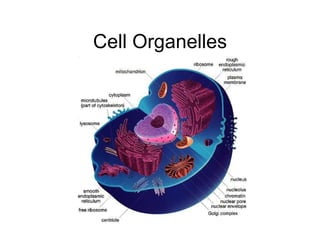
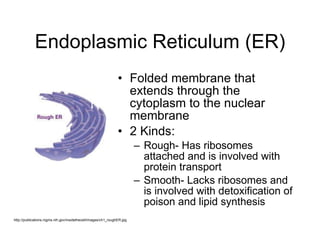
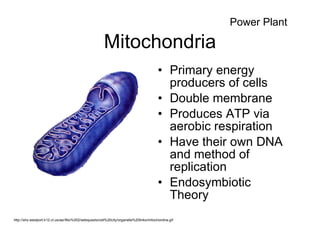
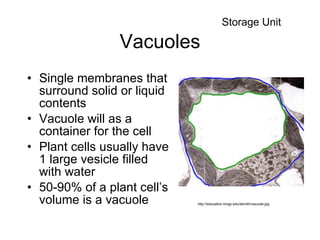
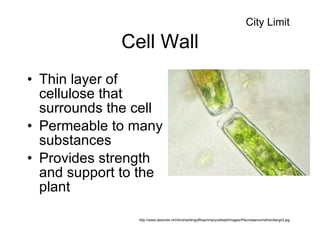
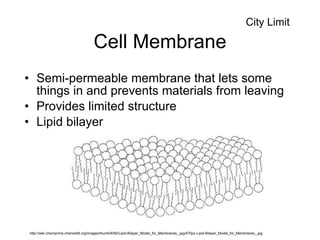
Cell organelles have specialized functions within cells. The nucleus contains DNA and controls the cell, the endoplasmic reticulum transports proteins and detoxifies toxins, and mitochondria produce energy through respiration. Other organelles like chloroplasts, lysosomes, vacuoles, and the cell membrane have important roles in photosynthesis, digestion, storage, and boundary definition.