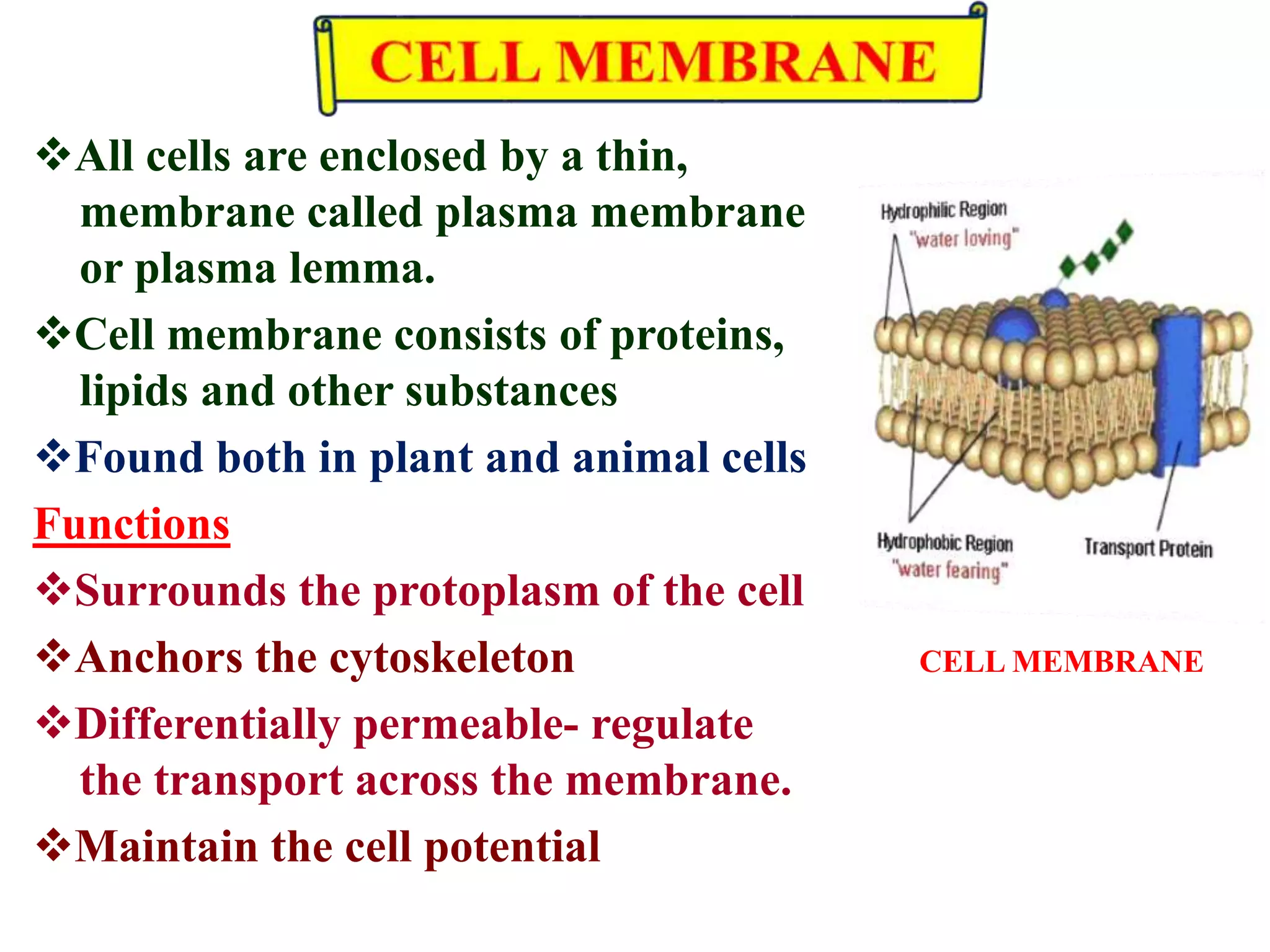
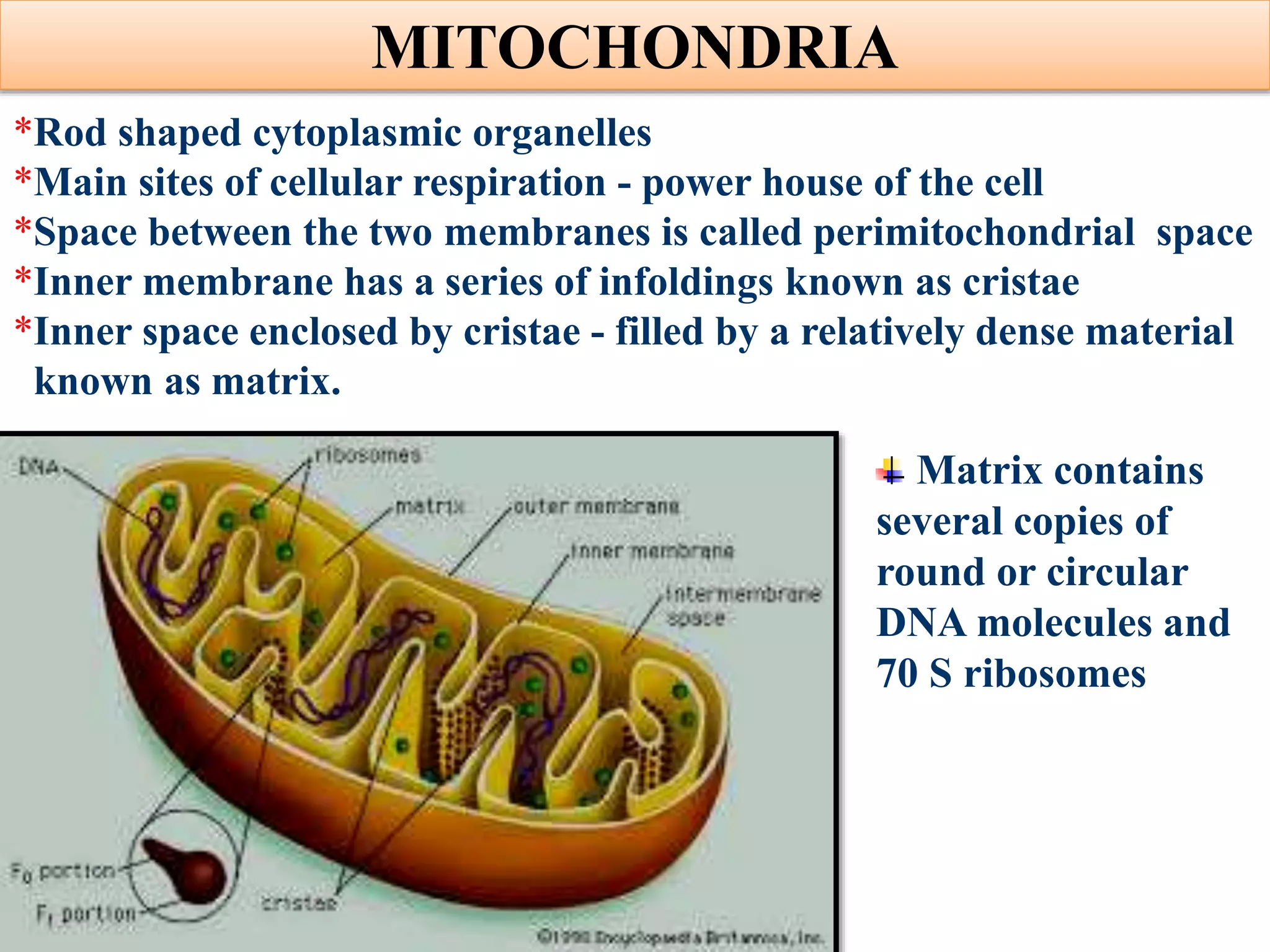
The document summarizes the structure and functions of key organelles in plant cells, including the cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, vacuoles, cytoskeleton, and plasmodesmata. The cell wall provides shape and protection, while the plasma membrane encloses the living contents of the cell. The nucleus houses genetic material and controls cell processes. Chloroplasts and mitochondria perform photosynthesis and respiration. Other organelles are involved in transport and sorting of materials within the cell.