1) Cell differentiation occurs after cell commitment, which involves two stages - specification and determination. Specification makes a cell's fate reversible, while determination makes it irreversible.
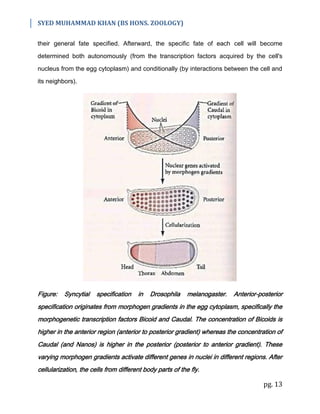
2) There are three types of specification - autonomous, conditional, and syncytial. Autonomous specification relies on cytoplasmic determinants, conditional specification relies on cell interactions, while syncytial specification involves cytoplasmic bridges between cells.
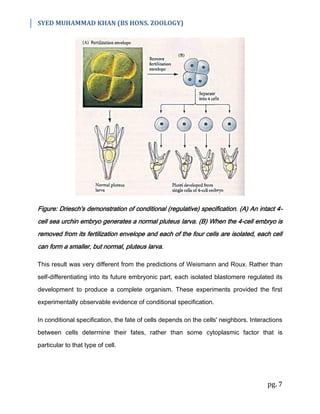
3) Early experiments by Weismann and Roux supported autonomous specification, but Hans Driesch's isolation and recombination experiments on sea urchin embryos provided evidence of conditional specification, where a cell's fate depends on its neighbors.