Cartilage
- 1. HISTOLOGY OF THE CARTILAGE DR. DEVI
- 2. Definition • Cartilage is a specialized type of dense connective tissue designed to give support, bear weight and withstand tension, torsion and bending. • Firm ground substance
- 3. General Features • Cartilage support regions of the body that require flexibility • Not supplied by blood vessels • Non nervous structure • Poor regeneration capacity(fibrous tissue) • Consists of all three components of a CT • Usually surrounded by perichondrium (except articular cartilage and fibro cartilage)
- 4. • Fetal skeleton • Ends of long bones • Ossification • Cartilage canals • Growth of cartilage- interstitial growth/appositional growth
- 5. COMPONENTS Cells - chondroblasts and chondrocytes Fibers - collagen and elastic Ground substance- mucopolysaccharides (chondroitin sulphate, Keratan sulphate and hyaluronic acid)
- 6. PERICHONDRIUM •Cartilage is covered externally by a dense connective tissue sheath known as perichondrium except articular cartilage and fibro cartilage. •Has two layers- outer fibrous layer (vascular) and inner chondrogenic layer (cellular) •Has cells which can regrow cartilage to some extent if the cartilage is damaged.
- 7. CELLS • They are derived from undifferentiated mesenchymal cells • Young cells are small with branched cytoplasmic processes known as chondroblasts, they multiply to chondrocytes • Older and mature cells are known as chondrocytes
- 8. • Chondrocytes are bigger in size and are found in spaces called as lacunae • They are found either groups of 2-4 cells together known as cell nest or individual cells • They are responsible forproduction of fibres and ground substance of the cartilage • Old mature cells are incapable of multiplication
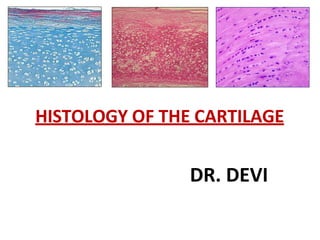
- 9. TYPES • HYALINE CARTILAGE • ELASTIC CARTILAGE • FIBRO CARTILAGE Differ from each other because of the type and amount of fibers present in them
- 10. HYALINE CARTILAGE • Hyalos=glass • Most abundant • Perichondrium present. • Characterized by the presence of highly basophilic homogeneous , transparent, amorphous intercellular matrix • Appear homogeneous as the collagen fibers present in them have the same refractive index as ground substance
- 11. Cells • Chondrocyte • Occupy in lacunae • Cells are shrunken in H& E preparation - gaps btw the cells and lacunae • responsible for the synthesis of collagen fibers and ground substances • Daughter cells – cell nests
- 12. Fibers • Ground substance – type II collagen fibers • Thick fibers have cross-striations • Thin fibers- form three dimensional network • Collagen- stability & strength • Fibers constitute about the 40% of dry weightof cartilage
- 13. • Sulfated proteoglycans (firmness) • Core protein- glycosaminoglycan • Chondroitin & keratin sulfate (Acidic) • Proteoglycans joined to form long hyaluronic acid • Hyaluronate proteoglycan aggregates • Bound to the thin collagen fibers present in the matrix Ground substance
- 14. •Highest concentration present around the lacuna • Matrix around the cells is brighter and deep blue in color than other areas, this matrix is known as capsule / territorial matrix. (newly formed) • Two groups of cells are separated by a lightly colored matrix known inter-territorial matrix
- 15. Hyaline cartilage- magnified Territorial matrix Interterritorial matrix Chondrocytes in lacuna Cell nest
- 16. Perichondrium • Fibrovascular membrane • Absent in articular surface & costal cartilage • Two layers – i) outer fibrous layer(dense irregular fibrous connective tissue ) ii) inner cellular layer
- 17. EXAMPLES• Fetal skeleton • nose • Costal cartilages • Articular cartilages (devoid of perichondrium) • Trachea, bronchi, larynx
- 18. Functions of hyaline cartilage • Articular cartilage provides smooth surface for movement at joints • Though it is flexible, it provides support because of its firmness • Firmness of the cartilage keeps the lumen of trachea and bronchi patent
- 21. ELASTIC CARTILAGE • Yellow fibrocartilage • Perichondrium present • Characterized by the presence of elastic fibers in abundance which branch and anastomose • Chondrocytes are larger than those of hyaline cartilage • Chondrocytes are found singly or group two in lacuna.
- 24. • Though the matrix of hyaline cartilage calcifies in old age, the matrix of elastic cartilage doesn't calcify with age Function : • It provides shape and support to the organ with elasticity
- 25. EXAMPLES• Auricle or pinna • Epiglottis • Tip of arten oids • Corniculate & cuneiform cartilage of larynx • External auditory meatus
- 26. White Fibrocartilage • Perichondrium is characteristically absent • Has thick bundles of collagen fibers (type I) • Dense regular connective tissue • Minimal amount of ground substance, few cells • Chondrocytes are seen between fibers in single or in narrow rows
- 27. • Function : • Fibrocartilage is capable of resisting compressive and shear forces
- 29. EXAMPLES • Pubic Symphysis • Manubriosternal joint • Intervertebral discs • Glenoidal labrum of shoulder joint • Acetabular labrum of hip joint, etc.
