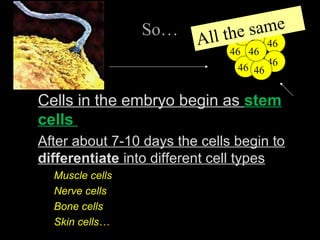
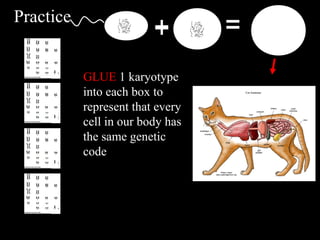
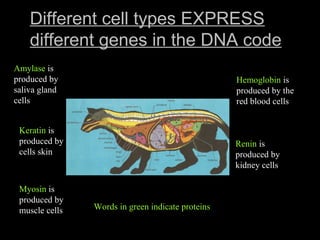
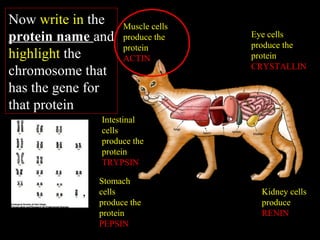
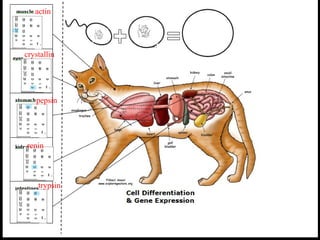
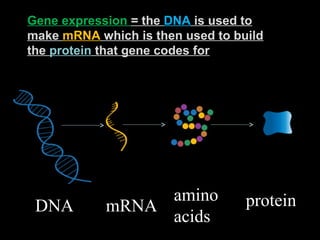
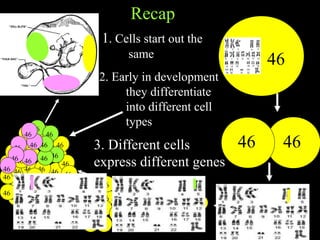
Cells from the same individual can have different appearances despite having identical DNA because cells can selectively express different genes. Early in development, stem cells differentiate into specialized cell types by activating different sets of genes through gene regulation. Gene expression involves using DNA as a template to produce mRNA and then translate it into specific proteins. Different cell types produce different proteins by expressing only the genes required for their function.