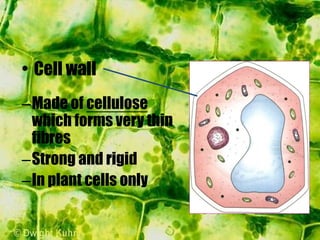
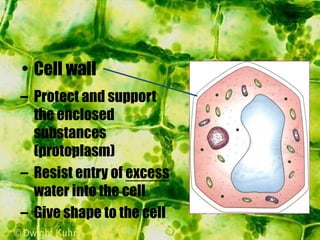
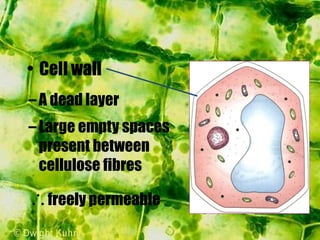
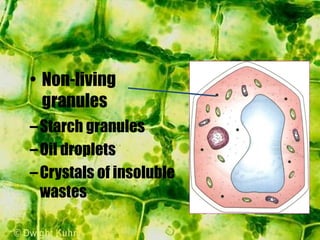
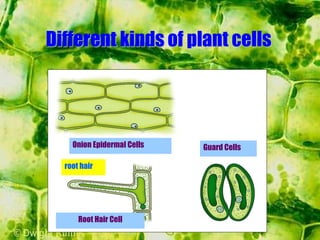
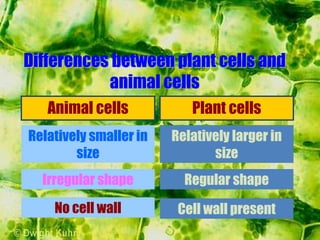
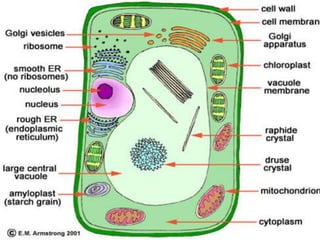
- Plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose that protects and supports the cell. The cell wall gives shape to the cell and resists excess water entering.
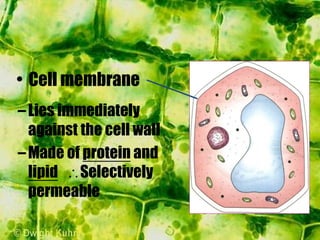
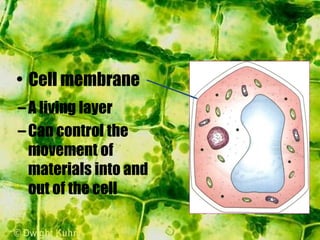
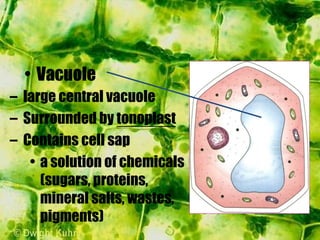
- Inside the cell wall is the selectively permeable cell membrane that controls movement of materials in and out of the cell.
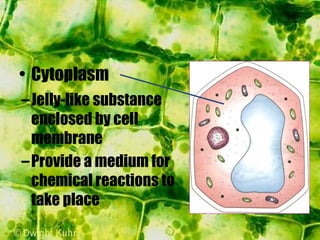
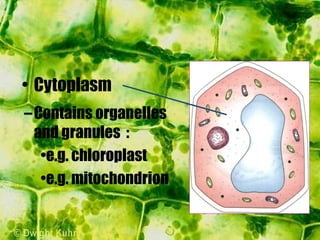
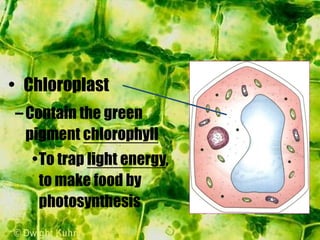
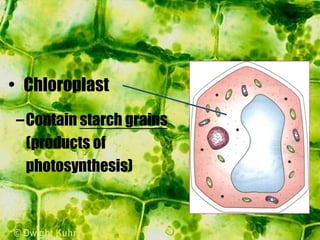
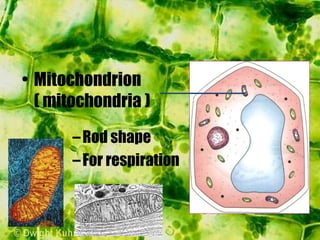
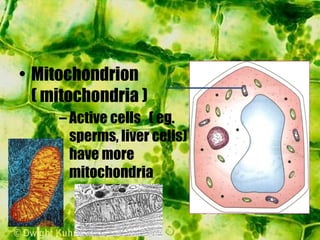
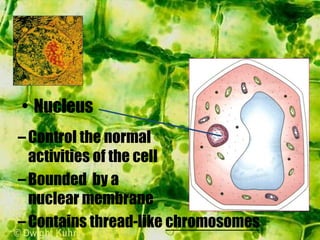
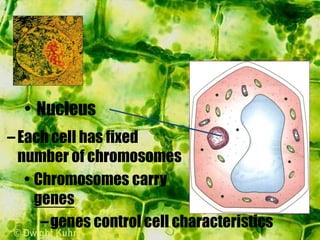
- The cytoplasm contains organelles like chloroplasts and mitochondria and provides a medium for chemical reactions. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll for photosynthesis while mitochondria are involved in respiration.