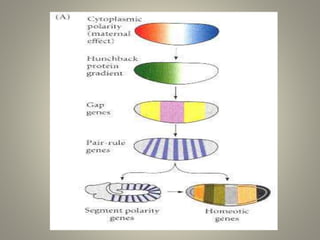
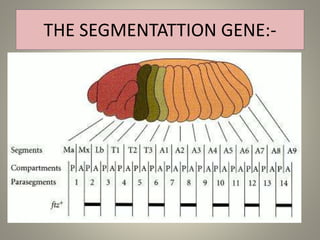
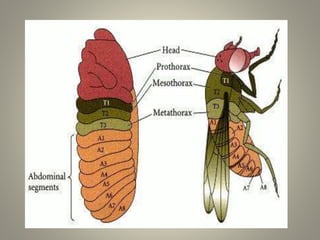
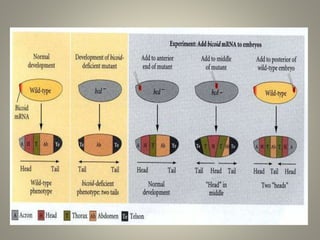
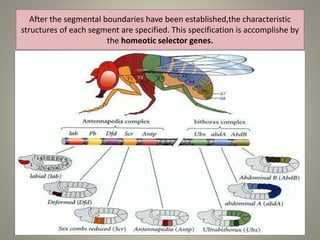
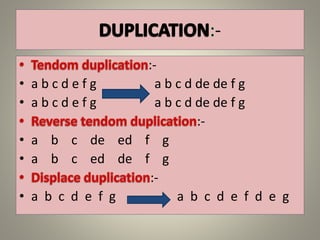
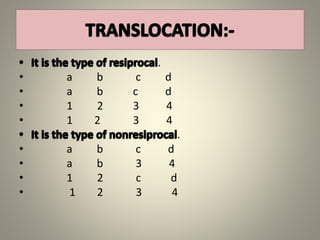
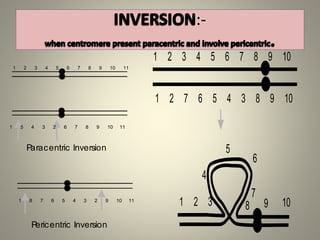
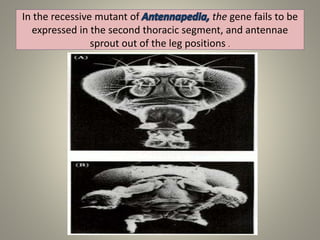
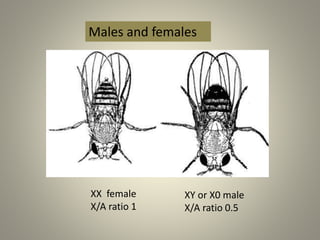
The document is a seminar synopsis on the development of Drosophila melanogaster, highlighting its significance as a model organism in genetics and developmental biology. It covers various topics including Drosophila's physical appearance, life cycle, genetic markers, and cell biology of its development, along with discussions on sex determination and chromosome aberrations. The seminar concludes with the importance of Drosophila in understanding developmental processes and its relevance to human genetics.





![CELL BIOLOGY OF DROSOPHILA
DEVELOPMENT :-
• Gamete:- A mature haploid insect germ cell
which able to unite with another of the opposite
sex in sexual reproduction to form a zygote.
• Embryo:- An unborn offspring in process of
development[the part of insect develops into new
insect.]
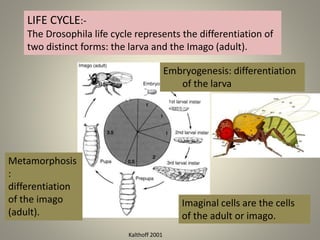
• Larva:- An active immature form of an insect that
undergoes metamorphosis.
• Pupa:- An insect in its inactive immature form
between larva and adult.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4-200503075414/85/Development-in-drosophila-7-320.jpg)