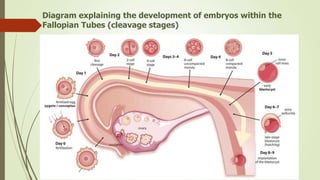
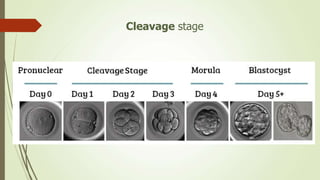
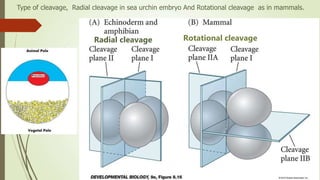
1. Cleavage is the first phase of embryonic development after fertilization where the fertilized egg undergoes rapid, indirect cell divisions (mitosis) without an increase in overall size to form a multicellular embryo.
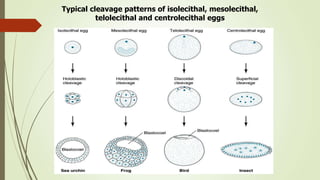
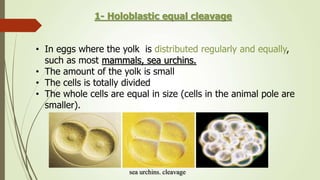
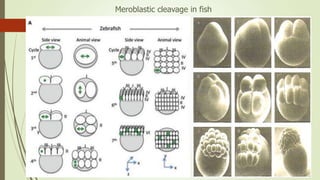
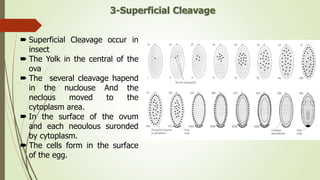
2. The pattern of cleavage depends on how much yolk is present in the egg. Eggs with little yolk (isolecithal) undergo total cleavage (holoblastic), while eggs with more yolk have partial cleavage (meroblastic).
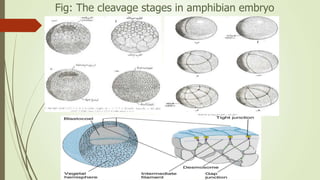
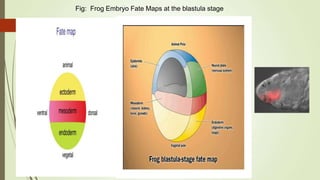
3. In amphibians, which have mesoleithal eggs, cleavage is initially equal but becomes unequal with larger vegetal and smaller animal cells. This leads to the formation of a blastula with a fluid-filled cavity (