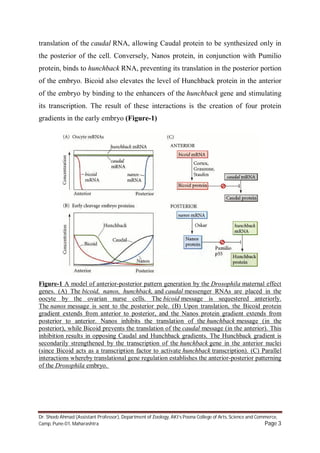
1) The anterior-posterior polarity of the Drosophila embryo is established by maternal mRNA gradients that are deposited in the egg during oogenesis.
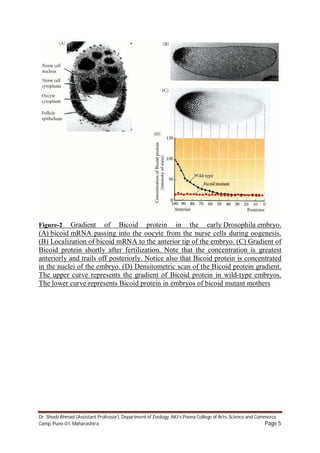
2) Key maternal mRNAs - bicoid, hunchback, nanos, and caudal - establish protein gradients in the early embryo that determine its anterior-posterior axis. Bicoid mRNA is localized to the anterior pole and translates into a Bicoid protein gradient, while nanos mRNA is localized to the posterior pole and translates into a Nanos protein gradient.
3) These opposing Bicoid and Nanos gradients regulate the translation of hunchback and caudal mRNA, producing complementary Hunchback and Caudal protein gradients along the anterior-